Suggestions with indirect speech on the topic of spring. Differences between direct and indirect speech. Indirect speech joins the main body of NGN
Read the suggestions. Which of them convey foreign speech literally, with all its features, and which only the content of foreign speech? What parts of these sentences match? What parts and how do they differ (in structure, in intonation)?
The teacher said: "Your class will go on an excursion." The teacher said that our class will go on an excursion.
The trainer advised me: “You breathe deeper!” The trainer advised me that I breathe deeper.
The doctor asked, “What was your temperature?” The doctor asked what my temperature was.
Offers with indirect speech serve to convey someone else's speech on behalf of the speaker, and not the one who actually said it.
Sentences with indirect speech convey only the content of someone else's speech, but cannot convey all the features of its form and intonation.
Suggestions with indirect speech are complex sentences, consisting of two parts (the words of the author and indirect speech), which are connected by unions that, as if, to, or pronouns and adverbs who, what, what, how, where, when, why, etc., or whether a particle.
With the help of unions, it seems that the content of narrative sentences of someone else’s speech is indirectly transmitted, for example:
The forester said: "I saw swans on the lake."
The forester said he saw swans on the lake.
The forester said he saw swans on the lake.
With the help of the union, to convey the content of incentive sentences of someone else's speech, for example:
The captain ordered: "Boats on the water!"
The captain ordered the boats to be lowered.
Sentences with pronouns and adverbs that, who, what, how, where, when, why, etc., or with a questioning particle, or indirectly convey the content of the interrogative sentences of someone else’s speech, for example:
“What time is it?” I asked.
I asked what time it is.
We asked the oncoming: “Where are you going?”
We asked the meeting where they were going.
“Will you solve this problem?” I asked a comrade.
I asked a friend if he would solve this problem.
A question conveyed in indirect speech is called an indirect question.
Have fun and success in learning. If you want to test your knowledge, solve problems! When we express ourselves in writing, we must consider relevance, text structure, hierarchical organization of ideas, grammatical correction, as well as spelling and calligraphy. All this is connected with a lot of knowledge, which, according to Frank Smith and Stephen Crashen, cannot be consciously studied using grammar exercises, because the language is too complex, but unconsciously through reading.
To learn how to write, you need to read as an issuer, and thus learn how to use written language in the same way that good authors use it. A well-written text should have specific organizational characteristics that are covered by the conditions of coherence and cohesion. Consistency is a property of well-formed texts that allows them to be considered as a whole, so that secondary ideas provide accurate information related to the central topic. A letter is consistent when its subject is clear and develops orderly with progression in information and without conflicting statements; while coherence is a semantic issue, cohesion is a linguistic and grammatical question, as it concerns the syntactic relationship between the parts of the discourse, so that it is coherent.
Translation of direct speech into indirect Direct speech Indirect speech I. 1. Narrative sentence Unions that, as if 2. Incentive sentence Union to 3. Interrogative sentence:
a) with an interrogative pronoun or adverb;
b) without an interrogative word. Interrogative pronoun or adverb
Particle II. 1. The pronoun of the 1st person. The person of the author of another's speech 2. The pronoun of the 2nd person. The person of the addressee of another's speech 1.
398. Read the sentences. Determine the type of direct speech by the purpose of the statement. Using the table, replace the sentences with direct speech with the sentences with indirect speech. Write them down. Explain the replacement of pronouns.
Sample. The teacher asked the student: “Are you ready for an answer?” Direct speech is an interrogative sentence without an interrogative word, therefore, in indirect speech, particles should be used. In direct speech, the pronoun of the 2nd person is used, when replacing direct speech with indirect one, the person of the addressee (student) is used instead, that is, the 3rd person. Indirect Speech Suggestion: The teacher asked the student if he was ready to answer.
1) The forester said: "Before the hunt you need to have a good rest." 2) We met friends and asked: “Where are you going?” 3) The teacher asked the attendant: “Please bring chalk.” 4) I asked a friend: “Will you go to the disco today?” 5) Grandma asked her granddaughter: “Read this letter to me.”
Read. Write off, replacing direct speech with indirect. Pay attention to the correct use of personal and possessive pronouns, as in indirect speech the author conveys other people's words on his behalf.
1) The taxi driver assured: "I will bring you to the station in fifteen minutes." 2) Nina asked her friend: “Tanya, will you go to the concert tonight?” 3) Kolya said: “My father is a geologist.” 4) “Be at the museum at exactly 11 o’clock,” the history teacher warned us.
I. Convert these sentences with direct or indirect speech into sentences with introductory words.
1) Eyewitnesses claimed: "The accident was caused by the pedestrian." 2) Newspapers report: "Spring sowing is going well." 3) Scientists believe that rivers can be protected from pollution2.
Convert these sentences into indirect speech sentences.
1) According to doctors, smoking is especially harmful to
lungs. 2) According to experts, forest fires most often arise from careless handling of fire. 3) According to weather forecasters, spring will be early.
A good book is a real celebration.
Attentive and quick reading is a very important off-road.
Read the verbs that are used in the words of the author. What verb groups can be used in sentences with direct or indirect speech? Which verb groups can be used only in sentences with direct speech? Make sentences with indirect speech, using the verbs of the 1st group in them.
1) Say, mutter, whisper, shout; 2) to be surprised, delighted, upset, amazed; 3) interrupt, stop, interrupt; 4) turn around, smile, nod; 5) inform, notice, whisper, blur, blur out.
Replace direct speech with indirect, pay attention to the forms of pronouns (see the table on page 205).
1) “Why didn’t you go with them?” The old woman Isergil asked with a nod of her head. 2) “I do not want,” I answered her. 3) “Tell me how it was!” - I asked the old woman. 4) He (Larra) said: “Untie me! I will not say bound. " 5) And when people untied him, he asked: “What do you need?” 6) Then one of the people shouted out loud: “Do not touch him! He wants to die! ”
(M. Gorky.)
Read and indicate what mistakes were made when transmitting someone else's speech. Write off, correcting sentences. О Explain the spelling of the highlighted word. Tell us about the spelling of prefixes pre- and pri-, give examples.
1) Pugachev told Grinyov that you are firmly in front of
it's my fault. 2) The Tsar tells Kiribeevich that I will try to help your grief. 3) The mayor tells the officials that I invited you to tell you some unpleasant news. 4) The hero of the story “After the Ball”, Ivan Vasilievich, assures that my whole life changed from one night. 5) The falcon answers I know that I know happiness, I fought bravely.
Text cohesion procedures can be divided into lexicons: repetition of words, wild words, use of synonyms, antonyms and hyperonyms, use of pronouns and verbal persons, demonstrative and temporary adverbs, etc. and grammar: discursive markers, connectors and punctuation marks.
Text Text Objectives To learn how to represent objects or events, to describe them or classify them. Learn to join ideas with the help of linguistic markers: causal, spatio-temporal, opposition, addition, conclusion. Text texts are displayed in very different contexts and allow variable expansion. They have general characteristics: objectivity, clarity and organization. The fundamental unit of text is a paragraph, as indicated by a separate paragraph.
Lesson topic: "Suggestions with indirect speech."
Today we repeat what we know about direct speech. Consider another way to convey speech in writing . And find out what is the difference between direct and indirect speech.
In the lesson we

Text “Pathogenic ecological environment” We are poisoning the world. World production of chemicals has grown from one million tons in the thirties to four hundred million today. These include pesticides with heavily polluted aquifers. Smoking and alcoholism are the most health-related addictions. However, campaigns in developed countries are beginning to bear fruit, and there has been a decrease in lung cancer in men. But the risk is shifting south.
Transport-related pollution is responsible for respiratory illnesses such as asthma and bronchitis, but the internal environment is even worse due to emissions from materials and internal activities. Write down what pollutants we have inside the house. Add two paragraphs to the text that talk about other pollutants, but keep in mind linguistic markers. Write a short text with three paragraphs and indicate your city as the topic. With the following words, write a document about the environmental situation in the world today: pollution, spills, climate change, the greenhouse effect.
We have already said that speech often has to be transmitted in writing. For example, a friend asks us to write what the teacher said about her project.
How can one convey someone else's speech in a letter.
We have already said that speech often has to be transmitted in writing.

The verbs you use should be indicative. Narrative text Objectives Learn to communicate events or events in an organized manner. Know the basic elements of narrative text. Use the past tense correctly. To tell is to tell something that happened at a given moment in time. The elements that make up the narrative are: what is counted, that is, the action; characters place and time. "Morning walk". He walked every morning, his nervous hands were hidden in the pockets of his already worn coat.
We know, that there are several ways to convey direct speech in a letter.
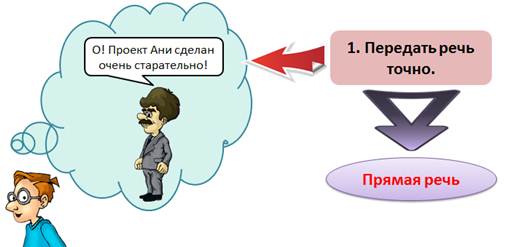
Teacher's statement: "ABOUT! Ani’s project has been done very carefully! ” - can be transmitted accurately using direct speech.
There are several ways to convey direct speech in a letter.
He looked at her silently, even forgetting about hunger in moments, sending funny images, jealousy, suffering. Focus on this arrogant air, this distance from him, his lost eyes in the distance. His indifference or his distant distance from his own suffering could never be discouraged. Sometimes she felt the warmth of her gaze; perhaps even once wanted to answer him, especially to smile at him or shed tears. But there are so many things forbidden for a mannequin locked in a stained glass window.
Despite this, he survived all this time thanks to her. Diego Munoz Valenzuela. This text tells us that the mannequin thinks of a woman walking past him every day. Make a story by changing the point of view and write what the woman thinks of the mannequin. Now you are about to create the beginning of this story. For example: who is a woman? What do you do before you pass the mannequin and where are you going? Imagine a mannequin coming out of a window and coming up with an end to the story. From the following sentences he builds a letter: "Rain."
Direct speech - This is the speech of a person transmitted on his behalf.
"ABOUT! Ani’s project was done very carefully! ”Said the teacher.
In this sentence, direct speech is enclosed in quotation marks, and the author’s speech follows it after the dash.
Features of direct speech in that speech is transmitted verbatim. Speech style and grammar are preserved. The intonation of speech is also preserved.
The following text tells a story that is messy. It belongs to Nicholas Guillen and is entitled “Poem about Love” and you need to order a story. Consider linear developments. You will see her and love her more than ever. Know that he will see her again. The touch is barely, electrical contact. This is love like this, this is love for the abyss in spring. Descriptive text. Learn to use adjectives correctly. Enrich the dictionary with synonyms to give variety to what is written.
Follow the order in the descriptions. Description is a photograph of reality through language, so it does not have enough time. It usually appears in a narrative or dialogue. You can describe objects, landscapes, people, etc. the verb of the time of description is indicative, although when it is in the narrative, it may appear in imperfect time. The fundamental element of the description is the adjective, in it we express the sensations of sound, touch and color, but there are other resources for the description, since they are a comparison or a metaphor.
Direct speechIs the speech of a person transmitted on his behalf
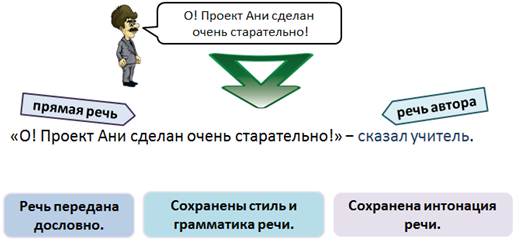
However, in life we \u200b\u200bdo not so often need to transmit speech verbatim, with such accuracy.
Imagine the situation: a friend asks you to convey what you and your friends talked about after class. “And what did Lesha say? What about Ira? What did Katya ask about? ” And so you begin to state verbatim.
This is the sound of seagulls. Seagulls slowly roll through the blue waters or sit on the waves - like white pieces of paper - and remain for a long time motionless, brought and carried, aupada and sunken, gently and gently swinging. the class is located on the second floor of the institute, at the bottom of a wide corridor. It is spacious and with large windows through which you can see the trees in the yard. In the background is the teacher’s table, behind a huge board that covers the entire wall, and in front of it is the table in which we sit.
In the previous texts you have three descriptions: the first of the landscapes, the second class and the third person. Make a description of the sea landscape in which the following words appear: reddish, calm, sunset, boats, waves, foam, sun, sky, clouds. Describe your room as you see it from the front door. The description of the person is in the narrative, therefore it is in the past. Describe in the same verb tension the one who for some reason impressed you. Look at the picture below and make an ordered description of what you see: in the foreground, in the middle and in the background.
Alex said: “Hey, hello! And you know, I saw a new film! ”And Ira said:“ Ha! So what! So I played a new game! ”And Katya ...
But wait, is it possible to literally convey the whole long conversation with friends?
But in life, we don’t need to transmit speech verbatim so often

Dialogue text Objectives To learn to distinguish dramatic dialogue from a dialogue of storytelling. Learn to distinguish between direct and indirect styles. Know how to use the resources that characterize the text of the dialogue. When characters in a plot or play express themselves directly through dialogue. Although the dramatic text is the most appropriate basis for dialogue, it is also an integral part of many stories when the narrator disappears and the characters face to face what they think and feel. The dialogue is aimed at reflecting oral communication, so it has its own characteristics, such as: dexterity, ellipsis, the use of deictics, the use of short phrases with interrogations and exclamations, and the use of the spoken register.
In such cases, we use another way to convey speech. Here is how our retelling of the conversation will sound:
Alex said he saw a new film. Ira replied that she was playing a new game. And Katya asked why Ira also had such red eyes.
We usually use a different way of transmitting speech.

From a graphical point of view, the dialogue is marked by the script when it is a story and the name of the character who speaks when the text is dramatic. When the narrator transcribes what the character says in a straightforward style, he is represented by quotation marks. Text I came to Komalu because I was told that my father lives here, a certain Pedro Paramo. This is called one and the other. He told me earlier: Do not ask for anything. It was a time of heatwave when Augustus air was hot, saponarium poisoned by hot air. The road went up and down; Up or down how this happens.
Today, with the example of the phrase we already know, we will consider how to convey only the content of the statement.
There are several ways to write someone else’s speech in writing
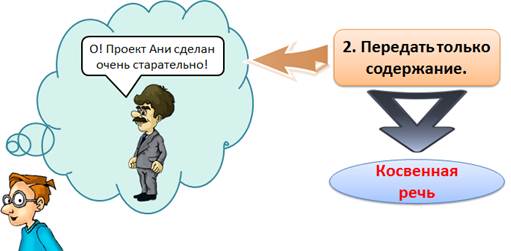
This can be done with indirect speech.
For one who walks, he rises; come down for the one who comes. “How do you say this is called the people you see there?” “Komala, sir.” “Are you sure this is Komala?” “Of course, sir.” “And why does it look so sad?” “Time, sir.” Separate dialogue from narration. Imagine how the dialogue continues and records it. You can make eight more lines. Place text dialogs in an indirect style. Now you are writing a small dialogue that combines direct and indirect style.
In short, why talk! What is in your factory? Since the last metallurgical strike, people have hurried. Let's see when you imitate independent. Write the differences you find between this dialog and the previous one. Conduct a dialogue in which two characters talk about a third person. Now bring this dialogue into the narrative and put it in an indirect style. Notebook for life Objectives Improvement of language correction, mastery of the written language and style of our students.
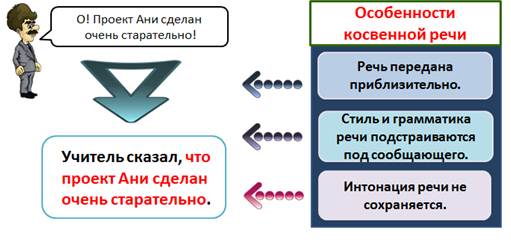
Indirect speech - this is a person’s speech transmitted on behalf of the person transmitting it.
The phrase of the teacher in an indirect speech will look like this: “The teacher said that Ani’s project was done very carefully.”
Paying attention:
Speech transmitted approximately. Speech style and grammar are tailored to the communicator. Speech intonations are not saved (for example, the interjection “O” is not transmitted).
Check out the writing of simple texts. Encourage our students to reflect on the need to write correctly. Finding a laptop is just as important as finding a good book: a blank sheet is negative of the printed page, and future words and images will appear in it in the slow development of time. You are not looking for a laptop because you feel the need or desire to write something. A complete notepad has some experience, completed and completed. Opening a laptop with all the blank pages looks like it lives in an intact house, for example, for life.
All these are features of indirect speech.
Indirect speech- this is the speech of a person transmitted on behalf of the person who transmits it.
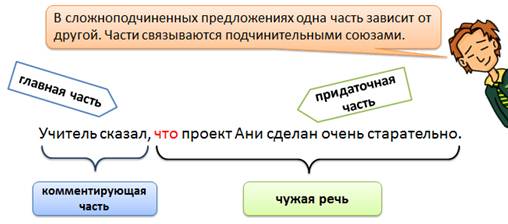
Indirect speech is made out in the form of a complex sentence.
As we remember in complex sentences, one part depends on another. Parts are linked by subordinate unions.
In our offer "The teacher said" - this is the main part. The main part in such proposals is commenting, that is, the author’s speech conveys.
The relative part of the complex sentence in this case conveys someone else's speech.
Indirect speech is made out as a complex sentence
Let's consider some sentences with indirect speech.
Anya asked me when the concert would begin.
And you answered Ana that you did not know this.
Anya asked us to find out when the concert will begin.
Let's consider some sentences with indirect speech

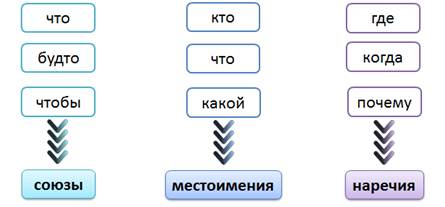
Communication tools used in indirect speech sentences:
Indirect speech joins the main body of NGN with the help of subordinate unionswhat if.
Indirect speech can also join using pronounswho what what.
- Adverbs where when and whycan also serve to add indirect speech to the main part of a complex sentence.
Indirect speech joins the main body of NGN
The choice of means of communication depends on the purpose of the statement in indirect speech.
Misha said that he was ill and therefore would not come. Union what here serves to express storytelling.
I asked when Misha will appear in class. Adverb when, allows you to transfer question .
Misha asked me to give him homework. Union so that used to express motives, requests.
The choice of means of communication depends on the purpose of the statement in indirect speech

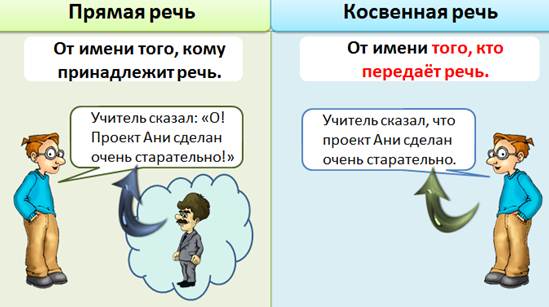
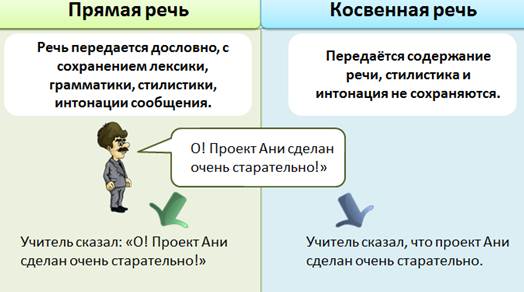
Differences between direct and indirect speech
- Direct speech is pronounced on behalf of the person to whom the speech belongs.
Master said: “Oh! Ani’s project has been done very carefully! ”- transmitted on behalf of the teacher.
- Indirect speech is delivered on behalf of the person who delivers the speech.
“The teacher said that Ani’s project was done very carefully” - transmitted on behalf of the one who will pronounce it.
- Direct speech is transmitted verbatim, while preserving vocabulary, grammar, stylistics, and intonation of the message.
- In indirect speech, only content is transmitted. Stylistics and intonation are not preserved.
Note. When converting our phrase into direct speech, the interjection "Oh!" Is preserved. In indirect speech, it is not saved.
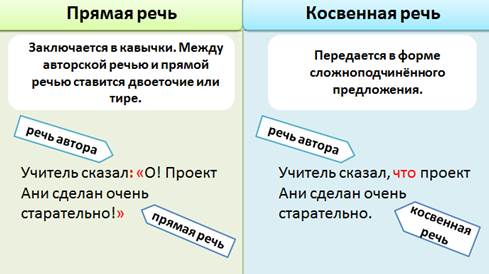
- Direct speech is enclosed in quotation marks. A colon or dash is placed between the author’s speech and the direct speech.We considered punctuation options in direct speech. Look at one of them: the author’s speech faces a direct speech, and therefore a colon is placed after it.
- Indirect speech is transmitted in the form of a complex sentence. Moreover, the main part of the sentence is the author’s speech, and the subordinate part is the indirect speech itself.
Summarize:
Indirect speech is such a way of transmitting speech when a person’s speech is presented on behalf of the person who conveys it