Base thickness for asphalt concrete pavement. Installation of asphalt concrete pavements in adverse weather conditions
The invention relates to the field road construction and can be used in the construction of structures of the upper layers of high category roads and aerodrome runways, as well as for asphalt concrete pavements on bridges and overpasses in all climatic zones. EFFECT: obtaining high-strength and durable asphalt concrete pavement with a minimum content of expensive high-strength granite crushed stone, reducing material consumption and facilitating construction. A method of arranging an asphalt concrete pavement involves preparing the base, laying and compacting the lower layer of the coating with further laying and compacting the upper layer onto the still-cooled lower layer, and surface treatment by crushing crushed stone. The top layer of the coating with a thickness of 1.5-3 cm is formed from granular asphalt-binding material obtained by rolling, with a bitumen content of not more than 15%, and for surface treatment use pre-prepared crushed stone with a particle size of 3-5 mm, the surface of which is coated with an asphalt binder obtained by the method of pelletizing, while the amount of asphalt binder in the shell is 5-10% of the mass of crushed stone, the consumption of crushed stone is not more than 5 kg / m 2, and the crushed stone is heated up after the laid layer cools down to a temperature 80 ° C. 1 tab.
The invention relates to the field of road construction and can be used in the construction of structures of the upper layers of high roads of high categories and runways of airfields, as well as for asphalt concrete pavements on bridges and overpasses in all climatic zones.
The installation of asphalt concrete pavements is carried out in accordance with applicable regulations and is determined by the project depending on the category of roads. A typical road structure is formed by sequential laying on a sealed and prepared subgrade sand drainage layer, on which the layers of the road base and pavement are laid. Asphalt concrete pavement is the top of the road structure, consisting of one or more layers laid on the prepared road base. The coating is obtained by laying the asphalt mixture on the prepared base with further compaction in accordance with technical recommendations TP 103-07.
The thickness of the asphalt concrete coating laid in one layer is 3-6 cm. Coatings of greater thickness are usually laid in 2-3 layers with an asphalt concrete mixture with separate compaction of each layer. The thickness of the upper layer is taken within 3-5 cm, and the thickness of each of the lower layers of the asphalt concrete coating is 4-8 cm. Thin-layer coatings with a thickness of 1.5-2.5 cm are usually made of asphalt mixtures of a special composition to ensure surface roughness.
For the lower layers of the coating mainly used porous asphalt concreteand for the top layer of the coating, the brand of hot, warm and cold asphalt concrete, the grade of bitumen and the type of particle size distribution are selected depending on the category of road and climatic conditions of the construction area. The top layer of asphalt concrete is the most critical element. pavementdirectly perceiving loads from moving vehicles. It is this layer that should provide reliable grip of the wheels of the car with the road surface. The top layer of asphalt concrete pavement is more susceptible to climatic conditions than other layers. The coating must be strong, even, rough, withstand plastic deformations at high positive temperatures, be crack-resistant and resist wear well - it must provide the necessary operational qualities of the roadway. In accordance with this, the most stringent requirements are imposed on him.
The present invention relates to methods for arranging asphalt concrete pavement of special composition asphalt mixtures. Such coatings are used in the following cases:
When installing coatings on roads with heavy traffic and in difficult climatic conditions to ensure high strength and durability of asphalt concrete pavement, reduce the cost of repairs;
When installing asphalt concrete pavements on bridges and overpasses, when the requirements are imposed on the coatings for increased deformability and water resistance with a minimum weight of the coating.
An analogue of the proposed method for the construction of an asphalt concrete coating can be a method for the device of an upper coating layer based on crushed stone-mastic asphalt concrete (ЩМА). In accordance with GOST 31015-2002 crushed stone and mastic asphalt concrete mix (ЩМАС) is a rationally selected mixture of mineral materials (crushed stone, sand from crushing screenings and mineral powder), road bitumen (with or without polymeric or other additives) and stabilizing additives, taken in certain proportions and mixed in a heated state. Crushed stone mastic asphalt concrete (ЩМА) - compacted crushed stone and mastic asphalt concrete mixture. Stabilizing additive - a substance that has a stabilizing effect on the alkaline earth matter and ensures its resistance to delamination.
Crushed stone and mastic asphalt mixes (ЩМА), prepared in accordance with GOST 31015-2002, differ from traditional asphalt mixes (GOST 9128-2009) with a high content of crushed stone (up to 70-80% by weight). Crushed stone mastic asphalt mixtures are hot dense mixtures prepared with the obligatory introduction of stabilizing additives such as fibers or polymers to prevent binder from draining during storage of the mixture in storage bins or during transportation.
ShchMA is recommended to be used for the device of upper layers of coatings with a thickness of 3-6 cm on highways of I-III categories and on city streets in all climatic zones. The minimum temperature of the mixture during installation should be at least 150 ° C. The use of crushed stone and mastic asphalt as the top layer of the coating with proper use and selection of the composition of the mixture provides high resistance of the coating to the formation of plastic deformations in the most difficult operating conditions. Residual porosity and water saturation of alkali metal oxide provide increased water resistance of such coatings. The high content of crushed grains (crushed stone and sand) creates a higher roughness of the coatings in comparison with traditional asphalt concrete.
The disadvantages of coatings from crushed stone-mastic mixtures include the stringency of the requirements for both the quantitative composition of the mixture and the properties of its individual components. When preparing such mixtures, it is necessary to accurately maintain the design composition of the mixture. The dosage error of the components of the mixture should not exceed ± 2% for crushed stone, ± 1.5% for mineral powder and bitumen, and ± 5% of the weight of each component for fiber additives. SCHMAS are dense asphalt mixtures. Low residual porosity of the material is achieved by careful selection of the granulation composition of the mixture. This takes into account not only the grain size of the mineral part, but also their shape. The structure of alkaline alkaline grains is formed mainly due to grains of crushed stone of a cuboid shape. The content of grains of another form is strictly limited.
No less stringent requirements are imposed on the strength characteristics of stone materials in the composition of the alkali metal alloy. In this case, there is a mismatch between the requirements for the strength of crushed stone used in the mixture and the strength of the asphalt concrete itself. The strength of crushed granite in the coating is 1000-1200 kg / cm 2, while the requirements of GOST for the coating itself are in the range of 20-25 kg / cm 2. This is due to the mechanism of perception of external loads in coatings of this type.
The stone material in such coatings forms a framework in which each particle of the mineral part of the mixture is in direct contact with neighboring ones. The stability of the coatings is ensured mainly due to the wedging of large grains of crushed stone into smaller fractions. The frame of the material perceives an external load and redistributes it between the particles. Taking into account the fact that most of the stone frame consists of particles of irregular geometric shape, many point contacts arise in the structure of the material, in which, when the external load is perceived, high specific pressures are formed, leading to cracking of the frame particles.
Due to the high content of binder in the gravel-mastic asphalt and the complete enveloping of grains of crushed stone with a binder film, as a rule, at the time of opening traffic sufficient roughness is not achieved. To obtain a rough surface, it is recommended to evenly sprinkle with washed high-strength crushed stone with a particle size of 2-5 mm or a mixture of crushed stone with crushed sand (1-4 kg / m 2). The bulk material is applied to a hot surface. With later application, the material cannot penetrate the surface layer and collapses upon rolling.
These problems are a serious obstacle to the widespread use of this method of device asphalt concrete pavement.
Closest to the proposed method for the construction of an asphalt concrete pavement is a method for the device of an upper coating layer of cast asphalt [TU 5718-002-04000633-2006. Mixtures of cast asphalt and cast asphalt] taken as a prototype. For the production of cast asphalt mixes, polymer bitumen binders, rubber bitumen binders and other types of modified bitumen with a wide range of ductility, providing increased crack resistance and shear resistance of the coating, are used.
Coatings from cast asphalt concrete are arranged on road sections that require increased performance in terms of wear resistance, water resistance, deformation and friction properties under operating conditions. Cast asphalt mixes are used in the device and repair of coatings and layers of monolithic road constructionsdesigned from the operating conditions of asphalt concrete pavement as an elastic plate lying on an elastic foundation. These types of coatings include coatings on bridges, overpasses, overpasses, etc. In the practice of building coatings on bridges, cast asphalt mixes are used, prepared both on standard bitumen and polymer bitumen binders. Cast asphalt mixes are laid in the top layer of the coating 4-5 cm thick along the previously compacted lower layer of compacted hot asphalt mix [VSN 60-97].
For the preparation of mixtures, mineral materials are used: crushed stone from natural stone obtained by crushing rocks, crushed stone from gravel and gravel. The requirements for the strength of stone materials are less stringent than in the ShchMA (strength is at least 1000 kg / cm 2). According to the shape of the grains, the crushed stone should be cuboid in shape, contain no more than 1% of dusty and clay particles, without impurities. The content of grains of weak breeds should not exceed 5% by weight. The number of large fractions with a particle size of more than 55 mm, depending on the brand of the mixture, ranges from 35 to 65%. The content of asphalt binder in such mixtures reaches 30% with a mass ratio of bitumen / mineral powder from 0.35 to 0.75. The laying temperature of cast asphalt mixes, depending on the brand, is 200-240 ° C. The finished mixture of aircraft is transported to the place of work by self-propelled units with a thermos boiler or a bunker with heating and a stirrer.
The advantage of cast asphalt concrete pavement is the fact that after paving, their compaction is not required due to the increased content of asphalt binder. Cast asphalt mixes (LA) are hot mixes and have good fluidity, which eliminates, in most cases, the need for compaction. Another important advantage of cast asphalt is almost zero porosity and water saturation, which ensures high water resistance of the coatings, as well as their high fatigue life. The rigidity of requirements for stone materials has been reduced since cast asphalt does not form a frame structure.
The disadvantages of asphalt concrete pavements of this type include a higher susceptibility to random fluctuations in the content of mineral powder and bitumen, which negatively affects the physical and mechanical properties of asphalt concrete. The experience of using such mixtures has shown that in coatings, especially on roads with heavy and heavy traffic, waves, shears and other plastic deformations are formed. Such manifestations are especially strong at high external temperatures. Cast asphalt mixes are prone to segregation, as a result of which the material is stratified in the pavement layer. Particles of large fractions of the mixture settle to the bottom, and asphalt binder is released in the upper part of the layer, the strength characteristics of which are determined mainly by the properties of the bitumen used. The content of mineral powder and bitumen in the asphalt binder is such that a significant part of the bitumen is in a bulk state, reducing the strength characteristics of the material. The strength of the cast asphalt is normalized only at a temperature of 50 ° C and is 7-10 kg / cm 2. The use of high temperatures in the production of asphalt concrete mix and its laying creates serious problems in transporting the material to the place of use and requires special equipment. The production of works on the device of pavements using cast asphalt requires a lot of experience and the necessary production skill.
The surface roughness of the cast asphalt pavement is insufficient to provide high adhesion to the wheels of cars, based on traffic safety conditions. Surface finish is used to provide the necessary grip. In this case, the surface of the coating is treated with black gravel fractions (10-15 mm) with its rolling in 10-15 minutes after laying with a light roller weighing 3 tons. This surface treatment is called the method of embedding crushed stone [VSN 38-90. Technical guidelines for the construction of pavements with a rough surface]. The crushed stone used must be pre-treated with an organic binder (black crushed stone). The consumption rate of crushed stone for incorporation into a cast asphalt concrete coating is determined by the size of its particles and is 7-10 kg / m 2. The use of finer gravel for surface treatment could reduce its consumption and increase its frictional qualities. However, the low strength of the material and its floating structure do not allow this. Small particles of crushed stone are buried under the influence of loads in the layer of asphalt concrete, reducing its adhesion to the wheels of the car.
In addition, problems arise when processing crushed stone with an organic binder. Each particle of crushed stone during surface treatment should be moistened with bitumen over the entire surface to ensure reliable adhesion of the binder to the stone material. An obstacle to this is the presence of dust particles on the surface of the gravel. In this regard, gravel is washed and dried before treatment with bitumen.
The objective of the invention is to develop a method for the device of the top layer of asphalt concrete pavement, having improved performance indices necessary for the device of coatings on roads with heavy traffic and in difficult climatic conditions, as well as the device of asphalt concrete coatings on bridges and overpasses, when the demands are made on the coatings of increased deformability and waterproofness with a minimum coating weight. At the same time, a reduction in the cost of production and operation of the road surface is achieved.
The problem is solved in that the top layer of the coating with a thickness of 1.5-3 cm is formed from granular asphalt-binding material obtained by the pelletizing method with a bitumen content of not more than 15%, and for surface treatment using pre-prepared crushed stone with a particle size of 3-5 mm, on the surface of which a layer of asphalt binder obtained by the pelletizing method is applied, while the amount of asphalt binder in the shell is 5-10% by weight of crushed stone, crushed stone consumption is not more than 5 kg / m 2, and crushed stone is heated after Bani-laid layer to a temperature of 80 ° C.
The basis of the asphalt concrete coating made in accordance with the proposed method is the material obtained by the method for producing the asphalt concrete mixture [RF Patent No. 2182136, 05/10/2002]. This material is a granular asphalt binder obtained from a mixture of mineral powder and bitumen by pelletizing by pelletizing. The application of the pelletizing method for producing granules allows to obtain a homogeneous asphalt binder structure with a uniform distribution of bitumen in the mass of mineral powder with a minimum bitumen content. In addition, an ordered arrangement of the grains of the mineral powder in the structure of the asphalt binder is ensured with the creation of bitumen films of nanoscale, providing a significant increase in the strength characteristics of the mixture. The high plasticity of the granules in the preheated state makes it possible to obtain practically monolithic samples of asphalt concrete with minimal water absorption and a water resistance coefficient exceeding unity.
Granular asphalt binder according to the method of [RF Patent No. 2182136, 05/10/2002] is used for its intended purpose, i.e. introduced into preheated asphalt mixby adhering between the particles of the mineral part. With such an application, the listed advantages of asphalt-binding material cannot be fully realized. Literary sources indicate that a composite material whose structure is ordered and the amount of binder is minimal is close to an ideal composite. This is indicated in the works of the creator of a new scientific field of physico-chemical mechanics, Academician P.A. Rebinder [Rebinder P.A .. Selected Works. Surface phenomena in disperse systems. C. Physico-chemical mechanics. - M .: Nauka, 1979. - 469 s]. In the works of L.B. Gesentzwei [Gesenzvey LB Asphalt concrete from activated mineral materials. - M .: Publishing House for Construction, 1971. - 255 pp.] It is noted that there is an optimal ratio of the contents of mineral powder and bitumen in the binary system, in which there is a sharp increase in the strength characteristics of the system. According to L.B. Gesenzwei this ratio is 87% and 13% of mineral powder and bitumen in weight fractions.
Example I of the method.
Samples of asphalt concrete were formed from granular asphalt binder based on dolomite flour with a BND bitumen content of 60-90 13.6%. The test results of samples of asphalt concrete are shown in table I.
| Table I. | |||
| The name of indicators | Granular asphalt binder | GOST 31015-2002 requirements for ЩМА | Requirements of TU 5718-002-04000633-2006 to cast asphalt concrete |
| Water saturation% | 0,3 | 1,0-4,0 | 1,0 |
| The compressive strength at a temperature of 50 ° C MPa | |||
| 3,10 | not less than 0.65 | not less than 1.0 | |
| Tensile strength at compression at a temperature of 20 ° C MPa | |||
| 9,00 | not less than 2.2 | not standardized | |
| Shear resistance: coefficient of internal friction; shear adhesion at a temperature of 50 ° C MPa. | |||
| 0,86 | not less than 0.93 | not standardized | |
| not less than 0.18 | |||
| 0,58 | not standardized | ||
| Water resistance coefficient | |||
| 1,03 | not less than 0.85 | not standardized |
The data presented in the table show a significant excess of almost all indicators of the properties of asphalt concrete from granular asphalt binding requirements of GOST and TU. The only indicator by which the material is inferior to alkali-ferrous alloys is the coefficient of internal friction. This result is quite obvious given the structure of the structure of the compared materials. The ALA has a skeleton structure formed of large gravel particles, which leads to a high value of the coefficient of internal friction. Granular asphalt binder does not contain crushed stone, but the shear resistance of the material is ensured by the high shear adhesion.
The data given are explained by the structural features of the granular asphalt binder obtained by the pelletizing method. With a uniform distribution of bitumen in the mass of material, bitumen films with nanoscale thicknesses are formed in the structure. This contributes to the manifestation of the nano-effect of system structuring, leading to a sharp increase in the bonds between the powder particles and the strength of the material. In cast asphalt concrete this effect is not manifested, despite the rather high content of asphalt binder in the material. The ratio of bitumen / mineral powder in this material is far from optimal, and therefore, the asphalt binder has the properties of bitumen, which softens with increasing temperature, and the coating layer forms inflows and waves from moving vehicles.
In addition, the strength of the structure is ensured by the mechanism of perception of external loads, which is fundamentally different from the load distribution of the coating core in multi-grained materials. Granular asphalt binder is a practically homogeneous material, and therefore, the external load is distributed evenly over the contact area of \u200b\u200bthe road surface and the wheels of the car, reducing specific pressures and particle strength requirements of the mineral part of the material.
A sharp increase in the strength characteristics of granular asphalt binder allows to reduce the thickness of the upper layer of asphalt concrete coating to values \u200b\u200bof 1.5-3 cm with guaranteed ensuring the strength of the coating and at the same time reducing the material consumption of the layer. A decrease in the layer thickness leads to a decrease in tensile stresses arising from bending deformation. It is known that asphalt concrete, like many building materials, works well in compression and is much worse in tension. Thus, the integrated use of the procedures described in the characterizing part of the claims provides strength characteristics of asphalt concrete pavement.
The durability of the coating is guaranteed by the minimum water saturation of the material by analogy with cast asphalt concrete. It is known that asphalt concrete pavement is most susceptible to destruction during thaws with alternating frosts. During the thaw, the material is saturated with moisture, the volume of which increases with freezing, leading to cracking of the material and its destruction. The asphalt concrete pavement made of granular asphalt binder, having minimal water saturation, prevents the implementation of such a destruction mechanism.
Laying a granular asphalt binder with a small thickness on the surface of a freshly laid lower layer with further compaction leads to a partial indentation of the granules into the body of the lower layer, guaranteeing reliable adhesion of the upper and lower layers of the coating. It also helps to increase the strength characteristics of the coating as a whole.
The use of surface treatment to ensure the necessary adhesion of the road surface with the wheels of the car is traditionally used in the construction of coatings of fine-grained or sand mixtures. At the same time, a serious problem when wetting crushed stone for surface treatment with bitumen is the insufficient adhesion of stone material and bitumen. This often leads to the tearing of gravel particles from the road surface, which leads to the creation of emergency situations. The reason is dusty particles on the surface of the stone material. In this regard, many asphalt plants crushed stone before treatment with bitumen is pre-washed with water and then dried and treated with bitumen.
When creating an asphalt binder layer deposited on the surface of crushed stone particles, adhesion of the asphalt binder particles to the crushed stone surface is ensured by the fact that during the pelletizing process, each crushed stone particle repeatedly interacts with microvolumes of bitumen and is guaranteed to be wetted by it. The asphalt binder shell on the surface of the gravel provides reliable adhesion of the particle to the upper coating layer, preventing it from flying out under the influence of the wheels of the car. This reduces the consumption of crushed stone for surface treatment of the coating. The optimum roughness of the surface of the coating in accordance with the experiments is achieved when the treated gravel with a temperature of 80-100 ° C is embedded in the roadway at a temperature of 80 ° C.
The measures considered make it possible to obtain high-strength and durable asphalt concrete pavement with a minimum content of expensive high-strength granite crushed stone. The increased content of bitumen in comparison with other types of coatings is compensated by the strength characteristics of the material, which allows to reduce the coating layer, reducing material consumption and facilitating the design. This allows the use of the proposed asphalt concrete pavement on bridges and overpasses.
A method of arranging an asphalt concrete pavement, including preparing the base, laying and compacting the lower coating layer with further laying and compacting the upper layer onto the still-cooled lower layer and surface treatment by crushing crushed stone, characterized in that the upper coating layer is 1.5-3 cm thick from granular asphalt-binding material obtained by the pelletizing method, with a bitumen content of not more than 15%, and for surface treatment use pre-prepared crushed stone with a particle size of 3 -5 mm, on the surface of which a layer of asphalt binder obtained by the pelletizing method is applied, while the amount of asphalt binder in the shell is 5-10% by weight of crushed stone, crushed stone consumption is not more than 5 kg / m 2, and crushed stone is heated after the laid layer cools down to a temperature 80 ° C.
Related patents:
The invention relates to a method for producing a waterproofing composition, which can be used in construction as a waterproofing material for sealing potholes and road cracks.
When the construction of a personal home is completed, the stage of registration of the personal plot begins. Making flower beds, sidewalks, planting different plants is just a small list of the necessary operations that a person has to do. Many homeowners have a personal vehicle. That is why the presence of a quality driveway to housing is simply necessary. Few people decide to perform asphalt coating on their own. However, in this article we will consider all the subtleties and nuances of such a process.
Asphalt is made from a special mixture. This solution is used everywhere. With its help, roads, squares, streets and even garden paths are arranged. However, there are certain standards for asphalt pavement. All this is prescribed in special state standards. It also indicates and. For more than a century, this dimple remains without any changes:
- Most importantly, the mandatory presence of bitumen material as a binder component.
- Mandatory presence, in a certain dosage, of quarry sand, as well as mineral additives.
- The last necessary component is a synthetically created additive.
When was it started? asphalt coatingapplied bituminous material was of natural origin. However, due to its limited amount in nature, a need arose for a synthetic analogue. This analogue is produced from waste oil. It is used now.
Sand is used in quarries, but crushed stone, slag and crushed rock are used as mineral additives. Additives are used to increase individual characteristics of the coating, such as frost resistance, viscosity index and much more.
What are the compositions?

The market for coatings is incredibly vast. Types depend on the dosage of internal components, type of additives. Professionals subdivide asphalt into the following types:
- For the design of paving, paths in the garden or courtyard. At the heart are sand mixtures.
- With finely ground solutions, city streets with non-heavy traffic are laid, and they are also patched.
- Coarse asphalt is used to create a bed. It is performed in the case of using a multilayer processing method.
- Coatings made using bitumen and polymers are used in the construction of roads on bridges or major road junctions. Their distinguishing feature is their higher durability and strength.
- Concrete, which includes crushed stone and building mastic, is recognized as the most durable. Therefore, it is used to create asphalt concrete pavement on highways.
- The processing of sports coatings is carried out using concrete with bitumen-rubber components.
Rules for laying coatings
The installation of asphalt concrete pavement is quite a serious matter and it does not matter who will carry it out. The technology of functioning on the arrangement of asphalt is prescribed in a special SNiP, as well as GOST. It is sometimes difficult even for professionals to understand everything that is written there, however, in this paragraph we will try to carefully understand everything.
Preparatory work
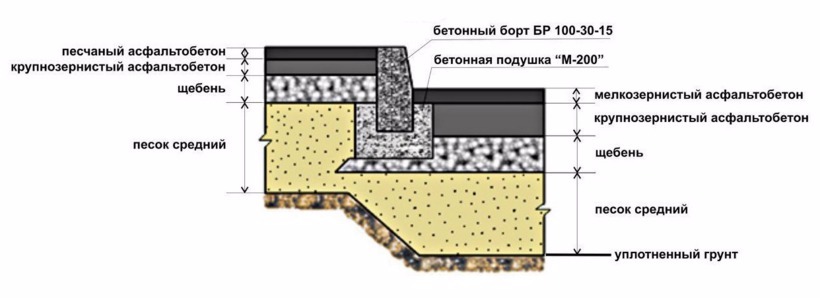 Asphalt pavement design.
Asphalt pavement design. No matter what you do, you need to start by marking up the territory. You need to determine exactly in which place the track will be. Previously, it is also worth performing drainage and drainage systems. Underground structures must be installed at the time the tracks are coated.
During the preparatory operations, it will be important to make a decision on the asphalt concrete pavement, or rather, on the materials of this coating. If motorists will periodically use pedestrian asphalt pavements, it is advisable to make a special gravel-crushed stone layer about 15 centimeters wide. The width of the surface layer of the coating will then vary from 5 to 6 centimeters. With asphalt concrete pavement at a gas station, the width of the gravel layer is about 30 centimeters. The top layer of asphalt is laid in about a couple of layers.
When the track is marked, begin to dig a trench under it. Often the street cover and pavement are performed at the same height, because of this the soil is cleaned to the full width of the asphalt “cake”. The technology for installing expressways is slightly different, but we will not disassemble it.
After the surface soil has been removed, the trench must be carefully compacted. This can be done using the ice rink. If provided, it is better to install them at this stage. Asphalt “pie” will be in such a peculiar formwork of curbs. You can also make special ditches for water drainage.
Further, the technology provides for asphalt concrete processes for the formation of a crushed stone layer. One ball is enough for sidewalks, if more powerful concrete is needed, then crushed stone is laid in several layers. The lower layer is a special drainage for groundwater. It is made from large gravel. A further layer will help to distribute the pressure on the surface of the asphalt.
The last treatment of bedding layers is the formation of the last crushed stone layer of a fine fraction. It will help make the entire pillow durable and monolithic. Each of the layers is subject to careful compaction. If asphalt concrete pavements will be subjected to severe pressure, they will compact the crushed stone with a roller at least 6 times. During this operation, additional processing of crushed stone with water should take place.
Making asphalt at home
Making a mixture of concrete and asphalt is considered a complex process. However, there are a huge number of people willing to experiment. Such mixtures cannot be applied to the tracks, however, they are quite suitable for decorating asphalt at home.
Classic method
 The additive makes cold asphalt more durable.
The additive makes cold asphalt more durable. For the manufacture of asphalt concrete paving, sand, bituminous material (resin), as well as fine gravel are required. From the inventory you will need a large capacity and a bucket. It is better to use a bonfire for cooking asphalt mixtures, it is cheaper and safer.
We place sand-gravel additives in a container in a ratio of 2 to 1 and mix thoroughly. Add water and place the container on the fire. At the same time, we are starting to prepare bitumen additives. Here you will need a metal bucket. Above the fire, melt the bitumen resin in a bucket. When the mixture additives in both containers boil, they can be mixed. After mixing, we again return the container to the fire and continue to boil until the water boils completely. Concrete surface finishes are performed while the mortar is hot.
Old coating
This method is used both to create a new canvas, and with its help it is possible to repair asphalt concrete pavement. For the most part, the process is similar to the previous method, but there are some nuances.
- The old cover is removed with a sledgehammer, the crushed stone pillow is not dismantled.
- The coating is subject to crushing into small fractions.
- The crushed coating is poured with water and melted in a container over a fire.
- After that, the surface work continues according to the previous method.
Cold Asphalt Method
It is suitable if there is a need not to make patches, but to arrange a large area. This method has gained its popularity relatively recently, about 5-10 years ago. According to the principle of operation, it resembles cold welding. One of the main components is special bitumen, which allows you to perform the entire necessary process even at low temperatures.
Its disadvantage is considered a rather big cost. But in cases where it is not possible to mount according to classical methods, cold asphalt is an excellent alternative.
The effect of materials on coating quality
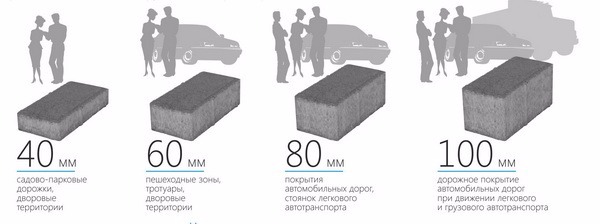 The thickness of the paving depends on the purpose of using the asphalt concrete pavement.
The thickness of the paving depends on the purpose of using the asphalt concrete pavement. The main nuance in operations related to styling asphalt pavement, is the correct and accurate choice of materials. So that you do not have to constantly perform patching, you must carefully consider this issue. Otherwise, the filling of cracks in the asphalt concrete pavement will become an eternal problem. All layers are important to carry out using the paver at the same time. This has a big impact on the quality of the track.
Despite the fact that classic concrete has good strength, this figure can be improved. The most popular method is to use special types of building mastic for asphalt. These mastics contain bitumen emulsions and rubber polymers. Ordinary bituminous mastic is used only in a hot state, but the emulsion is used in a cooled state. Mastics contribute to better sealing of cracks on the surface of the coating. This prevents water from seeping in and prevents.
Operation period roadbed depends not only on the condition of the materials, but also on the design pavement. Same type asphalt mix may behave differently on different types of foundation. On tracks and tracks located on a cement-concrete base, cracks appear over time. This happens due to the mismatch of thermal characteristics. The crushed stone base does not threaten such complications, but they can give a certain shrinkage of the entire path.
Conclusion
This article describes all the necessary nuances regarding the choice of material and the functioning with it. However, industry is constantly releasing new products that are more advanced.
With a thorough study of all the methods and subtleties of the coating, the installation process is not at all complicated.
Historians claim that the first mention of something similar to asphalt appeared in the 6th century BC in Babylon. But the technologies of those times were not reliable, plus unnecessarily expensive, as a result, such roads were forgotten until the twentieth century. The construction of asphalt concrete pavements in Russia began in 1928 and to this day it is predominant.
Photo of a country road laying.
What it is
This composition is used everywhere, starting with the laying of federal highways and ending with the arrangement of urban squares and garden paths in private construction.
According to GOST and SNiP, the device of asphalt concrete coating can be different.
But the overall composition of the mixture, for more than 100 years, remains unchanged:
- First of all, as an astringent, bitumen enters there..
- Surely, to one degree or another, sand and large mineral fillers are present.
- Various mineral or synthetic additives complete the list..

In those days when the composition was developed, natural bitumen was used, but since it is scarce in nature, an artificial analogue was synthesized based on oil products, which is still successfully used by road workers around the world.
The sand is taken quarry, as for the large filler, then, along with various types of crushed stone for concrete, crushed rock and some crystallized slag are widely used.
Natural mineral or synthetic additives are used to increase certain beneficial properties of the coating. In particular, it increases frost resistance, road adhesion, viscosity coefficient and much more.

Bitumen Resin
What formulations are produced
The assortment of the presented types is quite wide, depending on the percentage ratio of the components, as well as on what additives were used, experts divide asphalt into the following varieties.

Fine grained asphalt.
Slice coating.
Making asphalt at home
The manufacture of pavement is considered to be difficult and inaccessible. But, nevertheless, there are enthusiasts who are ready for experiments. Of course, such compositions are not designed for the federal highway, but in the country it is quite realistic to prepare such asphalt with your own hands.
Tip: from experience it can be said that a mixture prepared by a artisanal method, of course, is suitable for arranging a concrete garden path, but more often it is used to repair potholes on an already finished coating.
The temperature of the composition.
Classic recipe
For preparation, we need ordinary river or quarry sand, bituminous resin or bitumen, and fine gravel. From the equipment you will need a metal barrel and a bucket.
It is better to cook asphalt at the stake, since it is unsafe and expensive to use gas.
- Initially, we pour crushed stone with sand in a ratio of 2: 1 and mix well. All this should be filled with water and suspended over a fire.
- At the same time we are preparing a bitumen base. To do this, take a metal bucket and heat the bitumen in it to a boil, synthetic polymers can be added as a plasticizer, but it is cheaper to use shampoo or any detergent.
- When the resin has warmed up, and the water in the barrel with crushed stone has also boiled, they need to be combined. Water is needed so that crushed stone with sand does not heat up above 100ºС. Next, this broth should be stirred, maintaining a boil until all the water has boiled away. While the solution is hot it can be poured.
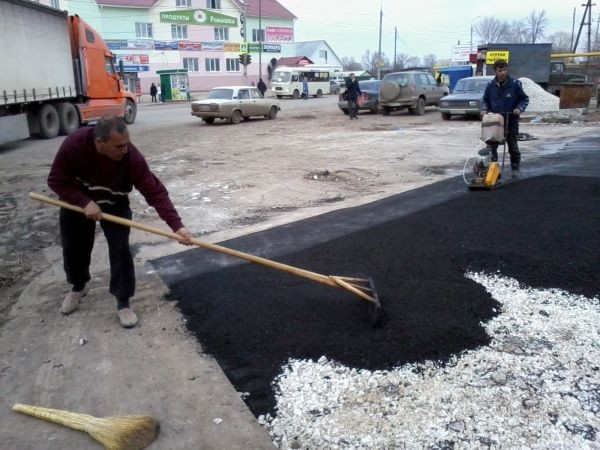

Manual styling.
Important: be careful, at 80 ºС the bitumen melts, and at 100 - 120 ºС it boils.
But even at 170 ºС, bitumen can ignite.
Actually, in order to prevent such a fire, we use water.
Use of old pavement
Dismantling of asphalt concrete pavements and substrates can be a good material for the preparation of new asphalt.
The technology is partly reminiscent of the previous version, but with some amendments.
- The dismantling of asphalt concrete pavement itself is carried out by the old-fashioned method, using a sledgehammer and other percussion instruments. Only the top layer of asphalt connected with bitumen is used, you can not touch the travel pillow.
- The old road surface is broken into pieces with a fraction of not more than 40 mm. For 100 kg of old asphalt, 10 kg of bitumen is taken.
- After that, the crushed substance must be poured with water and boiled in a barrel until melted. Further, the technology repeats the above option. Heated bitumen combines with molten asphalt and water evaporates.

Cold asphalt.
The two methods described above are well suited for economical repair of damaged asphalt in the yard or near the yard. If you need to cover an area with a large quadrature, then we recommend using cold asphalt.
In the market of our country, this coating appeared about 5 years ago. The principle of operation here is similar to the well-known cold welding. For ligament used modified bitumenthanks to which it can be laid even at subzero temperatures. Instructions are on the packaging.

Manual vibratory rammer.
The only disadvantage of this material is the significant price. But, as you know, the asphalt from the factory is released hot and must also be laid hot. Therefore, for remote locations, cold polymer asphalt is the only alternative.
Important: when repairing pavement, the problem is the quality of the joint seam in asphalt concrete pavement.
Cold asphalt based on polymers completely solves this problem, since it reliably fits with any composition based on bitumen.

A slice of cold asphalt.
Rules for laying coatings
The construction of asphalt concrete pavement is a responsible matter and it will not be so important whether you lay it yourself or hire professionals. Laying and acceptance of asphalt concrete pavement is carried out according to SNiP 2.07.01-89, as well as a number of GOSTs.
Only a specialist can understand these documents, therefore we have outlined the main provisions of these norms and rules in a more understandable language.
Laying scheme of roads with an average load.
Preparatory stage
Any work begins with markup. You need to clearly decide where the asphalt will be laid. Where the border will be mounted, and what it will be. It is also very important to make sure that the drainage, drainage system and drainage systems are fully installed.
All work on the installation of underground utilities by this time should be completely completed. If you are arranging a parking lot or access roads to an office, it is best to find out in advance where city communications are located, as if necessary, municipal services will tear your coverage and may still be fined.
It was mentioned above about the varieties and purpose of existing types of asphalt. So, at the preparation stage, you need to choose which material you are going to stack.

Work vibroplate.
Important: the estimate for the asphalt paving device should not only contain data on the cost of the material and the amount of work.
It will be useful to include transportation costs in it, as well as leave the column for unforeseen expenses, such as permission to work from the relevant official or service.
If a pedestrian walkway or a platform with occasional passage of cars is laid, then the gravel and gravel pillow can be made up to 15 cm thick. The thickness of the asphalt concrete coating will be in the range of 4 - 5 cm.
If you equip a gas station or any access roads on which, with a high degree of probability, heavy-duty equipment will periodically pass, then in this case the thickness of the gravel pillow will be about 25 - 35 cm. Plus, asphalt itself is laid at least in 2 layers.

Heavy skating rink.
After marking, the arrangement of the so-called trough or pit under the road begins. In the urban area or in private construction, as a rule, roads and sites are made at approximately the same level, so the soil must be chosen completely for the entire thickness of the “road cake”. Federal highways are equipped with a slightly different technology, but we will not dwell on it.
When the soil is selected, the entire site should be well compacted, this is done with a roller or vibrating plate. Pay attention to the presence of trees nearby, the roots may tear the asphalt over time, so it is best to remove them immediately if possible. Although the price of work will be slightly increased, we advise you to cover the soil with geotextiles, so that the vegetation does not break through the coating.

Mobile installation for thermal profiling of asphalt.
Important: at this stage, borders are installed, they play the role of a kind of formwork for the "road cake".
If laying paving slabs the curb is made below the level of the road, then here, on the contrary.
In this regard, it is necessary to immediately plan the drains for water drainage.
Now you can begin to dump the pillows from crushed stone. For footpaths with a pillow thickness of 10 - 15 cm, 1 layer of crushed stone of a fraction of 30 - 40 mm is sufficient. More powerful bases fit into several layers.
The lower layer is used for drainage in the event of a rise in groundwater; it is sprinkled with large gravel with a fraction of 40 - 70 mm. The next layer with a fraction of 20 - 40 mm will be responsible for the even distribution of the load on the base of the road.
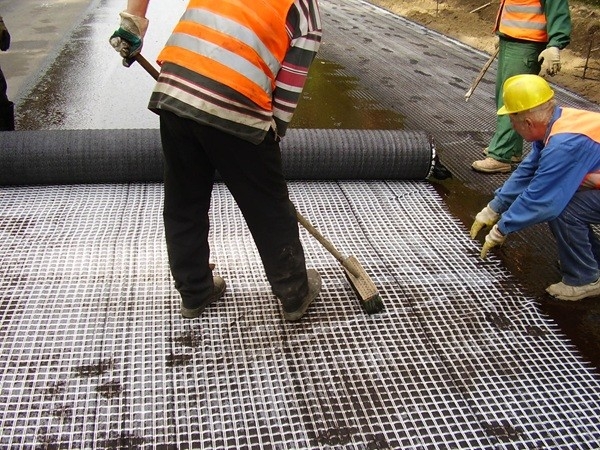

Road reinforcement with polymer mesh.
The final layer of filling is made of fine gravel with a fraction of 5 - 20 mm. He will also be responsible for the distribution of the load, but in addition he will turn the pillow into a dense, monolithic structure.
All layers laid must be tightly packed. For serious coatings, road rollers weighing from 2 to 10 tons are used. Each ball of filling is compacted separately, the skating rink must go through it at least 5 times, plus modern road skating rinks have a vibropress function, which increases the efficiency by several times. During tamping, the surface should be watered regularly.
Tip: in the process of tamping, you must immediately take into account the angle of inclination of the road, on average it is done on the order of 1º per 1 linear meter.
To do this, periodically check with the markup or level data.

Laying the federal highway.
Asphalt paving
After tamping the pillows, you can proceed directly to the laying of asphalt. As mentioned earlier, for sidewalks and adjoining territories, it is enough to lay a fine-grained composition with a layer of up to 50 mm. Heavy road rollers are also not required, you can do with a light roller or vibrating plate.
Note!
This type of coating according to SNiP is not recommended for laying in places for rest.
More serious objects are paved in 2 layers. In this case, the lower layer is laid coarse asphalt at the level of 40 - 50 mm. A fine-grained composition is imposed on it almost immediately, which in most cases is the finish.
Currently, technologies have been developed according to which a reinforcing mesh made of polymer materials should be laid between the layers of hot asphalt. As a result, the durability and strength of such a road increases significantly. This technology is used when laying federal highways and roads with increased load.
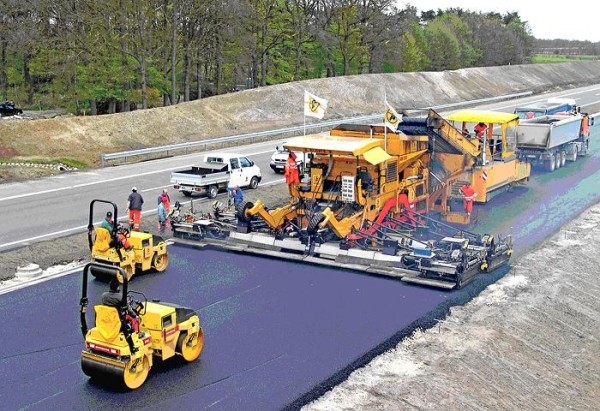

Integrated road laying.
Important: the restoration of asphalt concrete pavement with us is most often done only with the help of hot bitumen.
Although according to GOST, thermal profiling of asphalt concrete coatings should be carried out.
This procedure provides for the preliminary warming of the roadway to a depth of 2 - 5 cm.
The mixture must be delivered hot to the object, as a rule, it is brought by dump trucks with a lifting capacity of 7 - 20 tons. After that, asphalt is manually or mechanically distributed evenly along the road plane, observing the slope. On average, 1 ton of asphalt with a thickness of 40 mm is consumed per 10 m² of roadbed.
The construction of asphalt concrete pavements is a weather-dependent process. In the cold season, that is, at temperatures below +5 ºС, work is generally not recommended. Plus, during rain or in wet weather, the styling quality is significantly reduced, since the composition is moistened and cools faster.

The unit for removing the old coating.
We outlined the general basic principles of high-quality asphalt paving, but science does not stand still and technologies are supplemented and improved. In the video in this article, you can consider the process of laying asphalt in more detail.
Historians claim that the first mention of something similar to asphalt appeared in the 6th century BC in Babylon. But the technologies of those times were not reliable, plus unnecessarily expensive, as a result, such roads were forgotten until the twentieth century. The construction of asphalt concrete pavements in Russia began in 1928 and to this day it is predominant.
What it is
This composition is used everywhere, starting with the laying of federal highways and ending with the arrangement of urban squares and garden paths in private construction.
According to GOST and SNiP, the device of asphalt concrete coating can be different.
But the overall composition of the mixture, for more than 100 years, remains unchanged:
- First of all, as an astringent, bitumen enters there..
- Surely, to one degree or another, sand and large mineral fillers are present.
- Various mineral or synthetic additives complete the list..
In those days when the composition was developed, natural bitumen was used, but since it is scarce in nature, an artificial analogue was synthesized based on oil products, which is still successfully used by road workers around the world.
The sand is taken quarry, as for the large filler, then along with various, crushed rock and some crystallized slag are widely used.
Natural mineral or synthetic additives are used to increase certain beneficial properties of the coating. In particular, it increases frost resistance, road adhesion, viscosity coefficient and much more.
What formulations are produced
The assortment of the presented types is quite wide, depending on the percentage ratio of the components, as well as on what additives were used, experts divide asphalt into the following varieties.
- For the arrangement of sidewalks, garden paths or the inner space of urban courtyards, sand compositions are used.
- Fine-grained structures cover the city streets with medium and high traffic.
- Coarse-grained asphalt is used as a base layer in multi-layer paving technology.
- Bitumen-polymer coatings are used in the installation of bridges, three-dimensional parking or road junctions. They have increased strength and durability.
- Crushed stone mastic types of asphalt are considered the strongest; they are laid by federal highways and high-speed autobahns with increased traffic load.
- For stadiums, treadmills or bicycle paths, as well as other sports facilities, there is a rubber-bitumen coating.
Making asphalt at home
The manufacture of pavement is considered to be difficult and inaccessible. But, nevertheless, there are enthusiasts who are ready for experiments. Of course, such compositions are not designed for the federal highway, but in the country it is quite realistic to prepare such asphalt with your own hands.
Tip: from experience it can be said that a mixture prepared by a makeshift method, of course, is suitable for arrangement, but more often it is used to repair potholes on an already finished coating.
Classic recipe
For preparation, we need ordinary river or quarry sand, bituminous resin or bitumen, and fine gravel. From the equipment you will need a metal barrel and a bucket.
It is better to cook asphalt at the stake, since it is unsafe and expensive to use gas.
- Initially, we pour crushed stone with sand in a ratio of 2: 1 and mix well. All this should be filled with water and suspended over a fire.
- At the same time we are preparing a bitumen base. To do this, take a metal bucket and heat the bitumen in it to a boil, synthetic polymers can be added as a plasticizer, but it is cheaper to use shampoo or any detergent.
- When the resin has warmed up, and the water in the barrel with crushed stone has also boiled, they need to be combined. Water is needed so that crushed stone with sand does not heat up above 100ºС. Next, this broth should be stirred, maintaining a boil until all the water has boiled away. While the solution is hot it can be poured.
Important: be careful, at 80 ºС the bitumen melts, and at 100 - 120 ºС it boils.
But even at 170 ºС, bitumen can ignite.
Actually, in order to prevent such a fire, we use water.
Use of old pavement
Dismantling of asphalt concrete pavements and substrates can be a good material for the preparation of new asphalt.
The technology is partly reminiscent of the previous version, but with some amendments.
- The dismantling of asphalt concrete pavement itself is carried out by the old-fashioned method, using a sledgehammer and other percussion instruments. Only the top layer of asphalt connected with bitumen is used, you can not touch the travel pillow.
- The old road surface is broken into pieces with a fraction of not more than 40 mm. For 100 kg of old asphalt, 10 kg of bitumen is taken.
- After that, the crushed substance must be poured with water and boiled in a barrel until melted. Further, the technology repeats the above option. Heated bitumen combines with molten asphalt and water evaporates.
Cold asphalt
The two methods described above are well suited for economical repair of damaged asphalt in the yard or near the yard. If you need to cover an area with a large quadrature, then we recommend using cold asphalt.
In the market of our country, this coating appeared about 5 years ago. The principle of operation here is similar to the well-known cold welding. A modified bitumen is used for the bundle, so it can be stacked even at sub-zero temperatures. Instructions are on the packaging.
The only disadvantage of this material is the significant price. But, as you know, the asphalt from the factory is released hot and must also be laid hot. Therefore, for remote locations, cold polymer asphalt is the only alternative.
Important: when repairing pavement, the problem is the quality of the joint seam in asphalt concrete pavement.
Cold asphalt based on polymers completely solves this problem, since it reliably fits with any composition based on bitumen.
Rules for laying coatings
The construction of asphalt concrete pavement is a responsible matter and it will not be so important whether you lay it yourself or hire professionals. Laying and acceptance of asphalt concrete pavement is carried out according to SNiP 2.07.01-89, as well as a number of GOSTs.
Only a specialist can understand these documents, therefore we have outlined the main provisions of these norms and rules in a more understandable language.
Preparatory stage
Any work begins with markup. You need to clearly decide where the asphalt will be laid. Where the border will be mounted, and what it will be. It is also very important to make sure that the drainage, drainage system and drainage systems are fully installed.
All work on the installation of underground utilities by this time should be completely completed. If you are arranging a parking lot or access roads to an office, it is best to find out in advance where city communications are located, as if necessary, municipal services will tear your coverage and may still be fined.
It was mentioned above about the varieties and purpose of existing types of asphalt. So, at the preparation stage, you need to choose which material you are going to stack.
Important: the estimate for the asphalt paving device should not only contain data on the cost of the material and the amount of work.
It will be useful to include transportation costs in it, as well as leave the column for unforeseen expenses, such as permission to work from the relevant official or service.
If a pedestrian walkway or a platform with occasional passage of cars is laid, then the gravel and gravel pillow can be made up to 15 cm thick. The thickness of the asphalt concrete coating will be in the range of 4 - 5 cm.
If you equip a gas station or any access roads on which, with a high degree of probability, heavy-duty equipment will periodically pass, then in this case the thickness of the gravel pillow will be about 25 - 35 cm. Plus, asphalt itself is laid at least in 2 layers.
After marking, the arrangement of the so-called trough or pit under the road begins. In the urban area or in private construction, as a rule, roads and sites are made at approximately the same level, so the soil must be chosen completely for the entire thickness of the “road cake”. Federal highways are equipped with a slightly different technology, but we will not dwell on it.
When the soil is selected, the entire site should be well compacted, this is done with a roller or vibrating plate. Pay attention to the presence of trees nearby, the roots may tear the asphalt over time, so it is best to remove them immediately if possible. Although the price of work will be slightly increased, we advise you to cover the soil with geotextiles, so that the vegetation does not break through the coating.
Important: at this stage, borders are installed, they play the role of a kind of formwork for the "road cake".
If when laying paving slabs the curb is made below the level of the road, then here, on the contrary.
In this regard, it is necessary to immediately plan the drains for water drainage.
Now you can begin to dump the pillows from crushed stone. For footpaths with a pillow thickness of 10 - 15 cm, 1 layer of crushed stone of a fraction of 30 - 40 mm is sufficient. More powerful bases fit into several layers.
The lower layer is used for drainage in the event of a rise in groundwater; it is sprinkled with large gravel with a fraction of 40 - 70 mm. The next layer with a fraction of 20 - 40 mm will be responsible for the even distribution of the load on the base of the road.
The final layer of filling is made of fine gravel with a fraction of 5 - 20 mm. He will also be responsible for the distribution of the load, but in addition he will turn the pillow into a dense, monolithic structure.
All layers laid must be tightly packed. For serious coatings, road rollers weighing from 2 to 10 tons are used. Each ball of filling is compacted separately, the skating rink must go through it at least 5 times, plus modern road skating rinks have a vibropress function, which increases the efficiency by several times. During tamping, the surface should be watered regularly.
Tip: in the process of tamping, you must immediately take into account the angle of inclination of the road, on average it is done on the order of 1º per 1 linear meter.
To do this, periodically check with the markup or level data.
Asphalt paving
After tamping the pillows, you can proceed directly to the laying of asphalt. As mentioned earlier, for sidewalks and adjoining territories, it is enough to lay a fine-grained composition with a layer of up to 50 mm. Heavy road rollers are also not required, you can do with a light roller or vibrating plate.
Note!
This type of coating according to SNiP is not recommended for laying in places for rest.
More serious objects are paved in 2 layers. In this case, the lower layer is laid with coarse asphalt at a level of 40 - 50 mm. A fine-grained composition is imposed on it almost immediately, which in most cases is the finish.
Currently, technologies have been developed according to which a reinforcing mesh made of polymer materials should be laid between the layers of hot asphalt. As a result, the durability and strength of such a road increases significantly. This technology is used when laying federal highways and roads with increased load.
Although according to GOST, thermal profiling of asphalt concrete coatings should be carried out.
This procedure provides for the preliminary warming of the roadway to a depth of 2 - 5 cm.
The mixture must be delivered hot to the object, as a rule, it is brought by dump trucks with a lifting capacity of 7 - 20 tons. After that, asphalt is manually or mechanically distributed evenly along the road plane, observing the slope. On average, 1 ton of asphalt with a thickness of 40 mm is consumed per 10 m² of roadbed.
The construction of asphalt concrete pavements is a weather-dependent process. In the cold season, that is, at temperatures below +5 ºС, work is generally not recommended. Plus, during rain or in wet weather, the styling quality is significantly reduced, since the composition is moistened and cools faster.
Conclusion
We outlined the general basic principles of high-quality asphalt paving, but science does not stand still and technologies are supplemented and improved. In the video in this article, you can consider the process of laying asphalt in more detail.
TYPICAL TECHNOLOGICAL CARD (TTK)
ASPHALT-COATED PAVING DEVICE
I. FIELD OF APPLICATION
I. FIELD OF APPLICATION
1.1. A typical routing (hereinafter TTK) is a comprehensive regulatory document that establishes, according to a predetermined technology, the organization of work processes for the construction of a structure using the most modern means of mechanization, progressive structures and methods of performing work. They are designed for some average conditions of work. TTK is intended for use in the development of Work Projects (PPR) and other organizational and technological documentation, as well as to familiarize (train) workers and engineering workers with the rules for the production of a complex of works on the construction of sidewalks with asphalt concrete pavement in a residential building, with a width pedestrian sidewalk 1.5 m.
Fig. 1. Asphalt pavement construction
1.2. The map shows the flowchart of the technological process, sets out optimal solutions for the installation of sidewalks with asphalt concrete pavement, provides data on quality control and acceptance of work, industrial safety and labor protection requirements for work.
1.3. The regulatory framework for the development of the technological map are:
- working drawings;
- construction norms and rules (SNiP, SN, SP);
- factory instructions and specifications (TU);
- norms and prices for construction and installation works (GESN-2001, ENiR, VNiR, TNiR);
- production norms for the consumption of materials (NPRM);
- local progressive norms and prices, norms of labor costs, norms of consumption of material and technical resources.
1.4. The purpose of the creation of the shopping mall is to describe solutions for the organization and technology of the sidewalk device with asphalt concrete pavement in order to ensure their high quality, as well as:
- cost reduction;
- reduction of construction time;
- ensuring the safety of work performed;
- organization of rhythmic work;
- rational use of labor resources and machines;
- unification of technological solutions.
1.5. On the basis of the TTC as part of the PPR (as mandatory components of the Project for the production of works) Workers are developed technological maps (RTK) to perform certain types of work on the device of the sidewalk with asphalt concrete pavement.
Working routings regulate technological support tools and implementation rules technological processes in the production of work. Design features for the installation of sidewalks with asphalt concrete pavement are decided in each case by the Working draft. The composition and level of detail of materials developed at RTK are established by the appropriate contracting construction organization, based on the specifics and scope of work performed. RTKs are reviewed and approved as part of the PPR by the head of the General Contracting Construction Organization.
1.6. The routing is intended for manufacturers of work, foremen and foremen performing work on the installation of sidewalks with asphalt concrete pavement, as well as for technical supervision of the Customer and is designed for specific conditions of work in the 2nd road-climatic zone.
The routing should be applied to the following volumes of work:
|
Installation of concrete side stones of the brand |
- BR 100.20.8;
|
|
Sandy underlay |
- 0.20 m;
|
|
Crushed stone base M 600 |
- 0.15 m;
|
|
Fine-grained asphalt mix |
- 0.04 m;
|
|
The area of \u200b\u200basphalt concrete pavement is 1.5x100 m |
- 150 m . |
II. GENERAL PROVISIONS
2.1. The routing has been developed for a complex of works on pavement construction.
2.2. Work on the sidewalk device is performed in one shift, the duration of the working time during the shift is:
Where 0.06 is the coefficient of decrease in working capacity due to an increase in the duration of the work shift from 8 hours to 10 hours, as well as the time associated with preparing for work and conducting ETO, breaks associated with the organization and technology of the production process and the rest of construction machinery workers and workers - 10 minutes after every hour of work.
2.3. The structure of the work sequentially performed when paving the sidewalk includes the following technological operations:
- geodetic alignment work;
- a fragment of the trough under the base unit and compaction of the base soil;
- installation of side stones;
- the device of the sandy underlying layer;
- the device of the base of crushed stone;
- priming the base with liquid bitumen;
- device of asphalt concrete pavement.
2.4. The technological map provides for the performance of work by a complex mechanized link consisting of: backhoe loader JCB 3CX m
, (excavator bucket volume 0.48 m, jaw loading bucket volume 1.0 m) self-propelled, sidewalk, vibration, tandem roller compactor DM 02
(operating speed up to 8.0 km / h, operational weight 1.5 t); watering machine ПМ-3У
(tank volume 6000 l); asphalt distributor DS-39B
(tank volume 4000 l); paver paver VOGELE
SUPER BOY
(paving strip width from 1.2 to 3.1 m, paver mass 4.7 t, working speed 20 m / min, receiving hopper volume 5.0 t) as a driving mechanism.
Fig. 1. Working area of \u200b\u200ba backhoe loader JCB 3CX m
The maximum digging depth is 5.97 m; - The maximum reach of the bucket from the axis of the rear axle is 7.87 m; - The maximum reach of the bucket from the axis of the rotary column is 6.52 m; - Departure of the bucket from the axis of the rotary column at a maximum lift height of 3.66 m; - The maximum reach of the bucket from the axis of the machine when the boom rotates 90 ° - 7.09 m; - Maximum bucket lifting height - 6.35 m; - Maximum discharge height - 4.72 m; - Unloading height - 2.74 m; - The height of the horizontal bottom - 3.20 m; - The height of the axis of the hinge of the bucket - 3.45 m; - Departure of the axis of the hinge of the bucket - 0.36 m; - Departure of the bucket edge at ground level - 1.42 m; - The maximum reach of the raised bucket is 1.20 m; - Departure of the raised bucket during unloading - 0.83 m; - Digging depth (thickness of the cut layer) - 0.10 m; - Bucket tipping angle - 45 °; - Unloading angle - 43 °; Jaw opening width - 0.95 m
Fig. 2. Dimensions of JCB 3CX m backhoe loader
Overall length - 5.62 m; - Wheelbase - 2.17 m; - The distance from the axis of the rotary column to the rear axle of the bridge is 1.36 m; - Ground clearance from poles - 0.37 m; - Ground clearance from the rotary column - 0.52 m; - The height of the center of the steering wheel is 1.94 m; - Cabin roof height - 2.87 m; - Overall height - 3.61 m; - Overall width along the support frame - 2.36 m; - Width of loader bucket - 2.35 m
Fig. 3. Sidewalk Roller DM 2
Fig. 4. Paver VOGELE SUPER BOY
Fig. 5. Watering machine PM-3U
Fig. 6. Asphalt distributor DS-39B
2.5. When installing the sidewalk, the following building materials are used: crushed stone fractions 20-40 mm M 400
meeting the requirements of GOST 8267-93; medium sand
with a filtration coefficient of at least 3 m / day that meets the requirements of GOST 8736-93 *; concrete and reinforced concrete on-board stones
meeting the requirements of GOST 6665-91; road oil bitumen BND-90/130
meeting the requirements of GOST 22245-90; hot, sandy, asphalt mix
Grades II, Type G
meeting the requirements of GOST 9128-97 *.
________________
* GOST 9128-97 is not valid. Instead, GOST 9128-2013 applies. - Note by the manufacturer of the database.
2.6. Work on the installation of sidewalks with asphalt concrete pavement should be performed in accordance with the requirements of the following regulatory documents:
-. Labor safety in construction. Part 2. Construction production;
- NGO ROSDORNII-1993. Rules of labor protection during the construction, repair and maintenance of roads;
- ROSAVTODOR-2002. A collection of forms of executive production and technical documentation for the construction (reconstruction) of roads and artificial structures on them;
- RD 11-02-2006. Requirements for the composition and procedure for maintaining executive documentation during construction, reconstruction, overhaul capital construction facilities and requirements for inspection certificates of works, structures, sections of engineering support networks;
III. ORGANIZATION AND TECHNOLOGY OF PERFORMANCE OF WORKS
3.1. In accordance with SP 48.13330.2001 "Organization of construction", prior to commencement of construction and installation works at the facility, the Contractor is obliged to receive design documentation and permission (warrant) from the Customer for construction and installation work. Work without permission (warrant) is prohibited.
3.2. Before starting work on the sidewalk device, it is necessary to carry out a set of organizational and technical measures, including:
- develop RTK or PPR for the device of sidewalks;
- designate persons responsible for the safe performance of work, as well as their control and quality of performance;
- provide communications for operational dispatch management of work;
- develop schemes and arrange temporary access roads for traffic to the place of work;
- establish temporary inventory facilities for storing building materials, tools, equipment, heating workers, eating, drying and storing work clothes, as well as dry closets;
- prepare places for the storage of materials, equipment and other necessary equipment;
- provide the construction site with fire-fighting equipment and means of signaling;
- protect the construction site and put up warning signs illuminated at night;
- deliver to the work zone the necessary materials, devices, equipment, tools and tools for the safe execution of work;
- install, install and test construction machinery, means of mechanization of work and equipment according to the nomenclature stipulated by the RTK or PPR;
- instruct members of the safety team;
- draw up an act of readiness of the facility for work;
- obtain permission to perform work from the technical supervision of the Customer.
3.3. Prior to the commencement of work on the sidewalk device, preparatory work provided for by the RTK should be performed, including:
- accepted from the customer technical documentation on the creation of a geodetic alignment base (GRO) for construction and installation, and fixed on the ground signs of the points of this framework;
- the alignment work was completed and accepted to consolidate in nature the design position of the sidewalk in plan and in height;
- completed and accepted in the prescribed manner excavation on the device of the trough, under the construction of the sidewalk;
- arranged in a trough tray longitudinal drainage shallow (if necessary);
- side stones are installed along the edges of the sidewalk;
- prepared and delivered to the object sand and fractional crushed stone in the required volume.
The completion of preparatory work is recorded in the General Journal of Works (the recommended form is given in RD 11-05-2007).
3.4. Geodetic center base
3.4.1. The geodetic alignment base for construction should include:
- high-rise benchmarks (marks);
- points securing the longitudinal axis of streets, driveways, sidewalks and footpaths;
- points from which it is possible to break down the axes of driveways and control their position during the construction process.
3.4.2. Accepted signs of the geodetic alignment base during the construction process should be constantly monitored for safety and stability and checked instrumentally at least twice a year (in the spring and autumn-winter periods).
3.4.3. Acceptance of gas distribution equipment for construction should be formalized by an act of survey of the geodetic center of the capital construction object in accordance with Appendix 1, RD 11-02-2006.
3.4.4. A schematic plan for the improvement of the territory should be attached to the acceptance certificate for the GRO with an indication of the location of the points, the types and depths of the signs fixing them, the coordinates of the points, their picket values \u200b\u200band elevations in the adopted coordinate system and heights.
3.5. Geodetic centering works
3.5.1. The pavement axis can be broken down from the red lines of existing buildings and other permanent structures or the borders of the roadway. Vertical marks of the axial lines in the profile are carried out with the help of a level from a nearby benchmark.
3.5.2. To transfer the plan of the sidewalk designed and shown in the drawings to the terrain, it is necessary to have the same permanent objects, both on the plan and on the terrain. These items can be points of triangulation, points of intersection with by road (edge \u200b\u200bof the roadway), communication lines, power lines, etc. The breakdown data that is taken from the project is attached to them, and from them, the installation of side stones is broken down, the process is as follows (see Fig. 5):
- according to the plan, determine the distance from these points to permanent objects available on the plan and on the ground and determine the actual distance on an accepted scale;
- the received points on the ground are fixed with pegs and gatehouses (callouts);
- transfer the mark of the nearest benchmark to the control columns.
3.5.3. From the center line of the sidewalk, after 20 meters with a tape measure on both sides, a trough under the sidewalk is broken and at the obtained points, as well as at the turning points of the longitudinal profile, a number of wooden pegs are set along the theodolite and a cord is drawn along them.
The width of the trough is taken into account the installation of side stones. On pegs on the level mark the elevations of the bottom of the trough, the sandy underlying layer, the crushed stone base and the asphalt concrete pavement.
The design mark along the axis (bottom of the trough) of the bottom of the pavement (base layer) is determined by the formula:
Where is the mark of the top of the pavement;
Trough depth;
- trough width;
- the bias of the trough.
The transverse slope of the bottom of the trough should be equal to the slope of the surface of the coating 10-15 ‰ and are sent to the trays of the carriageways or to the drains.
The value of the required thickness of the sandy underlying layer is taken into account the material safety factor for compaction equal to 1.10, and crushed stone bases, taking into account the material safety factor for compaction equal to 1.25.