The device wall in the ground of reinforced concrete: the advantages of technology. Technology "wall in the ground" for the installation of underground structures
In the cramped, difficult urban environment, the construction of new buildings and technical facilitiesAs a rule, it is carried out using the “wall in soil” technology. It is a continuous reinforced concrete engineering structure enclosing a construction site and located directly in the ground.
What is the technology "Wall in the ground"
The essence of the technology is to create a trench around a building object, fill it with a thixotropic solution and then displace the solution with reinforced concrete mixture, or in a structure reinforced concrete wall from bisected piles. The advantages of the method include:
- Almost unlimited depth of underground work.
- The ability to enclose the perimeter of any configuration.
- Lack of vibration and noise.
- With the simultaneous installation of the foundation and basement - the absence of the need for removal of a large amount of soil.
- Freezing and dewatering of the soil is not required.
- No need to block traffic.
- Significant cost savings (on average about half the estimated cost).
- Reducing the timing of work.
- Smaller volume earthworks.
What is the “wall in the ground" technology used for?
Ground Wall Method applicable for the construction of structures located below groundwater level, and for land development: with it you can carry out work on a large area with minimal noise and virtually no vibration.
- In the construction of tunnels and subways.
- When installing underground garages and parking lots.
- Collectors, pumping stations.
- Mooring, port facilities.
- In case of land development: when due to tight conditions and due to vibration there is a risk of damage to neighboring buildings.
- In problematic hydrogeological conditions.

See also:
Types of walls
According to the method of construction:
- Pile. They are made from bisected piles. Used near structures below their foundations. To avoid movement under the foundations, casing pipes are used for wall installation.
- Monolithic (as well as prefabricated and precast monolithic). The installation process includes digging a trench and filling it with concrete, clay, clay and cement. The composition of the filler depends on the type of structure.
Antifiltration.
Protecting.
The airtight curtains constructed by the “wall in soil” method are used as a barrier to contaminated infiltration water (for example, from sedimentation tanks), and also to protect territories and structures from swamping and flooding.
The device wall in the ground, features
Pile walls
The process consists of several stages.
- Drilling of the wells using casing pipes in increments equal to the diameter of the pipe. The pipe has a concave section. Thus, neighboring wells are “layered” on top of each other.
- Reinforcement.
- Concrete pouring.
- After concrete hardening - pipe extraction.

Monolithic walls
- Construction ground shafts (reinforced concrete fences, the purpose of which is to prevent soil from falling into the trench).
- Digging a trench.
- Thixotropic clay filling.
- The room in the trench of the reinforcing cage.
- Filling with concrete (the thixotropic solution is forced out).
Clamshell trench development
Method The wall in the ground is a special technology for building the foundation and fencing before digging a foundation pit, it consists in the construction of vertical walls underground facilities in trench slots before the start of rock development inside the structure. It is used in the construction of urban underground structures (transport tunnels and metro stations, parking lots and garages, multi-level underground complexes, etc.), the foundations of houses and bridges, retaining walls, and air curtains. The method is applicable in almost any type of soil. Limitation: fluid and quicksand, dispersed bulk, soils with large voids.
Cost
The company BEST-STROY LLC works according to the method "Wall in the ground", the cost is from 22,000 rubles per cubic meter. m.
Ground wall

The main technological operations of the wall device
Slot trenches are developed in a dry way in the case of clay soils with a low yield index, to a shallow depth of up to 7 m. In other cases, during sinking, they are filled with thixotropic suspensions, which keep the shear walls from collapse. After that thixotropic  suspensions are replaced with special materials: concrete, various mixtures, prefabricated elements that form supporting and non-bearing structures in the soil.
suspensions are replaced with special materials: concrete, various mixtures, prefabricated elements that form supporting and non-bearing structures in the soil.
The “wall in the ground” device is advisable to use in difficult hydrogeological conditions, with a shallow occurrence of a water-resistant horizon (there is no need for water reduction, freezing, etc.), in the cramped conditions of existing buildings, during the reconstruction of existing enterprises. In conditions of large cities, such as Moscow, when the density of buildings is very high, there is a difficulty in fencing the construction pit. The BEST-STROY company satisfies the demand for technology, in which, firstly, the subsidence of the foundation is prevented from lying buildings, secondly, it becomes possible to be located in close proximity to existing underground networks, and thirdly, the configuration of the excavation can be quite complex - linear or broken outline.
A wall in the ground is effective in erecting foundations in built-up areas, small underground structures at a considerable depth (usually about 20 m). Technological advantages allow combining the production of base and basement elements, including multi-story underground structures.
Foundation wall in the ground
The "Wall in the ground" technology is available in two versions: bisecting and trench development. According to the first - drilling piles are carried out at a distance less than their diameter and thus they engage, “cut” each other, eventually forming a solid fence of sufficient strength. The method of bored piles provides the opportunity to carry out the fencing of a construction site, retaining wall, dewatering or air curtain, but it is not designed to equip the base of the house. But the technology "trench development" is calculated! It gives technological advantages in construction high-rise buildings, the project of which provides for a multi-tier buried part, underground parking, garage, storage, basement. Foundation The wall in the ground simultaneously serves as the walls of the basement of the building, simplifies construction, eliminates the need for digging a pit, saves time, and reduces costs. Reinforced concrete anti-filtration curtain reliably protects the underground part of the building from groundwater, reduces the cost of drainage and pumping water from the foundation during construction.
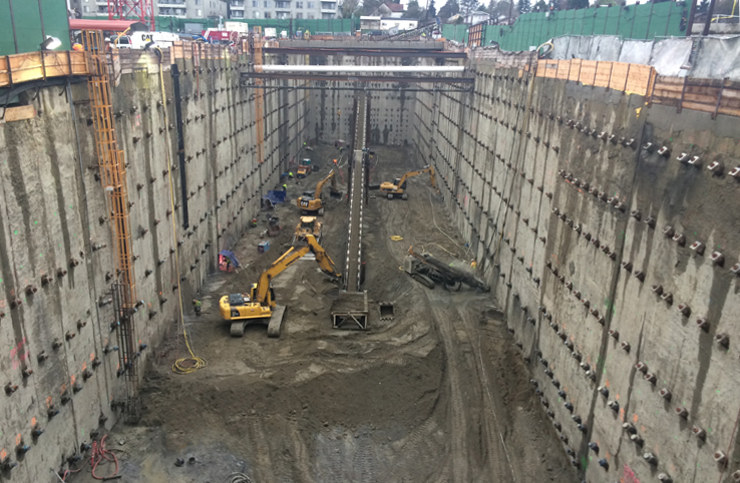

A wall in the ground serves as a foundation pit fence and as part of the foundation around the perimeter
The bearing capacity of the base of the house should correspond to the weight of the structure being built, plus the weight of the base structure itself. Design takes into account the ground conditions, the level of aquifer and bearing layers, the proximity and pressure transmitted by nearby buildings, the presence of communications in the ground under the territory of the construction site. When designing a foundation with a bed point below 3 meters, the indicator of freezing depth is not taken into account. The calculation of the bearing capacity, the calculation of soil pressure, thermal engineering calculation.
“Wall in the ground”: technology
 The method is based on the foundation device technology based on trench development. Narrow (0.6-1.2 m) and deep (up to 20 m and more) excavations are developed under the protection of a clay solution, which, thanks to a sufficiently high density, protects the cut from collapsing inward.
The method is based on the foundation device technology based on trench development. Narrow (0.6-1.2 m) and deep (up to 20 m and more) excavations are developed under the protection of a clay solution, which, thanks to a sufficiently high density, protects the cut from collapsing inward.
The technological map of works is developed taking into account the results of engineering and geological surveys. Limitations for the application of the technology are associated with the presence of certain soil conditions: groups of building soils above thirds, bogged and sandy rocks with boulders more than 300 mm in diameter; karsts, coarse soils with voids, quicksanding soils, mobile sludges, groundwater aquifers with excessive filtration exceeding the hydrostatic pressure of the protective clay solution.
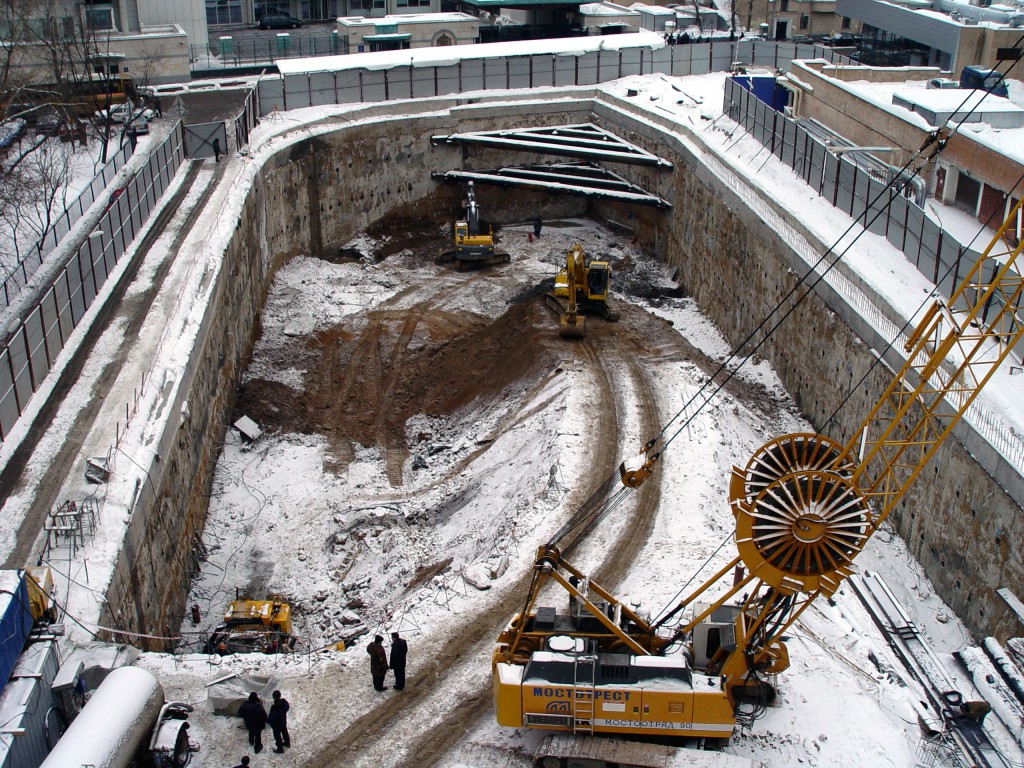
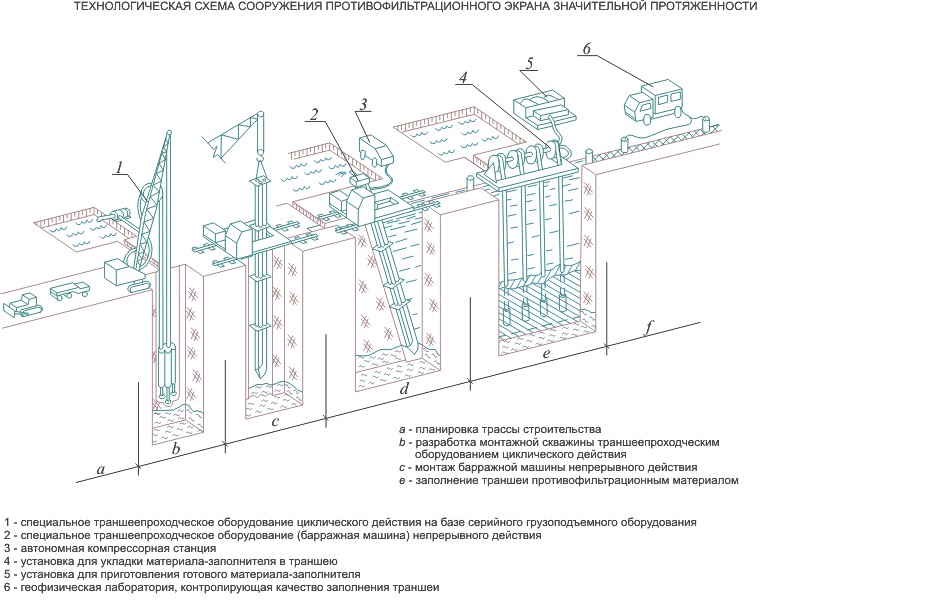
Schematically, the technology consists of a sequence of steps:
- foreshortening;
- trenching;
- lowering of reinforcing cages;
- concrete pouring.
Preparatory stage: removal of all surface and underground communications outside the development area; the site was planned and arranged with reinforced concrete slabs; territory is fenced; pre-treatment equipment for clay mud was installed and prepared for work.
Preliminary stage: surface excavation and implementation of foreshaft - rigid reinforced concrete structure, limiting the clearance of the development zone and the corresponding width of the future wall. Foreshacht protects against destruction and falling of the upper soil layers under its own weight and under the weight of the clamshell equipment. Breakdown of the trench is carried out.
Excavation of the rock occurs under the protection of a clay solution with a grab or hydroprotector. The soil is removed to the surface, removed from the production area, moved outside the construction site.
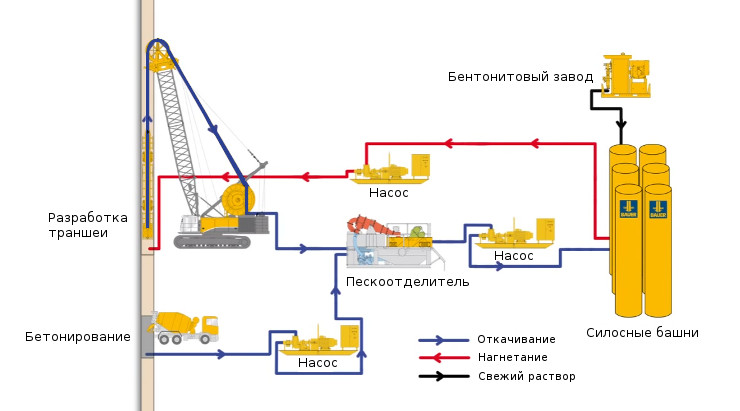
Development and concreting of a wall in soil using Bauer technology and equipment
Protection of the production of thixotropic hydro-solution allows to exclude the use of pile or sheet piling, for the organization of artificial water reduction. The volume of earthwork is reduced, and hence the complexity. Construction time is reduced.
Specialized drilling equipment is used for development, hydrophills are used in hard soils, and grabs (two-jaw narrow wide-grip grips mounted on a rigid rod) are used in soft soils, integrated as standard equipment or suspended equipment or mounted on crawler excavators in mass-produced equipment.
The trenches are torn off in stages through one in separate sections - grips, along the width of the grab grab. And they are fed a bentonite solution. In accordance with the technology, that part of the solution that is mixed with the soil due to the constant circulation enters the sludge separator, is cleaned of the rock and enters the tunnel.
Then, the open area is protected at the edges by removable or left restraints (in the form of iron beams, dowels or pipes) over the entire height. A prefabricated reinforcing cage is lowered into it.
Before concreting, the face is cleaned of sediment, particles of soil, sludge, mixed with a protective suspension. To do this, it is all removed and a new, cleaned one is downloaded. Concrete using a vertically moving pipe method. Vibration plants and hopper buckets or concrete pumps with a paver equipped with a sleeve on a telescopic boom are used. A concrete pipe with a receiving funnel is placed in a trench, not reaching the bottom 0.3 m. The protective solution displaced during concreting is pumped into a storage tank by a pump.
After the concrete gains strength, earthworks inside the perimeter begin. Excavation is being carried out in layers. If necessary, according to the calculations of the horizontal load on the fence, the walls are reinforced with soil anchors. The design feature of which allows you to leave the free space of the excavation for construction work.
Our technique
We use the following installations with a suspended grab bucket:



- BAUER GB-34 hydraulic grab: trench depth up to 60 m, width 0.3-1.2 m (built-in inclinometer, bucket set, sleeve and centrifuge pump, mixer, silo, slurry meter, concrete pipes)
- MAIT HR130
We use bored ground injection anchors instead of installing a spacer system, which greatly expands the possibilities of the method.
Order calculation of the cost of Walls in the ground
Fill in the data and send - in return you will receive a calculation of the cost in a first approximation. The final cost may depend on the features of the project.
The technology "wall in the ground" is a special method of building the foundations of buildings or installing walling, and is also widely used in cities for the construction of underground tunnels, parking lots, garages.
During construction using this method, the soil is disassembled inside the building after all installation work.
How such construction procedures are carried out and in which case it is advisable to use them will be described in this article.
The technology of erecting a wall in the ground is carried out in several stages:
- Preliminary laying and installation of foreshaft - monolithic reinforced concrete construction. This is done in order to prevent the subsequent collapse of the upper soil layers into the trench.
- With the help of a hydraulic cutter and a solution from clay, possible ingress of water into the trench is eliminated, as well as shedding of soil and rock.
- Assembly and welding of the frame from reinforcement and its further filling with concrete. After the construction is ready, it is installed in an dug trench. When pouring a reinforced carcass solution through a special pipe and funnel, the concrete residues that are displaced as a result of the procedure are pumped out for subsequent use.
- When the concrete gains its strength, the foreshaft is removed, and the soil inside the structure is selected from the pit. Spacers, as can be seen in the photo, prevent collapses, and, in the presence of several reinforced concrete wall panels in the ground, they are combined into one structure (not used in all cases).
- Finally, foundation slabs and walls are installed, and they are also finished.
The technological map of the wall in the ground, which is given below will help to visualize the work plan.
Using wall technology in the ground
 In what cases may it be necessary to use this technology? There may be several situations. For example, it is possible when construction is carried out in a big city, where there is a danger of intersection with communication lines and underground networks, and where pits are being constructed in close proximity to other buildings.
In what cases may it be necessary to use this technology? There may be several situations. For example, it is possible when construction is carried out in a big city, where there is a danger of intersection with communication lines and underground networks, and where pits are being constructed in close proximity to other buildings.
Regardless of the time of year, the use of the “wall in soil” technology is also appropriate, on the basis that there may be a large amount of moisture (groundwater) at the construction site of the base of the building. If the technology "wall in the ground" is used, then there is no need for its removal or freezing. In addition, this method minimizes the risk of destruction or deformation of the foundations of buildings located next to the construction site.
Important! Use the “wall in the ground” technology when arranging pits or underground structures in close proximity to other buildings or where there is a danger of intersection with communication networks.
Other features thanks to this technology
 In addition, in large cities, difficulties may arise in the construction of new underpasses or auto tunnels. A “wall in the ground” can be arranged to a depth of more than 20 m - just what you need for underground structures. It is widely used in the construction of underground garages and parking lots, underground highways and subways.
In addition, in large cities, difficulties may arise in the construction of new underpasses or auto tunnels. A “wall in the ground” can be arranged to a depth of more than 20 m - just what you need for underground structures. It is widely used in the construction of underground garages and parking lots, underground highways and subways.
Underground structures may be needed for various storage facilities, as well as for the construction of embankments, port pumping stations, etc.
Ground walls are not always used for construction in extreme underground conditions. Bonded together, reinforced concrete panels can become a solid base for a high-rise building or a private house.
This video demonstrates the construction of the "wall in the ground" technology
In limited urban areas, pit fencing is used modern technology "Wall in the ground", which has become widespread due to a large number of advantages. The method is suitable where work is carried out in close proximity to functioning underground utilities, when it is especially important to prevent the foundations of neighboring buildings from settling. The “wall in the ground” is being erected with minimal noise and on a sufficiently large area of \u200b\u200bthe construction site (since this method uses a fairly large amount of equipment).
The wall-in-ground technology is one of the most modern and innovative construction technologies widely used in the construction of facilities or parts thereof below groundwater. "Wall in the ground" is successfully used in urban planning to create underground parking lots, underground levels of buildings, bunkers, etc. Its use is justified in the construction of dams, dams, tunnels and other engineering structures - wherever deeper waterproof walls are required.
Prices and Cost
* Calculation of the cost is made after obtaining geology data, working drawings and other information necessary for calculating the cost of installing the wall in the ground.
Technology features
At the time of excavation, the trenches are filled with bentonite solution. The solution has the ability to exert excessive hydrostatic pressure on a vertical surface, which helps to strengthen the walls and protects the trench from destruction. The next stage is the reinforcement and concreting of the trench, in which the bentonite suspension is gradually displaced from the trench (the frame is lowered before concreting).
The “wall in the ground” can be built at a depth of up to 40, and when using specialized equipment up to 60 m, and the width of the trench can be extremely narrow - 0.4-1 m. The wall becomes a walling, and can also serve as a bearing element of the underground structure.
The wall-in-ground method involves the use of two types of equipment. Grabs and other bucket equipment are used to develop dispersed compositions - sand and clay. Hydraulic cutters develop any soil - from dispersed to semi-rock mudstone, siltstone or sandstone.
The method is implemented in the following order:
- A foresight is being built around the perimeter of the pit of the structure - a reinforced concrete fence that ensures the design accuracy of the future wall and prevents soil collapse from the top of the trench.
- A trench for the wall is being developed. In the process of excavation, it is filled with a solution of bentonite, which protects the walls of the trench from collapse.
- After reaching the bottom mark, the trench is prepared for concreting - frames from reinforcement are vertically lowered into it.
- After mounting the frames, the wall is directly concreted. To do this, concrete pipes are immersed in the trench, into the receiving funnels of which concrete mixture is fed. As this mixture is put into the trench, the bentonite solution is displaced and pumped out. Then the structure is left until concrete is completely solidified.
After the buried wall is completely ready, they begin the layered development of soil under the foundation pit of the structure, as well as carry out wall fastening.
Scope of the “wall in soil” method
Due to the universal nature and effectiveness, the “wall in the ground” technology has become widespread not only in housing construction - in the construction of foundations, underground parking lots and garages. It is widely used in the construction of underground passages and highways, tunnels and metro stations. In the hydraulic industry, the “wall in the ground” makes it possible to build embankments and ports, pumping stations located at great depths, berthing facilities and storage facilities.
In addition, the method is good for reconstruction of existing facilities, since it does not lead to deformation of the foundations of neighboring buildings, and is also indispensable in difficult hydrogeological conditions, since it does not require preliminary dewatering or freezing.
The construction technology "wall in the ground" is effective not only in the construction of facilities at great depths - underground walls at the same time serve as the capital foundation for the aboveground part of structures. It is also indispensable in cases where the foundation cannot be created using traditional technologies. The low noise level, the absence of dynamic fluctuations, the speed of construction of structures make it possible to apply the technology when carrying out construction work near already constructed buildings and communications.
Drilling support
Drill poles are concrete pillars that are erected by laying concrete mixture in pre-drilled wells. Concrete mixture is laid under the protection of either mud or casing pipes, extracted during concreting.
The technology of drilling pillars is the same as that of bored piles. In essence, they are bored piles of large cross-section (d\u003e 80cm).
The lower ends of the bored supports must be brought to dense soils, so they work like racks. Sometimes they are made with a broadened heel.
Drill poles have significant bearing capacity (≥1000t) and are calculated as piles.
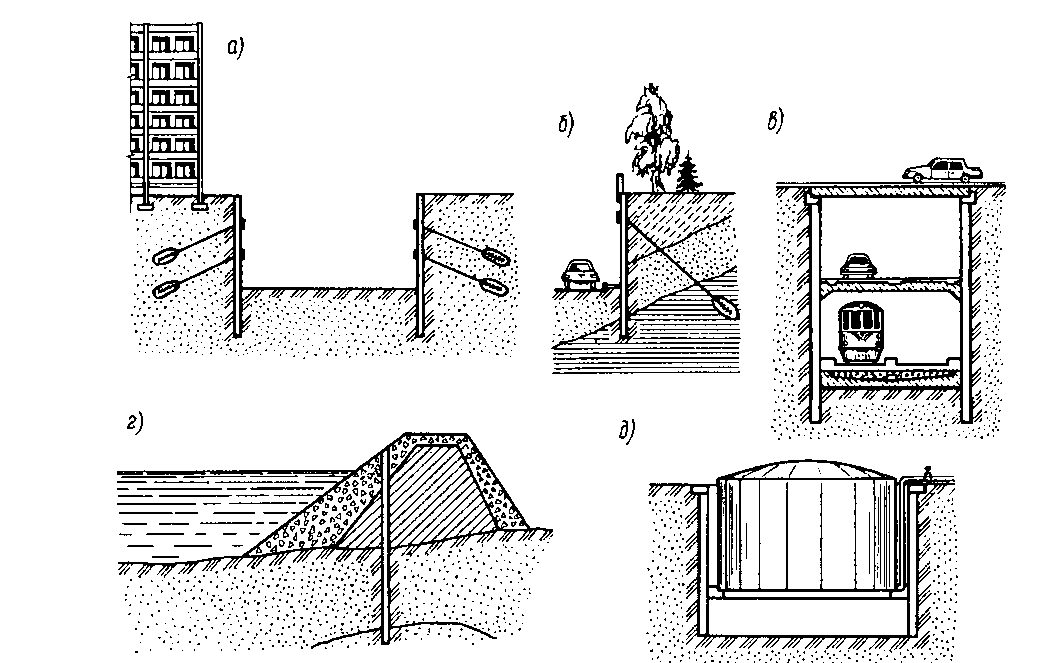
This method is intended for the installation of foundations and structures buried in the ground (Fig. 13.13).
Figure 13.13. Structures constructed by the “wall in soil” method: a - pits in urban conditions; b - retaining walls; in - tunnels; g - antifiltration diaphragms; d - underground tanks
The method consists in the fact that first, a narrow deep trench (b \u003d 60 ... 100 cm, H≤40 ... 50 m) is opened in the ground along the contour of a future structure with a rigid grab or a mechanized trencher to the design depth with an insert in the water stop, which is then filled concrete mix or prefabricated reinforced concrete elements.
A wall constructed in this way can serve as a structural element of the foundation, a foundation pit fence or a wall of a buried room.
In addition to buried structures using the “wall in the ground” method, it is possible to arrange anti-filtration curtains. The device "walls in the ground" is most appropriate in water-saturated soils with a high level of groundwater. The method is especially effective when deepening walls in water-resistant soils, which allows you to completely abandon drainage or deep water reduction.
Significant worth The method is the ability to arrange deep pits and buried rooms near existing buildings and structures without violating their stability, which is especially important during construction in cramped conditions, as well as during reconstruction of structures.
The technology of the device "walls in the ground".
1. The “wall in the ground” construction begins with the construction of a prefabricated or monolithic foreshaft, which serves as a guide for earthmoving machines, as a support for hanging armored frames, concrete pipes, prefabricated reinforced concrete panels etc. and ensures the stability of the walls in the upper part.
2. An excerpt of the pit with separate captures. Having dug up the first grab, to the entire depth of the wall, limiters are arranged along its ends, the reinforcing cage and the concrete mixture is laid.
3. Then they proceed to capture “through one”, and after its construction - to an intermediate one, etc., as a result, a continuous wall is obtained (Fig. 13.14).
Figure 13.14. The sequence of construction of the "wall in the ground":
a - the first phase of work; b - the second phase of work; 1 - mince; 2 - basic mechanism; 3 - concrete pipe; 4 - clay solution; 5 - grab; 6 - trench under one capture; 7 - reinforcing cage; 8 - concrete mixture; 9 - concreted section; 10 - finished "wall in the ground"
This method is called method of successive captures or sectional method.
To hold the walls, the grips against collapse are poured into it as they deepen thixotropic clay solution.
For the preparation of clay solutions, bentonite clays (clay containing a large percentage of montmorillonite) are used. The clay particles of the solution are not only wetted by water, but water penetrates into the crystal and the clay swells, increasing significantly in volume. Montmorillonite clay has the property thixotropy, i.e. in case of dynamic action, this is a solution, and in the absence of exposure after 4 ... 6 hours, the sol turns into gelthat allows you to hold the walls of the trench.
The level of the solution should be higher than the level of groundwater in order to exclude the filtration of water from the soil into the trench, and the pressure from the solution should be greater than the ambient pressure (ξ ∙ γ z).
After extracting the grapple and filling it with concrete mixture, the displaced clay solution containing particles of the developed rock goes for cleaning (regeneration) and again enters the trench (with some loss of ~ 10%).
After the construction of the “wall in the ground” around the entire perimeter of the structure (ie, the structure closes the future structure in plan), the soil is gradually removed from the inner space. If necessary, soil anchors or spacers are arranged around the perimeter at each stage. If fastenings are not made, then the stability of the wall during soil removal is ensured by its incorporation into the base. After complete removal of soil from the internal space to the design elevation, internal structures are erected.