Foundation damage and repair. What to do if the foundation is cracked? What happens if you don't repair a cracked foundation?
First, you need to place beacons from tile adhesive or cement-sand mortar, and they need to be placed on the masonry, not on the plaster, at the beginning and end of the crack. The lighthouse is made in the form of a figure eight, the top and bottom of which rest on the banks of the crack, and the middle runs along the crack. Usually they stick a “cake” made of mortar, but it falls off from the edge of the crack, and it is not possible to find out how much the crack has grown.
Throughout the year, once every two months, the results of observations of the state of the lighthouse are recorded in the journal (whether the lighthouse is cracked or not cracked and the width of the crack in mm) and a graph is drawn. It should be noted that if the width of the crack has increased to 15-20mm over the course of a year, this is unpleasant, but does not threaten collapse.
Examples of observation results for the year:
Over a month, the development of a crack in the wall is 3-5 mm. No attenuation is observed within a few months - urgent measures need to be taken to strengthen ground structures and foundations.
The development of cracks per year is 15-20 mm. If there is no attenuation of the process, you need to strengthen the foundation and walls.
Over the course of a year, the increase in the crack is insignificant 1-5 mm. Rapid stabilization of the process is possible. And if there is no attenuation within 3-5 years, the foundation and ground structures need to be strengthened.
The lighthouse cracked by an insignificant amount of 0.5 mm. – everything is in order, these are temperature changes.
It is dangerous - if a crack in stone structures reaches -50 mm, the floor slabs will move from the support up to 30 mm, the walls will deviate from the vertical by 1/5 of its thickness.
Common mistakes when building foundations and ways to solve these problems
Diagnostics of foundation settlement for wooden houses: frame, timber and timber
Wooden buildings, especially log buildings, are least sensitive to foundation shrinkage. But despite this, foundation settlement manifests itself in the form of skewed windows, doors, and floors. As a rule, in such cases the house does not collapse, unless the beams move if they are not nailed down.
If it is 3-4 cm per 10 meters of its length, and there are no visible distortions in the building, you should not worry about this.
But if your house is on a columnar foundation, then you need to check the inclination of the pillars. If they collapse, the house must be placed on another foundation, for example, on steel piles.
Note
In cases where foundation strengthening is required, do not do it yourself. It’s better to invite a specialist, otherwise the situation may worsen.
Shallow tape
- The occurrence of deformations from the effects of frost heaving forces due to the small thickness of the sand cushion;
- No sand bed drainage;
- Poor reinforcement of the concrete foundation;
- Different density of foundation preparation (cushion);
- The soil becomes very heaving due to siltation of the sand preparation.
- If groundwater is high, installing a drainage system and an insulated blind area can help;
- It is necessary to do drainage;
- If the house is wooden, it is strengthened with nails. And if the foundation and walls are made of brick, they are reinforced with prestressed steel strands;
- The draft of the house will most likely stabilize;
- We need to move the house onto stilts.
Pile-grill foundation in steel and reinforced concrete
Causes of damage and deformation:
- Frost heaving forces act tangentially on the side surfaces of the pile;
- The base under the tip of the piles is heterogeneous;
- Insufficient foundation thickness or poor reinforcement;
- Installing the tip of the piles above the freezing depth;
- The grillage rests on heavily heaving soil.
- Insulate the foundation and make an insulated blind area. Or dig up the piles in a circle and replace the soil with coarse sand plus drainage and wrap the piles with polyethylene, having previously coated them with grease and bury them;
- Install additional piles on the subsiding area;
- Install additional piles;
- Remove the old piles and place a grillage on the new ones. Or insulate the blind area and foundation;
- Dig a gap between the grillage and the ground or insulate the blind area.
Foundation on stilts
Causes of damage and deformation:
- Dangerous friction of highly compressible soils of the upper strata;
- The base is heterogeneous;
- Do not make parking lots with concrete slabs near the house. Do not fill the area (more than 10-15 cm);
- Make additional piles in areas where the house settles.
Strip foundation laid below the freezing depth
Causes of damage and deformation:
- The foundation is unevenly loaded or the soil has insufficient bearing capacity;
- The foundation depth is higher than the freezing depth;
- Impact of frost heaving forces on the side surface of the foundation;
- Poorly reinforced foundation, no anti-sediment belts in the above-ground part of the building;
- The building is not used in winter. The door or window in the basement is open all winter.
- Strengthen the foundation by widening the base and installing micropiles (not suitable if the soil is peaty or silty);
- Insulate the blind area;
- Replace the backfill with non-heaving soil or insulate the blind area and foundation;
- Strengthen the foundation and walls;
- Live in a house in winter.

Monolithic reinforced concrete slab
Problems are solved similarly to MZL.
Foundations in wetlands
It is not recommended to do drainage in wetlands, as this will aggravate the situation. Similarly, if a person is in a bathtub full of water, he floats in it and does not press with his weight, and when the water descends, the pressure from the body on the bathtub increases. By making drainage, you will get rid of the suspended effect of water in the soil.
It is possible that the settlement of your house is related to the organization of drainage in your neighbors.
The strength of concrete should be at least 10-15 MPa. Here is a table for assessing the strength of concrete.
Approximate assessment of the strength of concrete by tapping the surface with a hammer
| The results of one blow of medium force with a hammer weighing 0.4 - 0.8 kg. | Strength of concrete MPa |
|
| Directly on the concrete surface | Using a chisel mounted with a “sting” on the concrete |
|
| A faint mark remains on the surface of the concrete, around which thin flakes can break off. | Shallow mark, blades do not break off. | More than - 20 |
| A faint mark remains on the surface of the concrete, around which thin flakes can break off. | Sharp blades break off from the concrete surface. | 20 - 10 |
| Concrete crumbles and crumbles when hit on an edge, large pieces break off. Leaves a deep mark | The chisel penetrates the concrete to a depth of 5 mm, causing the concrete to crumble. The chisel is driven into concrete to a depth of more than 5 mm. | 10 - 7 Less - 7 |
Posted by ElenaO, a member of the House and Dacha forum
Editor: Adamov Roman
Good evening.
I have not yet received an answer from you, but I can already draw several conclusions and give recommendations.
The nature of the cracks indicates that the lower right corner of the house has sagged. There may be many reasons for this, but I think the problem here is that the depth of foundation is higher than the standard depth of soil freezing on heaving soil, and accordingly, since there is no loading of the foundation and water is being shed (rain, snow, and a body of water nearby), then most likely the soil is being squeezed out , and the corner sags. Very poor reinforcement, 8s are really very small, 8 mm in diameter is taken to tie together powerful longitudinal rods, and you took all of them, so in fact you just have a concrete foundation without reinforcement. You also correctly said that if the concrete was not made according to technology, then its grade is significantly reduced, and this is also an indicator for cracks.
1. You need to carefully dig out this lower right corner and see if the soil is soaked there and what generally happens to this corner. Perhaps it is simply covered in water due to the lack of a blind area and the water flows down the slope under it. Or is there some other problem there. If you dig it out and everything goes well, then next you will need to cover up the cracks. If there is a problem with the water or soil, it will need to be corrected.
2. For a small bathhouse, this is a completely normal foundation, even if we take into account that the reinforcement and grade of concrete are damaged. You will need to cover it with non-shrink cement mortar (that’s what it’s called in stores), you will dilute and seal it according to the instructions. Next, it’s better to put beacons. Make beacons at least for the summer and then tell us what is happening there. We need to look at the progress of destruction and intensity. Cracks can be sealed with any elastic putty or repair mixture. Just make sure they are suitable for outdoor use. Ideally, cracks are sealed 1 year after all measures have been taken to eliminate the causes of cracks. But in this case, it won’t be possible to seal it in a year (blind area, foundation, etc.), so cover it now to understand whether they will continue to creep after sealing.
3. Build walls and cover the roof so that the foundation does not become damp. Judging by the soil inside the foundation, you need to get it out from the inside, since it looks like it is not clay, but black soil. Although I could be wrong, the grass is growing, which means rotting processes are occurring in the soil, and accordingly the structure is shrinking. Floors cannot be built on such soil.
4. After construction, it is advisable to immediately complete the blind area, at least rough.
I'm waiting for the results of the excavations and questions.
answerThe most dangerous thing for an individual developer is pouring a foundation in winter, which leads either to a lack of design strength or to numerous openings of cracks. However, there are technological, structural and operational reasons that are fraught with similar defects.
A clear sequence of design and manufacture of monolithic foundations is given in the regulatory documents SP 20.13330 - SP 25.13330, departmental standards VSN, technical maps of the TTK. However, mixtures, formwork and reinforcing frames are often made at home in violation of technology, proper care of the concrete is not provided, and the geological conditions in the construction site are ignored.
The main reasons why concrete cracks after pouring are violations of technology, operation, structural design and even the choice of materials.
Acceptable crack opening
The standards SP 28.13330 regulate the complete absence of cracks exclusively in unique structures or in cases where absolute impermeability of the mass is required (gases, liquids under pressure inside). The foundations of cottages do not fall into this category, therefore they are standardized by SP 63.13330 standards. There are several types of cracks in reinforced concrete products, not all of which are dangerous for the performance of the structure:
- hair - got their name from the opening width of 0.1 mm, caused by violations of the outer layer, practically do not affect the strength;
- shrinkage - mainly operational (0.3 mm), geology is not taken into account (loose, weak, unstable, bulk soils);
- horizontal - dangerous for the foundations of heavy buildings, with excessively heaving soils, since they usually cut through the thickness of the structure, after which the operation of the reinforcement frame is disrupted.

Such cracks often form after pouring; the cause may be poor-quality vibration compaction, dilution of concrete with water, or neglect of concrete care. They usually pose no threat unless they exceed acceptable limits, as shown in the following photo. They are sealed with special repair compounds. They are called shrinkage cracks in concrete (not to be confused with shrinkage of the entire structure under load).
For MZLF it is acceptable if the concrete cracks after pouring within an opening of 0.15 - 0.18 mm (ACI-224), 0.1 mm (GOST 13015) or 0.3 - 0.4 mm (German standards for opening along reinforcement , perpendicular to the working axis, respectively, after pouring).
Nature and location of cracks
Crack opening can occur after application of external loads. Therefore, there is a classification of these defects according to the type of load.
- Connection crack - concrete is destroyed parallel to the rods of the lower and upper chords, the joints of the rods. This is caused by improper anchoring (usually at T-junctions and corners) or by soil compression, uplift from over-watering, or subsidence. In addition, the culprit may be early stripping, loading of weak concrete with masonry or frame crowns, or insufficient cross-section of reinforcement. With such cracks, there is a danger of the protective layer peeling off.
- Through crack - the culprit is central tension outside the center of the structure.
- Shear crack - usually runs diagonally to the frame rods, occurs due to transverse forces (for example, a pallet with masonry bricks was placed on the tape);
- A bending crack is perpendicular to the axis of the wall and begins at the edge of the stretched zone.

An example of strong shrinkage cracks, such cracks are already dangerous.
Situations often arise when cracks appear on the surface due to internal stresses. The main reason in this option is the significant difference in temperature between the core and the surface of the laid mixture (concreting in the heat, frost + heat released during the chemical reaction of cement with water).
If these stresses exceed the strength of the structural material itself, cracks can open anywhere. They penetrate deep and can close on their own when the temperatures of the layers naturally equalize.
Prevention of thermal stresses - the use of special cements. For example, with a reduced heat of hydration (marked VLH), Portland cement with slag (marked LH). An easier way is to control the temperature of the concrete before laying - within +20 degrees.
Armature
After laying reinforcement with peeling rust, cracks open after several months or even years. If the protective layer is not observed or the rods are released into the ground (for better support of the clamps), the situation is completely similar to the indicated case.
Aggressive advertising by manufacturers of composite reinforcement is aimed solely at increasing sales volumes. It is strictly not recommended for individual developers to lay it in concrete. For example, manufacturers indicate seamlessness as the main advantage:
- the composite is easy to deliver to the building site in the form of a bay;
- however, excessive plasticity and flexibility leads to unpleasant consequences;
- instead of immediately absorbing tensile loads, the reinforcement is first pulled out;
- this is usually enough to open cracks in the concrete.

Consequences of using fiberglass reinforcement.
In addition, despite the corrugation, the structure of fiberglass and carbon composite is too smooth, adhesion to concrete components is an order of magnitude lower.
Weather
Cracks often appear in concrete after winter concreting, usually in the area of concentration of voids in which water accumulates or along the reinforcement. Measures to combat the defect are high-quality compaction with the tip of a deep-well vibrator until bubbles completely stop, large fillers are hidden, and cement laitance appears (the funnel collapses almost instantly after removing the vibrating tool).

Vertical cracks after wintering indicate incorrect calculations or no geology at all.
The next reason is the accelerated drying of exposed surfaces in the wind, cold or heat. Stresses arise inside the surface layer and cannot be eliminated. Timely and high-quality care of fresh concrete is required.
Poor quality raw materials
Cracks may open due to the cement not meeting the declared quality. Individual developers are looking for cheap prices and often do not pay attention to packaging. The bags of a manufacturer that values its reputation must include:
- details - you can conduct an examination, file a complaint, at least partially compensate for the damage;
- packaging period - cement retains its properties under storage conditions for 3 months, after which it begins to “lose” its strength quite sharply;
- ratio of water and filler - for mortars and concretes;
- composition - addition of slag, grinding size significantly influence the hydration process, which is important for the thermal regime of massive structures intended for use in the ground and aggressive environments.

Concrete cracks on the surface immediately after pouring, including due to plastic shrinkage. The principle of this defect is determined by the process of formation of cement stone:
- the volume of the mixture increases with the release of heat as a result of a chemical reaction;
- the surface cools and dries faster and begins to shrink;
- in the core the process lasts more slowly and prevents surface compression;
- the result is cracks across the entire surface or individual sections of concrete.
There is no clear direction, everything depends on the circumstances. Or longitudinal cracks 1–3 mm thick and of insignificant depth appear. A wet compress made from periodically moistened sawdust, sand, and rags completely saves you from these troubles in the first three days.
Dilution with water
When ordering the mixture using mixers, developers sometimes receive delivery times of one and a half hours. After laying the first layer, time is required for compaction by vibration. Another 1 - 1.5 hours pass, the concrete begins to thicken, water is added to it.

Large shrinkage crack turning into a vertical one. When the concrete is heavily diluted with water and a vibrator is not used, this also happens.
In this case, cracks are inevitable, since the proportions balanced by the mortar unit are disrupted. Grade strength decreases, hydration time increases (water-cement ratio W/C increases).

Side view of the top crack.
"Long Run"
Downtime of mixers is expensive for the developer, so concrete is often dumped in one place and shoveled to distant areas without a tray. This leads to the separation of the mixture into separate fractions - large crushed stone is better captured by the entrenching tool, the liquid practically remains in place.

Pronounced consequences of concrete delamination.
The result is an uneven concentration of sand/crushed stone in individual areas, which cannot but affect the quality. There will be no design strength in any section of such a foundation, crushed stone is physically unable to envelop the reinforcement, cracks are inevitable.
Exceeding the technological break
The recommended technological break is 1 - 2 hours, depending on the specific pouring conditions, due to the hydration time. If the next portion is laid after the specified time on the previous layer, the tip of the deep vibrator will destroy the formed bonds without the possibility of their restoration.
In addition, a large volume of concrete on the surface of the previous layer will push through the emerging structure, which will lead to the formation of cracks and a loose consistency incapable of absorbing loads.
What can be done or methods of correction
There are several ways to repair cracks that formed immediately after concreting:
- discrepancy before setting begins - if defects were noticed on the surface within 2 hours, the concrete can be compacted with a vibrator again to completely correct the situation (time is calculated from mixing the concrete at the factory, and not from the time of laying in the formwork);
- discrepancy after setting - a solution made in a 3/1 ratio (cement, water, respectively) with the addition of 3 - 4 drops of plasticizer (detergent is suitable) is rubbed into the cracks; you can use a special repair mixture, which must be purchased in advance.
If a network of small cracks is found in the concrete within 8 hours from the moment of laying the formwork inside, it can be eliminated using several methods:
- cleaning with a wire brush, foam glass;
- dust removal with a vacuum cleaner;
- putty with repair compound (for example CN83 from Ceresit);
- repeated cleaning with foam glass/brush after drying.
Larger cracks in concrete are removed from dust, widened with a spatula, rubbed with compounds containing fine-grained sand, and rubbed with an abrasive tool. If the groundwater level is high and there is a possibility of their seasonal rise, injection formulations, for example Penetron or similar, should be used.
The article discusses the main reasons for the opening of cracks in concrete, which are acceptable or make operation impossible. Almost any violation of the foundation concreting technology can lead to a sharp decrease in the service life of the structure immediately after removing the formwork. Small cracks in concrete can be repaired in the first days after pouring. To solve other problems, you will need expertise, development of a reinforcement project or dismantling of a reinforced concrete structure.
Advice! If you need contractors, there is a very convenient service for selecting them. Just send in the form below a detailed description of the work that needs to be performed and you will receive proposals with prices from construction teams and companies by email. You can see reviews about each of them and photographs with examples of work. It's FREE and there's no obligation.
All cracks that appear on the foundation of the house indicate that the base of the structure needs to be strengthened or repaired. But in order to do this with your own hands, you need to know about the reasons for the destruction of the foundation, as well as how exactly restoration work should be carried out
Why are cracks dangerous?
If the foundation of a building is cracked, work must begin immediately to restore it. If this is not done, after a while, due to the skew of the house, the doors and windows will begin to jam. If the house is made of brick, the crack may spread to the wall, causing the entire structure to begin to collapse. That is why it is necessary to begin work on strengthening the foundation as soon as possible.
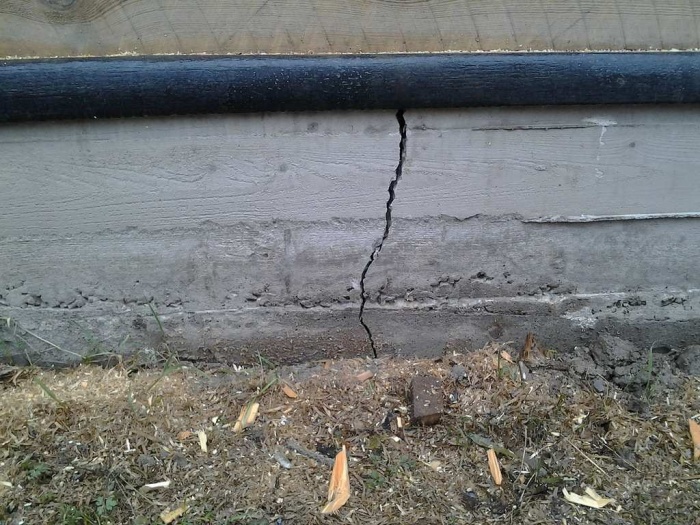

Before starting restoration work, it is worth determining the type of crack. To do this, just clean it from dust and rinse with water. After this, you need to install a beacon on the fault. The date of fixation is marked on it. This is necessary to determine the rate of destruction of the base. If the lighthouse remains intact within two weeks, the crack can simply be sealed with concrete mortar. If the lighthouse breaks, it is necessary to begin work to strengthen the base.
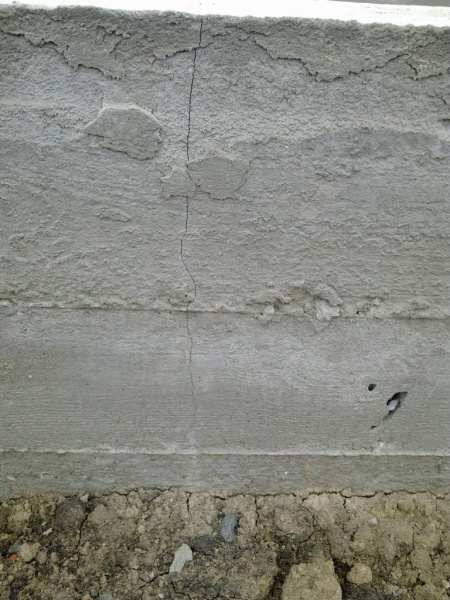

Typically, cracks begin to appear in winter or spring, since it is at this time that an improperly created foundation begins to rise or settle unevenly. It is worth remembering that the foundation can burst due to many reasons, so it is necessary to think about this problem at the stage of designing a house.

Causes of faults
Before starting restoration work, it is necessary to determine the reason why the destruction began. If these actions are neglected, even after repair the foundation will gradually collapse. The causes of destruction can be divided into several groups:
- Technological. An example is the creation of the foundation of a house with violations of reinforcement or installation of formwork. Mistakes also include choosing the wrong brand of concrete. Laying the foundation above the groundwater level is also considered a technological error.
- Operational. Such mistakes are made already in the process of using the constructed structure. For example, an increase in the load on the foundation as a result of the creation of a second floor. Another violation is an increase in humidity in the basement or poor-quality installation of a drainage system near the house.
- Structural. An example is the preparation of incorrect calculations during the design of a structure. Often the foundation begins to collapse prematurely due to the fact that geological studies were not carried out before construction began.
Important! In order to avoid encountering the problem described, before building a house, it is necessary to accurately calculate the load on the foundation.

Types of cracks
Cracks in the foundation of a wooden house, which can occur on the foundation, are divided into several types:
- Hairy. Such cracks are hardly noticeable and have a thickness of no more than 3 mm. Their presence only indicates a change in the outer layer of the base. Such flaws can be corrected quite easily.
- Horizontal. Such defects do not affect the integrity of the foundation.
- Shrinkage cracks. Such defects arise when the rules for creating a foundation are violated.
- Vertical. It is these cracks that are a sign that the foundation needs repairs. They often appear under the influence of groundwater on the base or due to soil heaving.
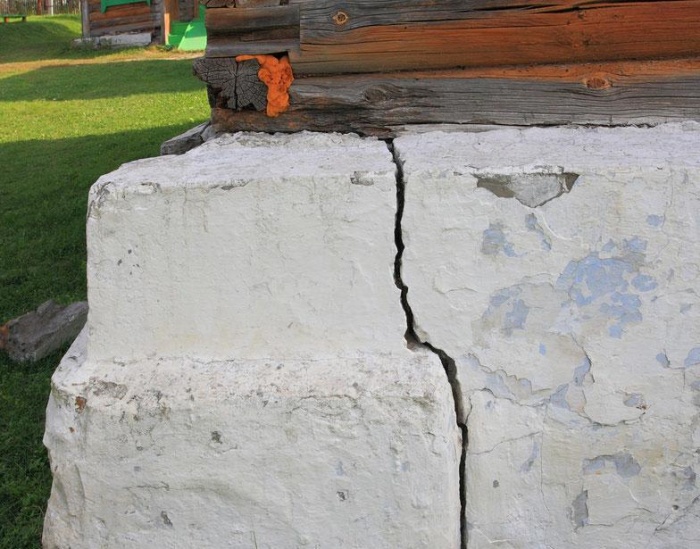

How to fix the problem
If you notice that the foundation of your house is cracked, you need to begin strengthening it as quickly as possible. Such work is carried out as follows:
- first, using a jack, the sagging parts of the base are raised to the design level;
- after this, holes are drilled, the diameter of which ranges from 20 to 40 cm;
- the resulting void is filled with liquid glass, cement laitance or hot bitumen.
This reduces the permeability of the soil, which will make the soil more stable. The described strengthening method can only be used when using special equipment, so for such work it is necessary to hire professional builders.
Strengthening the foundation of a stone house
The main task of repairing the foundation of a house is to stop the process of settlement of the structure. therefore, you cannot dig under the foundation without securing it. A strengthening method is often used, in which a reinforcing concrete belt is erected on all sides. Such work is carried out as follows:
- A trench is dug along the strip base of the house, the width of which is approximately 45 cm. During such work, the base of the foundation must not be exposed.
- After this, the foundation is cleaned of dirt and dust. In this case, all cracks must be expanded with a spatula.
- Then the falling off parts of the old foundation are removed.
- At the next stage, the concrete surface is treated with a primer. It is worth remembering that you need to choose deep penetration formulations.
- After this, holes are drilled in the foundation. The distance between them should be about 60 cm.
- Anchors are driven into the created holes, which are subsequently welded to the reinforcement frame. The diameter of the reinforcement should be approximately 12 mm.
- At the last stage, the concrete mixture is poured into the created trench. To ensure that the concrete solution is evenly distributed throughout the trench, it is necessary to use a construction vibrator. This also helps to fill cracks in the old foundation. If this stage of work is neglected, voids may remain in the concrete, which will subsequently cause the destruction of the foundation.
Backfilling of soil occurs only after the concrete has completely hardened. If the cracks are not caused by subsidence or deformation of the foundation, they can be repaired with mortar and plastered.

It is worth remembering that if the work is carried out incorrectly, the foundation will quickly begin to collapse even with additional reinforcing structural elements.
Repair of the base of a wooden house
A cracked foundation of a wooden house can be strengthened quite simply, since such structures can be lifted with a jack and installed on temporary supports. But it is worth remembering that if the lower logs are rotten, the structure cannot be raised.

If the crowns are unreliable, rotten areas are cut out of them, after which the house is raised. After this, you can restore the foundation using one of the common methods. Often, owners of country houses install a concrete bandage around the base. You can also dig under the base and pour concrete pillars. This will make the foundation resistant to significant loads.
It is worth remembering that before raising the house, it is necessary to dismantle part of the roof at the place where it connects to the chimney. It is better to invite professional builders to carry out such work.
Reinforcement with piles
In some cases, it is not possible to increase the density of the soil under a building. In such a situation, it is necessary to strengthen the foundation with piles:
- If the house is wooden, the entire structure is lifted onto temporary supports, after which the tops are tied together with a grillage. After this, the structure is lowered onto a new foundation.
- In cases where it is necessary to strengthen the foundation without raising the house, “bulls” are used. They are piles that are driven obliquely from different sides of the corner. Beams are welded onto the heads of these elements, which will serve as support for the structure.
When using piles, it is worth remembering that their length must be sufficient so that they rest on solid ground.
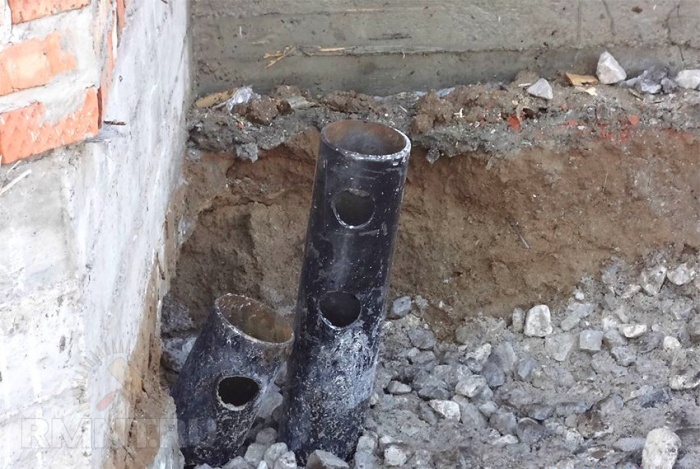

Monolithic slab repair
Monolithic foundations are destroyed quite rarely, but under certain conditions this is possible. If a serious crack appears on such a base, it can only be replaced with a new slab. No method will help stop the destruction of a monolithic foundation if it is already beginning to deform.

Conclusion
If it is impossible to completely replace the foundation for some reason, the walls are strengthened and old sections of the slab are removed. In these places, concrete mortar is poured, which helps to temporarily maintain the integrity of the structure. You can also install concrete blocks or piles as supports.
One of the main problems that relate to the structural integrity of the foundation is the appearance of cracks in the foundation. According to statistics, the appearance of cracks is caused by temperature changes (90% climate change), and cracks can also arise due to other reasons. It is about ways to solve the problem that has arisen, as well as cracks of a different nature, that will be discussed in this article. Instructions for installing a pile-strip foundation are here:.
What to do?
What to do if a crack is found in the foundation? If the size of the resulting crack is insignificant, then surgical repair should be abandoned. This does not mean that the matter will be left to chance. It is necessary not to touch it for the reason that it will be necessary to track any changes that will occur to it in the future. Will they happen at all or will everything remain in place? Also, its “naturalness” should indicate the root cause of its occurrence, and this requires a lot of time.
If the owner of the house is in a hurry to seal the crack, then soon it will appear not only on the foundation of the house, but also on its walls. Also, in the future, this may lead to jamming of doors in rooms, deformation of the structure itself and, as a result, destruction.
A number of steps must be taken in order to monitor crack formation.
The first step is to prepare any cracks found. Clean them from various dirt and rinse thoroughly with water. Then a beacon is placed on the cracks. The beacon is a cement or plaster strip 12-20 cm in size. There are thickenings at the ends of the beacon; it is on them that the installation number should be written. The third step is to monitor changes in the nature and structure of the crack.
Acceptable cracks in the foundation are those that do not continue to grow over time, i.e. they form on the outer surface of the foundation.
Causes
Based on the opinions of experts and architects, this kind of problem worsens during the demi-season period (winter-spring). Even the slightest deviation from the norms for laying the foundation in a given period of time can lead to large deformations, because in winter, under the influence of frost heaving forces, uneven lowering and raising of the structure can occur. Read how to do it and what brand of cement is needed for this.
In the spring, due to differences in soil thawing, uneven settlement of the support may occur. Practice shows that a high-quality foundation can withstand this kind of load, but this lasts for a certain period of time.
If there were any violations during the pouring of the foundation, then after twelve months the entire foundation may be dotted with cracks of varying depths.
There are now three main causes of cracks:
- Operational. This type of violation is associated with improper operation of the building: an increase in the level of load on the foundations (for example, the construction of an additional floor), poor drainage in the building area, as well as high levels of humidity in the basement and plinth.
- Structural. These reasons are associated with calculation calculations, namely: with an incorrect calculation of the load produced on the foundation of the building, from the bearing capacity of the soil at the site where the foundation is installed. You can also add here the refusal to conduct a soil analysis, and a number of other design and architectural errors.
- Technological. These types of reasons include violations that occurred during the construction of the foundation: incorrect installation of formwork, incorrect reinforcement of the base, incorrect approach to choosing the brand of building mixture, as well as installation of the foundation of the house above the level of groundwater flow.
Types of foundation cracks
At the moment, all cracks that occur on the foundation are divided into the following types:

Cracks in the foundation of a house
Cracks can occur in the foundation of any structure. It doesn’t matter at all what the structure is made of:
- A crack in the foundation of a wooden house is a rather rare phenomenon, but it still happens. It occurs due to a long period of operation and increased load on the foundation of the building.
- a crack in the foundation of a brick house is common and requires serious action. Cracks in such houses grow quickly, because the brickwork is not a monolithic structure.
Repairing foundation cracks
It would be more correct to talk about repair work and strengthening foundations, which are most often encountered in practice:
- Shallow type strip foundation;
- Pile foundation;
- Concrete type foundation.
At the moment, innovative injection technologies can be used to repair concrete foundations. Such a foundation involves drilling holes at the base, which are then filled with synthetic resins or concrete.
The diameter of such a recess is 0.3 cm, and the required depth can be calculated using the formula: 1/2 x SF (base width). To eliminate the crack, the solution is injected under high pressure.
To seal cracks in a shallow strip-type foundation, it should be deeper. This is accomplished by forming a reinforced concrete structure under the foundation itself, which significantly increases the base area of the structure.
But as for strengthening the pile foundation, it should simply be converted into a strip foundation. The foundation area will increase and the load will decrease. In practice, it is necessary to rely on external factors.
Video
Watch video tips that will help you decide what to do if the foundation cracks: