Building a house from monolithic reinforced concrete walls. Concreting of walls: features of concrete blocks, thickness. Dismantling concrete walls
The construction of any structure is divided into several stages, where the stage responsible for the construction of vertical supporting elements - walls plays an important role. Most private developers believe that it is impossible to perform concrete walling on their own, or, in extreme cases, you will have to spend two to three times more time and money on this process. We will try to convince you of this.
You can get a pretty good idea of \u200b\u200bthe load-bearing capacity of the soil in the bottom of the trench with a manual penetrometer. This handheld device is a spring-loaded probe that measures the pressure that the soil can exert and is calibrated to give readings in tons per square foot. In my opinion, each contractor and building inspector should have one of them - it can help you avoid many troubles.
Dimensions. So, how is the soil bearing capacity related to the size of the foundations? The base transfers the load to the soil. The lower the bearing capacity of the soil, the wider the foundation. If the soil is very strong, then the foundation is not absolutely necessary - only the soil under the wall will be enough to hold the building.
Walls - as the basis of the structure
Perhaps the most important issue in building design is the choice of building materials for the construction of basic structures.
The walls of the building perform several functions simultaneously:
- Guarding.
- Carrier.
- Aesthetic.
Therefore, the most thorough approach should be made to the choice of material for them.
Monolithic concrete walls
You can find the recommended size of the base, based on the size and type of the house and the bearing capacity of the soil. As you can see, heavy houses on weak ground need foundations 2 feet or more wide. But the lightest buildings on the strongest soil require bedding as narrow as 7 or 8 inches. Under an 8-inch wall, this is the same as saying that you have no legs.
These figures are based on assumptions about the weights of building materials and live and dead loads on roofs and floors. The permissible bearing capacity of the soil under the base should be equal to the load imposed by the structure. The same dimensional foundation is called under a one-story house, if it has a brick veneer - it is assumed that the brick will weigh the whole second story.
The construction market offers us a wide range of different options, while each has its own plus or minus:
- Concrete wall slabs;
- Brick;
- Cinder blocks;
- Foam concrete blocks;
- Silicate blocks;
- Concrete blocks for walls.
Private developers prefer masonry materials, as they are light and easy to use. For the construction of brick or gas concrete walls special equipment is not required, just get a hand tool. And probably almost every man knows how to build a wall with his own hands using such resources.
If you had a design engineer based on the number of soil samples and your prints, he will add the actual weights of concrete, wood and brick that you will use in your building, the factor of required live loads and come up with an estimate of the weight that your actual home puts on support. This may be a little less or a little more than the code suggests. Then he will take the known load-bearing capacity of the soil - that which can be scooped into a square foot of the soil, and construct the base so that the area under the base, multiplied by the strength of the soil, is equal to or exceeds the actual load.
Modern professional urban planning relies on the construction of monolithic reinforced concrete buildings both civil and industrial. The main load-bearing structures of this structure are reinforced concrete walls and foundations, which have increased strength.
Monolithic concrete walls
The device of monolithic reinforced concrete bearing structures at first glance does not present any complexity.
In practice, you do not need to do this technique in most homes. The amount that you differ from standard code compatibility is not worth worrying about. Unless you have walls or any other special situation, the engineer is probably not justified. Regardless of the bearing requirements, masons and spilled wall contractors want bases on their block or their forms. But the lesson to be taken is that when the soils are very strong, the bases may not necessarily be strictly in terms of bearing.
The device of monolithic walls
This means that it is less important, for example, whether the wall is correctly placed in the center of the support. Corrections for erroneous supports It is sometimes difficult to place supports in trenches, so contractors often see walls that are not in the center of the support. The foundation wall must be positioned correctly to support the house, of course, which is why it has been placed off-center on a support.
Simplified process can be divided into three stages:
- Formwork preparation and assembly.
- Perform structural reinforcement.
- Directly pouring concrete.
But with all the apparent simplicity, the construction of monolithic concrete structures have their own nuances. And, of course, they must be carried out in strict accordance with the requirements of GOST and SNiP "Monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete structures."
Full support width is not needed to support loads; you can pour the wall right on the edge of the base and still have enough support. However, if you start to walk along the edge and stick the wall past the support on the side or at the end, then you begin to apply rotational force, which is not intended for processing.
In this case, you should consider engaging an engineer. As an engineer, I was asked to recommend solutions in cases where the base was placed so that the wall, when it was thrown, actually went beyond it. My suggestions are different in strong soils than in medium or below average soils. This should be adequate to support the wall. If there is a keyway in the wall, fill it, and if it is threaded from the base, cut it off. Drill holes and epoxy steel into the base to tie the wall to the support, and then form and discard the wall.
For your information!
At each stage of the device of monolithic structures, before proceeding to the next stage, acceptance of the work performed is mandatory.
Acceptance consists of checking compliance with the project, taking into account the amount of materials used and compiling hidden works based on the results of the act.
Technology and organization of work
Any construction process is preceded by preparatory work. The technological sequence of construction cycles and the organization of optimal working conditions at the construction site is regulated by the work production project (PPR).
In weaker soils, you need to increase the foundation with steel and concrete. Excavate as before, but instead of using gravel, drill supports and epoxy steel dowels to the side, then place concrete to extend the support to the appropriate width.
In weaker soils you should increase the foundation with steel and concrete. Dig as before, but instead of using gravel, drill the supports and epoxy steel dowels to the side, and then place the concrete to level the base to the desired width.
Usually you find such places when you hammer pegs for base forms - you fall into a cola and it just disappears with one hit. Maybe there is a layer of soft clay that rises from the old bottom of the lake at an angle and just crosses your trench in one or two places.
This document, a practically comprehensive construction instruction, is prepared in accordance with the regulatory requirements prescribed in SNiP:
- Bearing and enclosing structures.
- Concrete and reinforced concrete structures.
- Concrete works.
- Safety regulations and labor protection.
- Requirements for the composition and procedure for maintaining executive documentation, etc.
According to the PPR, before starting to concrete walls, the following should be done:
Cast-in-place retaining walls
If the percentage falls easily under pressure, this is a concern. You may need to dig past a soft spot and place a deeper support, and then pour a higher wall. Or you may need to lean against soft material to get good material. Another option is to dig up soft soil and replace it with compacted gravel or low-strength concrete, also called depleted filler.
But in many cases, expanding the foundations is the easiest solution. If you get a 16-inch support, increasing it to 32 inches, double the area of \u200b\u200byour bearing, making the base suitable for soil with half the power. If you increase the width of the base, the code also requires increased thickness. This is because a leg that is too wide and not thick enough will experience bending force that can crack concrete. It is assumed that the projection of the support on both sides of the wall should not exceed the depth of the base.
- The device of temporary porches and roads for the passage of construction vehicles and mechanisms to the concreting site.
- Providing power supply and site lighting.
- Delivery from the on-site warehouse and preparation of all necessary:
- Mechanisms.
- Tools.
- Inventory.
- Assistive devices.
- Finish preparing a horizontal surface on which concreting is planned:
- Waterproofing.
- Lay fittings.
- Embedded parts in accordance with the working drawings.
- Execute an act for hidden work.
- Assemble and install formwork and scaffolds for concrete workers.
The correct assembly of the formwork is controlled by a linear worker at the master site.
For example, a base 32 inches wide under an 8-inch wall should be at least 12 inches thick. Instead, however, you can strengthen the support with transverse steel. Steel should be placed approximately 3 inches from the bottom of the base. Despite the fact that many contractors do this, one thing that does not help you cover a soft spot in the soil is to add more steel to the long base size. Throwing more longitudinal steel into the foundation in this situation is just a waste of time and money.
If you are going to add longitudinal steel, place it where it will do something good: in the wall, not in the base. A wall with two bars number 4 on top and two at the bottom can fly through a small soft area without any problems. Excavated water When you work in an area with raised ground during the wet season, you sometimes find that groundwater is moving into your trench. If the flow is slow enough, so you can pump out water that does not flow straight back in, then this is the best solution.
Note!
The readiness of scaffolding and scaffolds for work at heights is taken by the safety officer.
He also instructs in the safe conduct of work with clearance for each employee involved.
Concrete Workers
The link on the wall concreting consists of three people (on most sites, the number of people is not limited to three):
You might want to thicken the bases in this case, because the bottom of the concrete can absorb water and be slightly weaker than usual. But if the soil is loose and porous, and the water and soil return to the trench again when you pump out the water, use a large aggregate to build the trench.
When you form supports, place a large enough stone in a moist, dirty area to rise above groundwater. Bend the stone into the mud, then pour your foot. A large aggregate allows filth to fill the pore space, but as long as all the pieces of stone are in contact with each other, the stone can still carry the load.
- One concrete worker of the fourth category.
- Two concrete workers of the second category.
Important!
If the conduct of concrete work will be associated with the involvement of a crane, concrete workers must have a slinger certificate.
Concentration
According to technological maps for reinforcement, formwork and concrete walls, workers receiving and laying concrete at heights use scaffolds collected for the previous stages.
If the stone is so tall in those shapes that your legs become too thin, place a transverse reinforcement to strengthen it, as shown in Figure 6. Changes in height It is quite common for a short wall to tie into a high wall, especially in the north, where most homes have full basements, but garages only have short walls of frost. The code requires continuous support at all points. part of the code dates from the days when the foundations were made mainly with a concrete block, rather than poured concrete.
Walls of masonry do not have a real possibility of laying, so they must be removed when changing hills. On the other hand, concrete walls can be reinforced with steel openings. This means that supports can be intermittent when jumping from 4 feet to 8 feet or 9 feet. A shorter wall may take a distance.
In this case, the following can be used as a means of pre-treatment:
- Decking with consoles on consoles mounted directly on the formwork.
- Changeable scaffolds and platforms.
Attention!
Concreting vertical structures with ladders is strictly prohibited.
Features of laying concrete mix in the design of partitions and load-bearing walls
The nuances of laying concrete in vertical structures depend on several parameters:
Concrete must be reinforced accordingly. A typical home situation where a 4-foot frosty garage wall should fly 4 feet or less and tie into the main foundation requires two No. 4 bars at the top of the wall and two No. 4 bars at the bottom. Steel should extend 3 feet into the main wall and 3 feet into the shorter wall beyond where the base begins.
For this part, the basics are formed and performed as usual. When you form walls, the lower part of the molds should be covered with a piece of wood where the molds pass through the empty space. In a termite country, this wood must be removed when the molds come off.
- The thickness of the concrete wall.
- Her height.
- Type of formwork used.
Here are some of them:
- On device monolithic walls in precast concrete formwork, the concrete mixture is laid in sections to a height of not more than 3 meters.
- If the thickness of the reinforced concrete wall is more than 500 mm with the planned weak reinforcement, use a concrete mixture with a mobility of 4-6 cm.
- For thin and frequently reinforced structures of walls and partitions, more mobile mixtures from 6 to 10 cm can be used.
- Concreting of elements up to 150 mm thick is carried out in tiers up to 1.5 m high. Formwork is erected on one side to the entire height, and from the supply side of the mixture to the tier height. This ensures ease of work and improves quality.
Note!
When the first tier is filled with concrete, the formwork is increased for the next.Brent Anderson is a consultant engineer and concrete contractor who works for the American Concrete Institute 332 Committee, Residential Concrete. Connect with customers who want to make your most profitable projects in the areas you like.
Concrete building structures
The industrial nature of concrete is well established in modernist architecture. Concrete structure can be identified by thick walls and deep windows and doors. Reinforced concrete structure usually consisted of 4 or 6 thick, cast in place, concrete external walls that were full height to the parapet and continuous with the foundations. The wall thickness was determined by their height, while the walls of the foundation were thicker, for example, 6 thick foundation walls were reduced to 4.
- If the concrete support wall is designed to be more than 20 m long, it is divided into sections of 7000-10000 mm and delimited by a separation formwork.
- The concrete mixture is fed directly to the formwork in several sections at once along the length of the section, chosen by the method:
- Tubs.
- Vibration chutes.
- Concrete pumps.
For your information!
Concrete pumps are a rather complicated and expensive equipment, requiring the involvement of concrete workers and highly skilled mechanics.
Therefore, a similar technique is used in exceptional cases.
- When the concrete mixture is supplied using a concrete pump, it is allowed to set the formwork immediately to the full height. But at the same time, the end of the concrete pipeline must be immersed in the concrete to be laid. This method is called-pressure concreting.
- When pouring concrete over walls with a height of more than 3,000 mm, link trunks are used and the solution is distributed in horizontal layers from 300 to 400 mm thick with mandatory subsequent vibration compaction.
- Concrete delivery to one point is not recommended, since this reduces the surface quality, the concrete is not homogeneous due to the formation of inclined loose layers.
Care
At the end of laying the concrete mixture in the formwork, the process is not considered completed, since freshly laid concrete requires some care.
During the recruitment process, you should protect against:
- The effects of precipitation.
- Rapid moisture loss.
- Freezing (in winter period of the year).
- Accidental movement of people on it.
Interesting!
If necessary, carry out concrete work in frosty weather, fresh concrete is subject to mandatory heating, to accelerate the hardening process and curing.
Concrete Finishing Work
At the end of the construction of the main structures of the building begins the stage of insulation (if necessary) and finishing work. For almost any finish, you will have to decide how to level the concrete wall before installing the finish.
Depending on what the final decoration of the wall will be and the state of its surface, the degree of preparatory alignment depends.
There are two ways to level the walls:
- Dry, that is, plasterboard lining.
- Wet, involving the use of various leveling mixtures.
- In the case of the presence of only small defects in the form of cracks or small irregularities, stop your choice on puttying continuous or in places.
- If there are big concreting flaws on your face, then it is better to immediately turn to drywall.
- Before filling the holes with mortar, you must first clean the base from dirt, dust or cracked old plaster.
- The large hole (the old socket from the outlet or switch) is first filled with pieces of dried alabaster (gypsum), and then putty.
- To eliminate a large hole or gap, you can use mounting foam. Before the foam is injected, the repair site should be dusted off and moistened with water. When the foam dries, cut off the excess with a construction knife and you can proceed with the mixture.
- Fill very large openings with broken concrete or brick. If the hole is through, fasten the plaster mesh on both sides and fill with mortar.
- Bulgarian.
- Jackhammer.
- Powerful hammer drill.
- How laborious the process will be.
- With what degree of clutter or dustiness of the apartment are you ready to put up with.
Before applying any finishing materials, coat the surface of the wall with a primer
Although the price of building mixtures is not very high, nevertheless, when consumed in large volumes, this will significantly affect your pocket. In addition, multi-layer application of the mixture on the shoulder is only to experienced plasterer, but a beginner can cope with drywall alignment on his own.
Concrete wall repair
It so happens that a hole has formed in a concrete wall or a hole for a number of reasons that does not suit you. How to deal with it? The question of how and how to seal holes in a concrete wall is also not difficult to solve with the help of a building mixture, but with a special additive for quick.
For quality repairs, there are several conditions:
Attention!
When working with quick-hardening mixtures, remember that you should work live while the mixture is plastic.
In this regard, it is better to knead the repair mixture in small portions.
Dismantling concrete walls
If you are planning a redevelopment of rooms and this is permissible in your case, the question of how to break a concrete wall becomes relevant.
Important!
The first thing you need to do when deciding to dismantle a part of the wall or completely remove it, figure out if this is possible and get permission to redevelop.
The next stage is the choice of a tool with which you eliminate the obstacle to a new vision of the space of the apartment.
It can be:
In principle, each of the proposed tools can do an excellent job, the only difference is:
Important!
In the process of demolishing the wall, do not forget about the possible engineering communications hidden in it.
They must be dismantled first.
Now it’s easy to guess how to break through a concrete wall. We take a puncher, a drill of a suitable caliber and, observing all the above precautions, we drill many holes around the perimeter of the area we want to get rid of. We leave between the holes small "bridges" with a thickness of 3-5 mm.
Note!
For small diameter holes, a drill similar to a drill is suitable.
For a socket for a socket, you need a crown nozzle.
Conclusion
A concrete wall that seems monolithic in terms of construction, as you already understood, still requires special attention during the work process. Of course, you might think that such an option (pouring formwork several meters high) is suitable only for professional builders, however, what prevents you from doing this on your site?
Practice on small elements, such as a concrete fence. In the submitted photos and videos in this article you will find additional information on this topic.
Nowadays, a variety of building materials are used, both known from ancient times, and recently appeared. Hollow walls made of reinforced concrete began to be erected in the twentieth century. At first concrete appeared, but in Russia and England at the same time it was invented by two people who did not even know each other. This happened at the beginning of the 19th century.
Reinforced concrete was not created at all by a builder, engineer, constructor or architect. A simple French gardener in 1867 made concrete instead of wooden flower tubs by placing wire in concrete.
Wall reinforcement technology
Steel wire or rods that are placed in concrete to increase its bending and tensile strength are called reinforcement. The word in Latin means "weapons."
Armed and steel-reinforced concrete (more precisely, already reinforced concrete) is a completely new material in which the components have high adhesion strength. Properly executed technology for reinforcing walls will make them strong for many years. For example: a steel rod with a diameter of 1.2 cm, immersed in concrete 30 cm, can be pulled out of concrete, with a force of about 400 kg. This adherence is not affected by temperature changes (in steel and concrete, the thermal expansion coefficients are almost the same).
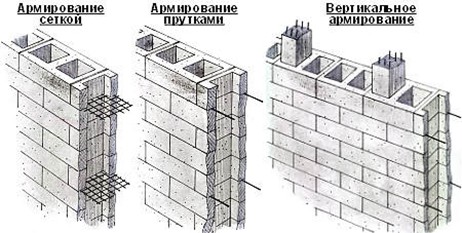
In reinforced concrete, each component does its job: the tensile load is steel, and the concrete is compressive. And if steel equips concrete, then concrete protects steel from corrosion and strong heating, which allows reinforced concrete to withstand strong fires. Therefore, wall reinforcement in construction is used very often. Appearing hair cracks are inevitable at ultimate loads, but these cracks are not critical from the point of view of material strength, nor from the point of view of resistance of steel to corrosion.
In construction practice, such reinforced concrete products: concrete beams over door and window openings, floor slabs, reinforced concrete panels, beam beams, crossbars of shop buildings in industrial buildings, monolithic walls, etc.
For better adhesion, steel reinforcement has a relief surface, various notches are applied to it.Reinforcement of monolithic walls will be much better and stronger when connecting the reinforcing cage into one welded structure.

Not always the materials from which these or other structures are erected, endure the maximum loads. Therefore, wall reinforcement can be made with fiberglass mesh. Covered with a layer of plaster, it also participates in the thermal insulation of the structure. Thus, reinforcing monolithic walls is one of the important steps in the construction of houses.
Cast-in-place retaining walls
Monolithic reinforced concrete is a very successful and economical material for creating the following structures:
- sexes;
- overlappings;
- stairs
- roofing;
- walls, including retaining ones.
The retaining wall is being erected on those slopes where staircases and platforms are designed, since its direct purpose is to strengthen inclined sections of the landscape and to connect various sections with a contrasting relief. They keep the soil from slipping. Such hollow walls should not only be solid engineering structures, but also fit into the landscape, not disfiguring it, but emphasizing the originality and participating in the formation of the overall landscape composition.
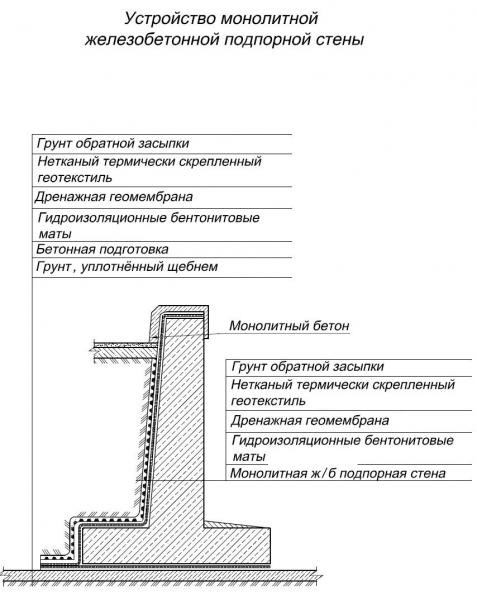
Retaining walls are made of various materials, but reinforced concrete is one of the most successful solutions, since when using it there is no need to make a very deep trench under the foundation. For a retaining wall made of reinforced concrete, a depth of 15-20 cm is sufficient. Also, due to the high strength of reinforced concrete, the retaining structure fully performs its function at a thickness of 10 cm. At the same time, the cost of the structure is also reduced due to the cheapening of the foundation. When installing monolithic reinforced concrete retaining walls, the result is a seamless design that not only looks good from an aesthetic point of view, but also is more durable and durable.
Retaining walls from monolithic reinforced concrete casting method in the formwork, which is assembled, depending on the configuration, from boards or finished panels with a curved or broken configuration.
The first formwork walls are installed on the lower terrace: the finished panels are mounted to the wall of the dug trench, are interconnected, and outside they are equipped with supports, the purpose of which is to help the panels stand directly under the weight of the concrete mass.
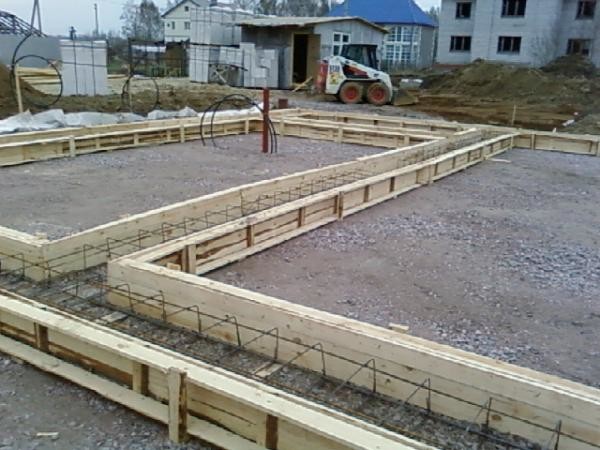

In order for the retaining wall to be even, the inside of the formwork is sheathed with the appropriate material, roofing material or plywood.
When the first row of shields is already installed, you can put the second. When it is ready, it is strengthened with props, like the first, and at the top both rows are connected by bars.
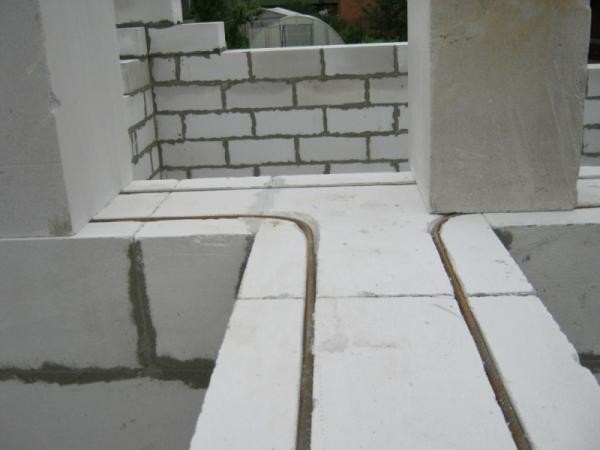
Since we are talking about reinforced concrete, 2 rows of steel reinforcement in the form of a grid are placed between the shields inside the formwork, but it is allowed to use metal rods and even scraps of water pipes connected by wire.
When installing a monolithic beam, one must not forget about drainage. To drain ground water due to a monolithic wall of reinforced concrete, in the lowest part, 5 cm above the surface level, drainage pipes of plastic of the desired diameter are laid, the distance between them should be 1 m.
Wall formwork
Formwork is something without which the formation of monolithic structures, both concrete and reinforced concrete, is impossible. These structures, depending on the folding, are divided into 2 types:
- removable wall formwork;
- fixed formwork.
The most common formwork is removable, in a variety of variations. The name "removable" implies that the panels or boards from which the formwork of the walls are made are removed after the concrete has completely dried or its initial setting. Removable formwork is used not only to form the foundation - it is a full-fledged participant in the construction of monolithic walls and frames high-rise buildings, with its help spans of stairs and decor elements are made.

What is used for the manufacture of removable formwork:
- wood (boards, boards, etc.);
- plywood;
- steel sheet;
- aluminum (both sheet and form);
- polyvinyl chloride;
- various combinations of the above materials.
Regardless of the formwork material, there are a number of requirements that are the same for everyone:
- The frame must have sufficient rigidity and be fixed in place.
- The gaps between the structural elements should be minimal, for which you need to carefully adjust them. Cement milk may leak through the gaps, which will affect the quality of the finished concrete product.

Fixed wall formwork is a structure that, after pouring concrete and solidifying it, remains in the concrete mass as part of the overall structure. The materials used for its manufacture should be:
- heat insulating;
- strong (when pouring concrete, significant pressure forms on the formwork design);
- with low thermal conductivity (a monolithic concrete structure has high thermal conductivity, so concrete and formwork must form a single heat-insulating pair).
When using non-removable formwork, concrete is more reliable than in a removable structure, it is protected from various adverse external factors, primarily from moisture and extreme temperatures. This is a kind of multi-layered sandwich of formwork and concrete, where concrete provides strength and formwork - thermal insulation. In this case, a design scheme should be made indicating the proportions of the mixture.

Fixed wall formwork can also be constructed from cladding panels, which is very beneficial to achieve an aesthetic result. In private housebuilding, heat-insulating materials such as polystyrene foam and arbolite (material from a mixture of waste wood industry with cement mortar with the subsequent formation of hollow blocks) are very interesting for use as formwork.
The construction of hollow walls made of reinforced concrete
Due to the specificity of the design, hollow walls need to be made thicker than monolithic. To erect a low-rise building, you need to take hollow reinforced concrete walls with a thickness of 20 cm. The cavity, also called the air pocket, is located in the middle of the wall, occupying from 3 to 6 cm. This cavity is not left empty: the pocket is filled with foam or mineral wool.

The use of foam suggests the absence of additional waterproofing. This material is simply placed in the formwork with the already installed fittings and poured concrete mortar. When concrete hardens, the wall is obtained with great strength and retains heat well. Of the minuses, it can be noted that such a phenomenon as a cold bridge is inevitable in this design, but the plus is that when warming you can do with less.
When to mold hollow reinforced concrete walls they use mineral wool as a heater, first they make formwork with a cavity in the middle, fittings are set in the formwork, then concrete is poured. After a day, the formwork is removed, and the structure rests for several days. Before filling the air pocket with mineral wool, the insulation is placed in moisture-resistant briquettes and already in this “sheathed” form it is mounted in the structure. The peculiarity of these hollow walls is that they need to be further strengthened with special columns.