Staphylococcal infection in the throat in a child treatment. Signs and treatment of staphylococcus in children. What is it? Indicators of the norm, possible danger
Staphylococci are conditionally pathogenic microorganisms that live in the mucous membranes of the respiratory system and on the skin. With a sharp increase in the number of microbes in the respiratory tract, various infectious diseases arise - tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, etc.
How can you destroy staphylococcus aureus in a child's throat? Treatment methods depend on what type of bacteria caused inflammation of the mucous membranes of the larynx.
To destroy pathogens, antibiotics, staphylococcal antitoxin, bacteriophage, immunoglobulin and symptomatic drugs are used.
In addition to medicines for the treatment of children, physiotherapy procedures, in particular ultraviolet radiation, can be used.
Features and types of staphylococci
Generally speaking, staphylococci are normal representatives of the microflora of the laryngopharynx, nasal cavity and skin. In small quantities, they live in the body of a healthy person, without causing inflammatory processes and infectious diseases. However, with a decrease in immunity, anaerobic microbes begin to multiply rapidly. Waste products of staphylococci poison the body, causing infectious and allergic reactions.
Clinical manifestations and the severity of the course of ENT diseases largely depends on what kind of bacteria caused the inflammation. When carrying out a bacterial culture in sputum, the following types of staphylococci can be detected:
- golden - provokes purulent inflammation of almost any type of tissue and organs;
- saprophytic - affects mainly the organs of the genitourinary system;
- epidermal - localized in the upper layers of the epidermis, but if untreated, it can affect the nasopharyngeal mucosa;
- hemolytic - one of the most resistant to antimicrobial agents of staphylococci, affecting the respiratory, excretory and cardiovascular systems.
Hemolytic staphylococcus aureus develops rapidly, causing severe complications such as sepsis, meningitis, and pyelonephritis.
It should be noted that Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus aureus in a child's throat multiplies very quickly. Anaerobic bacteria readily adapt to the action of antibacterial agents, in particular to penicillins and cephalosporins.
Therefore, it is rather difficult to find the best medicines for the treatment of staphylococcal diseases in children. In the absence of drug treatment, microbes mutate and cause serious complications, which in rare cases lead to death.
Possible diseases
Decreased immunity, hypothermia, iron deficiency anemia, hypovitaminosis and antibiotic abuse can cause the rapid multiplication of microbes in the respiratory system. Staphylococcal infection leads to the development of a number of bacterial diseases:
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis;
- sphenoiditis;
- sinusitis;
- laryngotracheitis;
- bronchopneumonia;
- otitis media;
- acute tonsillitis.
Each disease has its own distinctive symptoms that need to be considered in more detail. The difficulty lies in the fact that the general clinical manifestations of staphylococcal infection can be easily confused with the symptoms of a viral disease. Many parents believe they can cope with the disease on their own and rely on personal experience. However, inadequate treatment of staphylococci in the throat can lead to disastrous consequences, up to the general damage to the body by bacteria that have penetrated the systemic circulation.
Sore throat symptoms
Staphylococcal angina is a bacterial inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa and palatine tonsils (tonsils). Fever, muscle weakness and sore throat when swallowing are characteristic symptoms of the disease, which appear several hours after infection of the body. Because young children are more susceptible to infections than adults, angina is more severe.
Typical manifestations of streptococcal sore throat include:

Staphylococcal angina in children often develops against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, scarlet fever and chronic rhinitis. Typically, pathogens are localized in the glands and lymphoid tissues at the back of the throat. When characteristic signs appear, it is advisable to examine the child's throat. The presence of white plaque on the root of the tongue and the walls of the pharynx, as well as a slight increase in the palatine tonsils, is 100% confirmation of bacterial inflammation of the respiratory tract.
Laryngitis symptoms
Laryngitis is an acute inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa, which is characterized by hyperemia (redness) and swelling of the larynx. The development of the disease in children is often preceded by chronic rhinitis, tonsillitis, influenza, scarlet fever and overstrain of the vocal cords. Typical manifestations of staphylococcal laryngitis are:
- dry throat;
- pain in the larynx;
- dry or moist cough;
- subfebrile temperature (not higher than 38 degrees);
- separation of sputum with impurities of pus when coughing;
- decrease in the timbre of the voice;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat.
One of the most dangerous manifestations of the disease is laryngospasm. An involuntary contraction of the pharyngeal muscles causes the glottis to close, which can cause loss of consciousness or asphyxiation. Untimely passage of antimicrobial therapy entails the development of sluggish inflammation in the laryngeal mucosa and, accordingly, chronic laryngitis.
Pharyngitis symptoms
Staphylococcus aureus in the throat often causes the development of bacterial pharyngitis in children. Hypothermia, high-carbohydrate food intake, diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases and congenital immunity deficiencies can contribute to the growth of bacteria. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the throat walls, which leads to tissue swelling and difficulty breathing.
The classic symptoms of the development of staphylococcal pharyngitis include:
- sore throat;
- dry cough;
- general malaise;
- hoarseness of voice;
- high fever;
- soreness of the lymph nodes;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- mucus on the walls of the throat.
In frequently ill children with lowered immunity, the risk of developing bacterial pharyngitis is approximately 40-45%.
If the inflammation is left untreated, pathogens can invade the nasal mucosa and Eustachian tube. This can lead to complications such as bacterial rhinitis, rhinosinusitis, or tubo-otitis. In infants, the symptoms of pharyngitis practically do not differ from the manifestations of a cold. The child becomes whiny, refuses to eat and does not sleep well.
Antibacterial therapy
 Staphylococcus aureus is practically immune to antimicrobial agents, therefore, new generation antibiotics are used to treat bacterial inflammation. They contain active substances that prevent the replication of pathogenic DNA and, accordingly, the reproduction of microbes. For the treatment of children, antibiotics are selected that have the least pronounced toxic effect, namely:
Staphylococcus aureus is practically immune to antimicrobial agents, therefore, new generation antibiotics are used to treat bacterial inflammation. They contain active substances that prevent the replication of pathogenic DNA and, accordingly, the reproduction of microbes. For the treatment of children, antibiotics are selected that have the least pronounced toxic effect, namely:
- Rifaximin;
- "Kanamycin";
- Ofloxacin;
- "Amoxiclav".
Pathogenic bacteria that cause the development of tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other ENT pathologies secrete substances that lead to poisoning of the child's body. Therefore, delayed treatment of staphylococcal infection can often provoke the development of toxic shock, leading to the death of the patient.
Etiotropic agents that eliminate pathogens should be taken for at least 7-10 days.
It should be understood that uncontrolled intake of antibiotics can worsen the patient's well-being and even provoke the development of multidrug resistance of microbes, i.e. their insensitivity to most antimicrobial agents.
Antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin
Antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin is an injection drug that contains antibodies to most strains of pathogenic gram-positive microbes. The medicinal solution is obtained from donor blood or serum. The dosage and duration of intramuscular injections depends on the child's age and weight.
Direct indications for the use of the drug are any staphylococcal infections in patients aged 6 months. Typically, antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin is used in conjunction with antibiotics to enhance the action of antimicrobial components. With the help of the drug, it is possible to eliminate even generalized forms of inflammation, up to sepsis.
Advanced forms of purulent tonsillitis and laryngitis are treated with hyperimmune antistaphylococcal plasma. It contains specific antibodies that destroy almost any strains of gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus. The medicinal solution is administered intravenously to children for 2-3 days, after which the symptoms of the disease are smoothed out.
Staphylococcal bacteriophage
Bacteriophages are viruses that literally devour disease-causing bacteria. It should be noted that some types of pathogenic microbes are capable of producing substances that neutralize the action of bacteriophages. For this reason, before using medications, it is necessary to accurately establish the sensitivity of phages to pathogens of bacterial inflammation.
Important! Before use, the bottle with the drug must be shaken to completely dissolve the precipitate.
Staphylococcal bacteriophages are widely used in the treatment of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the throat, trachea, bronchi, nose and gastrointestinal tract. The drug is available in the form of ointments and injection solutions, which are injected directly into the foci of inflammation. The active components of the product almost instantly neutralize pathogenic bacteria, which helps to alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Bacteriophages can be used to treat localized and generalized septic inflammations not only in the airways, but also in the urogenital canals. The medicine is recommended to be used to eliminate staphylococcal infections complicated by otitis media, pneumonia, tracheitis, pleurisy, etc.
Staphylococcal toxoid
Staphylococcal toxoid is an immunocorrecting drug that stimulates the so-called antistaphylococcal immunity in the child's body. Regular use of the drug enhances the production of antibodies that can resist the development of staphylococcal flora in the respiratory tract. Toxoid can cure bacterial inflammation not only in the throat, but also on the skin.
Staphylococcal toxoid can be used to prevent pyoinflammatory infections in immunocompromised patients. The drug is used to treat patients aged 16 and over, since its active ingredients can provoke severe allergic reactions in young children. To achieve the desired results, the solution is injected subcutaneously every two days, gradually increasing the dosage.
Gargling
In addition to specific drugs for the destruction of staphylococci in the throat, antiseptic rinsing solutions are used. Regular sanitation of the oropharynx allows you to clear the mucous membrane from about 50-60% of pathogenic agents that provoke purulent inflammation. The scheme of pediatric therapy for sanitizing procedures includes:
- "Propolis solution" - disinfects and softens the throat, preventing the penetration of microbes deep into the respiratory tract;
- "Ingalipt" - eliminates local manifestations of pharyngitis, tonsillitis, stomatitis and other ENT diseases;
- "Chlorophyllipt" - increases the concentration of oxygen in the tissues, which makes it possible to multiply the effect of antibiotics and accelerate the regeneration processes in the mucous membranes of the throat.
From folk remedies for gargling, decoctions based on echinacea, medicinal chamomile, burdock root and yarrow are used. Phytoreparations gently affect the mucous membrane, helping to eliminate inflammatory processes and flushing out pus from lesions.
However, it should be borne in mind that alternative medicine can cause adverse reactions in children. Therefore, before using decoctions and infusions, it is advisable to consult with a local therapist or pediatrician.
 Symptoms
Symptoms

 In the nose
In the nose

- Injuries to the nose.
 In the throat
In the throat

Diagnostics



 Complications
Complications

 Treatment
Treatment






Staphylococcus aureus is the most common childhood disease. Translated from the Greek, the meaning of this word means "a handful of grains", because under a microscope, a cluster of cocci resembles a bunch of grapes.
Staphylococcus aureus is not only an infection that has settled in the body, but also the beginning of many diseases.... This is due to the fact that bacteria and bacilli of infection significantly reduce the defenses of the child's body, weaken the immune system.

Symptoms
The infection affects the baby's skin, stomach and mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. To date, science knows up to 30 types of microbes of this disease, the symptoms of damage in many groups pass in different ways. Among them there are both very dangerous to life and health, and neutral, completely harmless.
For example, Staphylococcus aureus in children, sapphoric and epidermal can infect a baby who is in a weakened state. It is these three types of disease that undoubtedly pose a threat to the health and life of the child. Most often, mothers hear about such ailments even in maternity hospitals, since infection can occur during the infant's adaptation to the environment, in the first days of life through the skin, during feeding (in breast milk or in the nose) or through the cut umbilical cord (in the intestines , and then in the baby's feces)
Since this disease belongs to the "contact" group, then most often the baby becomes infected by contact with an already ill person. The first and main thing that parents are obliged to do when they see signs of staphylococcus in a child is to immediately go to the clinic. Symptoms of the infection, which should definitely alert adults:
- Colds and ARVI. Symptoms - intestinal disorders, pain in the intestines, fever;
- Cough and runny nose, eyelid edema, nasal inflammation, conjunctivitis;
- Symptoms in infants - skin lesions in the form of "scattered" red pimples;
- In the late advanced stage of the disease, symptoms such as headaches, pneumonia, sepsis.
Staphylococcus aureus in children, detected in the nose, in the feces and on the genitals, manifests itself most often in infancy, by infection in the mother's milk. In older children, symptoms are marked by lesions of the skin of the hands, in the later stages these are signs such as boils and ulcers, lesions of internal organs, chronic pain in the intestines. Late diagnosis and improperly prescribed treatment lead to staphylococcus in the intestines of the child, the treatment of which is very difficult.
Symptoms of the disease in children in the early stages are expressed exclusively in nausea, vomiting and diarrhea (liquefied feces) with general lethargy and a slight increase in temperature.
The causes of infection in the body
Staphylococcus aureus in a child is the most common infection that occurs in babies from infancy. The studies have revealed the main causes and symptoms of the onset of this disease in babies:
- The use of strong antibiotics in the treatment of infants. An organism already weakened by ailments is exposed to the so-called "immune stress", as a result of which medications simply cease to work and the infection easily affects a weakened child, appearing on the skin, in the nose, and then in the intestines;
- The cause of infection with Staphylococcus aureus in children in the nose or intestines may be its long stay in the hospital. Most often this applies to weakened or premature babies in a pressure chamber or connected to a ventilator and lacking the immunoglobulins contained in breast milk;
- Tubes, catheters and implants, used when necessary, can also cause infection - staphylococcus in the throat of a child;
- Congenital diabetes, weakened immune system;
- Chickenpox and flu at an early age;
- Infection from sick parents (staphylococcus in mother's breast milk).
Pediatricians in maternity hospitals and children's clinics have several standard definitions of the risk of infection. If the disease is found in the feces of a child and in his mother's breast milk, and the child feels normal at the same time, then, most often, there is no reason for concern, and the disease is left untreated. In this case, the disease is classified as the fourth form and the baby is prescribed general immunity-strengthening drugs and preventive examinations. Bacteria and bacilli in milk and feces usually disappear quickly and treatment is supportive.
There are cases when a disease in the nose or even in the intestines passes without any obvious signs of infection at all, and the fact that the child is sick is only found out by finding a stick in the child's feces, a swab in the nose, or during the delivery of a general blood test.

Treatment
The final diagnosis of the disease requires a thorough examination and determination of the stage of the disease, the classification of the virus and the readiness of the child's body to fight the infection. Treatment of ailment in children causes some difficulties, since with the development of the disease, the bacterium forms such an unusual and inconvenient enzyme in the intestine, such as penicillinase. It is he who does not allow you to fight the disease with the help of familiar antibiotics, developing the body's resistance to them.
As soon as an infant has the first signs of Staphylococcus aureus in the form of rashes on the skin or in the nose, the doctor prescribes treatment - prescribes a regimen for taking antibacterial drugs, vitamin supplements and medications that increase the protective properties. If a baby is born with an infection (the bacillus is found in breast milk), he is left in a hospital, where he undergoes treatment, being in a sterile chamber under the supervision of specialists. At the same time, the baby is not weaned from the mother's breast, because this food is the only natural remedy for strengthening immunity. An infection found in the intestines requires hospital treatment.
If staphylococcus aureus in the throat and nose of a child is prescribed treatment by irrigation with bacterial preparations, in older children - by rinsing and washing the nasopharynx with oily, alcoholic preparations and herbal infusions. pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, the doctor's approach may be individual, and depending on the degree of damage, the baby may be prescribed certain antibiotics in the form of ointments. If the general condition of the baby is normal, and he is active, then Staphylococcus aureus in children in the nasal sinuses is treated with sulfa drugs.
And, of course, the first thing that every doctor will pay your attention to is disease prevention. It is much harder to cure an infection than to prevent it. Therefore, pay more attention to hygiene, cleanliness of the baby's hands and be sure to support the immune system by saturating it with the necessary vitamins and minerals.
Staphylococcus aureus in a child's nose is a very common infectious disease, which is more common every year. The good news is that science has already studied staphylococcus well and easily copes with the manifestations of infection in children and their parents.
Features of staphylococcal infection and transmission routes
Staphylococcus aureus is a very resistant and tenacious bacterium, it can retain its abilities and infect a person even in a favorable environment. Bacteria are not killed by sunlight and low temperatures. In drought conditions, they can live up to 8 months. Staphylococcus aureus is able to withstand heating up to 70 ° C. However, for all its stability, it dies from banal boiling. By treating the products with boiling water, a person will protect himself from this infection. Staphylococcus aureus is sensitive to brilliant green, if you treat a cut with it, then it is quite possible to avoid infection. Of course, in the case of an infection that has developed in the nose, brilliant green will not help; more serious drugs are needed here.
I would like to note that staphylococcus is a conditionally pathogenic microorganism, in a small amount of bacteria do not harm the human body. According to statistics, 70% of the population is infected with staphylococcal infection. Treatment should be started when Staphylococcus aureus becomes the cause of chronic or recipient inflammatory processes in the body. A certain amount of infection is found in most people, as mentioned above, but the bacterium is activated only under the influence of certain factors, such as, for example, a decrease in immunity, emotional turmoil, a lack of vitamins or respiratory viral diseases.

Staphylococcus aureus in a child's throat or nose can appear in several ways:
- contact transmission method;
- airborne droplets;
- while breastfeeding;
- through the placenta during childbirth;
- due to insufficient processing of food.
There are many ways of infection, as can be seen from the above facts, so you should not be careless about this disease and ignore its symptoms.
Symptoms of staphylococcal infection
Staphylococcus aureus in children in the nose has pronounced symptoms, among them it can be noted:
- dark green nasal discharge, prolonged rhinitis;
- redness of the skin around the nose;
- violation of the sense of smell;
- voice changes;
- itching and discomfort in the nose;
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of abscesses if staphylococcus lives in the throat;
- violations of the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract, which are manifested in diarrhea, constipation and nausea;
- in hypersensitive children, staphylococcal infection is accompanied by a skin rash;
- abdominal pain, intestinal colic is possible;
- lowering blood pressure;
- general weakness and intoxication of the body.
The symptoms are most intense in newborns, since their body has not yet had time to adapt to the effects of the external environment. The baby, who has caught the epidermal staphylococcus, does not sleep well, loses its appetite, is very moody. Often parents confuse such a condition of children with intestinal colic or signs of cutting teeth, thereby complicating the situation. If a parent notices such signs, it is better to visit a doctor who will accurately diagnose. It is much wiser to play it safe and exclude staphylococcal rhinitis or tonsillitis than to deal with its consequences later.
Diagnostics of the staphylococcus

In order to start treatment, a diagnosis is initially required. Many doctors do not stop claiming that a correct diagnosis is the key to an effective and quick recovery. First of all, the doctor, based on the complaints of the patient or his parents, will conduct a visual examination of the skin. The analysis by which the presence of infection is diagnosed in most cases is bacterial culture on a nutrient medium. A swab is taken from the child's nose or throat, if there is a suspicion of its location in this part of the body. It is very important to prepare your child. Before taking a smear in the morning, you should not eat or drink tea, you should not use toothpaste and gargle. These seemingly unrelated procedures may affect the reliability of the analysis. Before taking the analysis, you should not use medications, if they cannot be canceled, you need to inform the doctor about it.
The principles of treatment of staphylococcus in the nose
Few know how to treat staphylococcus, therefore, upon hearing the diagnosis, they begin to panic, but this is not worth doing. Modern pharmacology offers a huge number of drugs that are sensitive to this infection. It is important to note that the drug should only be prescribed by the attending physician. It is forbidden to prescribe medication to a child on his own. You should not listen to the advice of friends and neighbors who have encountered similar diagnoses, because the remedies that cured them can harm your baby.
After a detailed diagnosis, the doctor must decide how exactly the treatment will be carried out, and antibacterial or sulfa drugs will be used. The selection of medications is carried out on an individual basis, taking into account the patient's age, body weight and other characteristics of his body. Most often, agents such as:
- Flemoklav;
- Ancomycin;
- Oxacillin;
- Amoxiclav;
- Vancomycin;
- Unazine;
- Clindamycin;
- Erythromycin;
- Azithromycin;
- Cephalothin;
- Cephalexin.

Treatment can be carried out by local means, for example, rinsing the nose using saline solutions Miramistin or Chlorhexidine. Drops, such as:
- Polydex;
- Isofra;
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Protargol.
If the nasal congestion is very severe, then the use of vasodilating drops is recommended.
Tetracycline and erythromycin ointments will help to remove pustular lesions of the nasal mucosa. If the abscesses are large, then the doctor will open them and treat them with antiseptic agents. You cannot delete them yourself. The fact is that the liquid contained in the abscess is precisely the source of staphylococcal infection, if it gets on healthy areas of the skin, it can also affect them. With staphylococcal infection in the throat, frequent gargling with hydrogen peroxide, Furacilin, Miramistin is prescribed.
Treatment will include general tonic, as an integrated approach is required to eliminate pathogenic bacteria. Among these drugs are:
- Taktivin;
- Immunorix;
- Poludan;
- Immudon;
- Supradin;
- Alphabet;
- Vitrum.
The use of strengthening agents allows you to increase the patient's immunity, because as you know, an organism with a stable immunity copes better with pathogenic processes. To accelerate the action of antibiotics and other drugs, it is required to eat more foods containing vitamins and beneficial micro- and macroelements. You also need to try to reduce the child's physical activity, let him rest more.
If there is swelling of the wings of the nose and a skin rash, then treatment with antihistamines is required, such as:
- Tavegil;
- Diazolin;
- Zyrtec.

If side effects from the above drugs are observed or they do not give a result, then it is necessary to inform the doctor about this, and he will replace the treatment regimen.
The duration of treatment, the dosage of the drug is individually prescribed by the doctor. Before using the product, it will not be superfluous to read the instructions and exclude possible contraindications for use.
Traditional medicine
Staphylococcus aureus can be eliminated with alternative methods of treatment. Of course, first of all, preference should be given to traditional methods, but there are a number of cases when it is not possible to seek qualified help, then home recipes will also come to the rescue.
A decoction is prepared from dried chamomile flowers, insisted for half an hour, and then instilled into the nose. Chamomile is a well-known anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agent, so its use is quite justified.
Dried herb sage herb is prepared in the same way as chamomile, but gargle with broth in the presence of pustules.
Burdock root is crushed and mixed with a small amount of boiled water. The resulting juice with water is instilled into the nose, 5 drops every 3 hours.
To rinse the throat, use an alcoholic tincture of propolis, diluted in boiled water. It removes pustular rashes and makes swallowing easier if your throat is sore.
Compresses are used to eliminate staphylococcus. To do this, use an ordinary cotton swab dipped in water diluted with apple cider vinegar. Such lotions are made to each nostril for half an hour. According to people who tested the product, the effect will be noticeable after three uses.

A plant such as aloe has shown itself very well, the juice from this plant not only increases immunity, but also removes staphylococcal infection. It is necessary to bury the juice from the fresh leaves of the plant 3 times a day. It is important to note that this gives the result very quickly, since the aloe provokes a sneezing attack in the child. Green clots that prevent the baby from breathing come out very quickly.
You should not get carried away with traditional medicine, and if it does not work, then it is better to stop using old recipes for treatment. Sometimes they can only worsen the well-being of the child and provoke a number of complications, which will be more difficult to deal with than to treat the infection itself.
The best effect is achieved when traditional medicine is combined with folk medicine. In such a case, synthetic drugs are used as the main treatment, and as a supplement, fortifying agents on a natural basis, as recommended by traditional medicine.
It is strictly forbidden to warm up the nose or use hot baths to warm up the body. If you act with heat on a sick organism, then staphylococcus begins to multiply even faster, affecting new areas, because favorable conditions are created for its life. You should not use such folk remedies that include honey, sweet fruit juices, dairy products, they also provoke the multiplication of staphylococcus.
Do not insert tampons soaked in alcohol to your child, as pseudocylators advise. Bacteria of this group are not at all sensitive to alcohol, with such treatment you will only irritate the mucous membrane and lead to dry nose and burning.

Like any disease, staphylococcal infection is easier to prevent than to deal with its consequences. As a preventive measure, you can advise:
- constantly monitor the hygiene of the child's hands;
- give food only from clean dishes;
- process food thoroughly before cooking;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning in the house;
- constantly strengthen the immune system;
- humidify the air, conduct ventilation in the rooms where the child is;
- avoid contact with sick people.
Adhering to such simple preventive measures, it will be possible to protect the baby from the effects of bacteria and the development of unpleasant diseases.

A lingering runny nose and sore throat are often caused by staphylococcal flora. The most dangerous forms of the disease are usually provoked by Staphylococcus aureus. This article will tell parents about what features such infectious diseases have in babies.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Staphylococcus aureus are highly pathogenic microorganisms. Once in a child's body, they are capable of causing multiple lesions. The severity of adverse symptoms varies and depends on many factors. Staphylococcal infection in newborn babies and infants is quite difficult.
One of the favorite sites for Staphylococcus aureus is the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. In this case, infection occurs by airborne droplets.
You can get infected from any sick person or carrier of infection with microorganisms in the nasal cavity and oropharynx. Even a simple conversation with him can lead to infection. Staphylococcus aureus has a whole arsenal of various toxic substances that lead to severe inflammation. A pronounced inflammatory process leads to the appearance of unfavorable symptoms in a sick child. These symptoms appear, taking into account the predominant localization of the inflammatory process.

The severe course of the disease is usually accompanied by a pronounced intoxication syndrome. It is manifested by an increase in body temperature. With a severe course of the disease, it rises to 38-39 degrees. The sick child does not sleep well, often wakes up at night. Babies have decreased appetite. They become more moody and lethargic.
 In the nose
In the nose
Staphylococci that live in the nasal passages cause many adverse symptoms. A characteristic symptom of staphylococcal rhinitis is the appearance of a cold. Discharge from the nose at the same time has a yellow or green light. They are usually thick and difficult to separate. In some cases, the runny nose becomes lingering. Staphylococcal nasopharyngitis is an infectious pathology in which the mucous membranes in the nasopharynx become inflamed. This clinical variant of the infection can occur in babies at any age.

The incidence increases during the cold season. Massive outbreaks of the disease occur mainly in crowded collectives. Toddlers attending preschool education are at a higher risk of infection.
The development of staphylococcal rhinitis is caused by the influence of some provoking reasons:
- Weakening of local immunity. Quite often occurs after severe hypothermia.
- Injuries to the nose. Injuries to the mucous membrane make any infection easier to penetrate. Operations on the nasopharynx for the removal of adenoids or polyps also contribute to the active multiplication of microbes.
- Abuse of drops for the treatment of the common cold. Excessive use of these drugs contributes to the development of atrophic changes in the mucous membranes of the nasal passages. This leads to the fact that pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus easily enter the nasal cavity.
 In the throat
In the throat
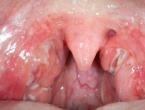
By airborne droplets, Staphylococcus aureus easily penetrate the oropharynx and pharynx. This contributes to the development of a strong inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract. A fairly common manifestation of staphylococcal infection is bacterial pharyngitis. This pathology is manifested by the appearance of a purulent plaque that covers the outside of the tonsils. Palatine arches with staphylococcal pharyngitis increase and hang strongly over the entrance to the pharynx.
The neck of a sick baby turns bright red. The tongue is coated with a gray or yellowish coating. During illness, the child develops severe soreness in the throat, and decreases appetite. Toddlers may refuse to breastfeed or are poorly attached to the breast.
Acute staphylococcal tonsillitis is accompanied by the development of many adverse symptoms. The pharynx in this condition becomes bright red, and in some cases even becomes flaming in color.
The palatine tonsils increase in size and loosen. Outside, they become covered with a purulent bloom, which in some cases can harden and form dense crusts. When you try to remove plaque yourself with a teaspoon or spatula, bleeding appears. Staphylococcal angina has, as a rule, a rather severe course. In weakened babies and children with chronic diseases of internal organs, acute tonsillitis can lead to the development of multiple complications and adverse long-term consequences.

A fairly common manifestation is the development of bronchopneumonia.
It occurs in more than 10% of cases of acute staphylococcal tonsillitis.
Diagnostics
When the first adverse symptoms appear in the nose or throat, it is imperative to show the baby to the treating doctor. A pediatrician or pediatric otolaryngologist will be able to examine a sick child. After a clinical examination, the doctor establishes a preliminary diagnosis. To identify the causative agents of the infection, additional laboratory tests are required. A general blood test is performed for all babies with signs of bacterial diseases. Staphylococcal pathologies of the upper respiratory tract are accompanied by the appearance of leukocytosis - an increase in the number of leukocytes.

A strong inflammatory process causes an acceleration of ESR. There are also changes in the leukocyte formula. A blood test allows you to detect any deviations from the norm at the earliest stages. The causative agents of infection can also be found in the pathological secret. Determine staphylococcal nasopharyngitis or tonsillitis by conducting a bacteriological study.

The biological material for such examinations is the discharge from the nasal cavity or mucus from the back of the pharynx. Research is carried out in a special laboratory. The effectiveness and specificity of these tests are quite high. A marker study that allows you to identify dangerous microbes is a smear. After applying the biological material to a glass slide, it is placed in a thermostat.

The result of bacteriological research is usually ready in a week. For the study, in some cases, sputum is taken, which the baby coughs up during the acute period of the disease. To establish the complications of acute staphylococcal tonsillitis, an additional instrumental study is carried out - radiography of the lungs. This method allows you to detect pneumonia at the earliest stages of the development of the disease.
 Complications
Complications
A prolonged course of staphylococcal rhinitis often leads to the development of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses. Especially often this disease develops with untimely prescribed treatment. Staphylococcus aureus, getting into the sinuses, contributes to the development of severe inflammation in them. Ultimately, this leads to the development of acute bacterial sinusitis or frontal sinusitis. These pathologies are accompanied by the development of a severe debilitating rhinitis. The discharge from the nose in this condition is rather thick, yellow or brown in color.

A toddler with sinusitis feels constant congestion. Nasal breathing is severely impaired. The child has an aggravated headache, which is bursting and persistent. Staphylococcal pneumonia is also a fairly common complication that occurs as a result of an unfavorable course of acute tonsillitis, turning into bacterial bronchitis. This pathology is accompanied by a pronounced intoxication syndrome. Young toddlers may develop symptoms of respiratory distress. Therapy of staphylococcal pneumonia is carried out only in a hospital setting.
 Treatment
Treatment
Therapy of staphylococcal infections includes the appointment of a whole range of different drugs. The main goal is to eliminate bacterial foci and normalize the beneficial microflora that lives in the upper respiratory tract. For this, various antibiotics are prescribed. Reviews of the parents of babies who took these drugs indicate that these drugs have a pronounced positive effect. The disadvantages of using antibiotics are the development of side effects, which in some cases can be very unpleasant.

Staphylococcus aureus are especially sensitive to antibacterial drugs of the penicillin and cephalosporin series. The dosage, frequency and duration of use are determined individually, taking into account the age and weight of the baby, as well as the severity of the course of infectious pathology in a particular child. The duration of the therapy regimen may be different. On average, therapy for staphylococcal nasopharyngitis is 5-10 days. Acute tonsillitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus is treated in 1.5-2 weeks. In some cases, an alternative method of treatment is used using specific bacteriophages. These drugs have a narrowly targeted effect and cause the death of pathogenic microbes.

Treatment with bacteriophages has fewer side effects than antibiotics. This therapy is quite successfully used to treat staphylococcal infection in the smallest patients. Various sea salt solutions are used to improve nasal breathing. They are used to irrigate the nasal passages. These products help to flush out the nose of babies and help soften secretions that are too dense. These solutions can be used 3-4 times a day.

In some cases, vasoconstrictor nasal drops are used, which are prescribed by a doctor according to indications, taking into account the age of the baby.
The nasal cavity can also be treated with special medications. For the treatment of inflamed nasal passages, "Chlorophyllipt" is well suited. This agent can reduce inflammation and has a detrimental effect on pathogenic staphylococci. Various decoctions of medicinal herbs are suitable for washing a sore throat. These affordable herbal remedies are always found in every home medicine cabinet. To rinse your throat, you can use a decoction of chamomile, sage, calendula. Rinse the neck 3-4 times a day one hour after eating. Only warm solutions can be used for rinsing.

Many bee products also have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. For rinsing the throat, ordinary propolis is suitable. Such rinses should be carried out 2-3 times a day for 10-14 days. This treatment can only be used by babies who do not have allergic reactions to bee products. Ordinary honey is also suitable for rinsing your throat. When the temperature rises above 38 degrees, antipyretic drugs should be used.

For children, drugs based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are quite successfully prescribed. These funds are taken in an age dosage.
Doctors do not recommend taking acetylsalicylic acid during the acute period of an infectious disease in babies, as this can lead to the development of dangerous side effects of this drug. During the height of the illness, the baby should be at home. If a child's illness proceeds with severe fever, then the baby must necessarily comply with bed rest. Such a forced and simple measure will help to significantly reduce the risk of developing dangerous complications of an infectious disease. During massive outbreaks of staphylococcal infections, quarantine is introduced in educational institutions. All babies who have been in contact with sick children receive preventive treatment.

To restore the lost strength during the illness, the baby is prescribed general strengthening therapy. For this, multivitamin preparations are prescribed. The vitamins and microelements they contain help to restore immunity and improve the well-being of the child. They should be used for at least 30 days. Children with severe immunity disorders are prescribed immunomodulatory therapy.
Whether the detected staphylococcus aureus in the nose is dangerous, see the following video:
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most common bacteria found on human skin or mucous membranes. But for some reason, when it is found in children, parents start to panic. You should not worry too much, but it is also undesirable to ignore the first symptoms. The sooner staphylococcus aureus is found in a child's nose, the less likely it is that serious complications will develop.
Infection routes
Children can become infected with staphylococcus already at birth, passing through the birth canal of the mother. Often, the bacterium penetrates the umbilical wound when it  improper processing. Infected mucus can also end up in a child's nose, and then spread further through the body.
improper processing. Infected mucus can also end up in a child's nose, and then spread further through the body.
Premature babies are at the greatest risk, since they do not have developed immunity. No less dangerous is infection for babies who are artificially fed from the very first days - their own immunity is not yet strong enough, and he does not receive ready-made antibodies present in mother's milk. Therefore, if there is an opportunity to provide the baby with breast milk at least in minimal quantities, it cannot be refused.
Staphylococcus aureus often nests in clinics, hospitals and child care facilities. It is easy to find it on the hands of almost half of the medical workers, nannies, educators, kitchen workers. And since the bacterium is very tenacious, it is easily transferred to the skin and mucous membranes of the child, gets on food, remains on dishes, towels, bed linen.
Thus, by the age of 2, about half of the children are carriers of various types of this bacterium.
Manifestation of symptoms
Getting on the mucous membrane of the child's nose, staphylococcus begins to actively multiply and very quickly reaches the throat, penetrates the respiratory system and the digestive tract. In the course of its life, the bacterium releases toxins that destroy mucous cells and poison the baby.  A child's body is much more sensitive to toxic substances than an adult, so the first symptoms in children usually appear differently:
A child's body is much more sensitive to toxic substances than an adult, so the first symptoms in children usually appear differently:
- a sharp increase in temperature, which after a while decreases to subfebrile;
- the appearance of signs of severe intoxication: nausea, vomiting, upset stools;
- weakness, complete lack of appetite, drowsiness, frequent crying;
- severe flatulence and diarrhea are possible.
And those symptoms that appear first in an adult develop later in a child, and their localization is not so clearly expressed.
A red and / or purulent rash appears throughout the body or in certain areas. The mucous membranes of the nose become very inflamed and swollen, a profuse rhinitis begins, sometimes purulent. Purulent ulcers, boils, pimples can form in and around the nose.
Features of different types of staphylococcus
Staphylococci are very diverse. There are 27 species in total. Only four are dangerous to health, one of which does not settle in the nose, but affects the genitourinary system. The other three staphylococci on the nasal mucosa feel great and manifest themselves in different ways:

It is possible to determine exactly what type of staphylococcus is present in the child's body by conducting a diagnostic examination.
Diagnostic methods
In the smallest, in order to sow staphylococcus, it is enough to take a feces analysis. This bacterium quickly penetrates the intestines and actively develops there. Another way to detect it is by bacterial seeding of mucus from the nose. This analysis allows not only to determine the strain of the pathogenic microorganism, but also to check its sensitivity to various drugs.
If the doctor suspects that the infection has already caused various complications, then he may suggest taking an x-ray of the nose or an ultrasound of the internal organs. In some cases, urine and blood tests may additionally be prescribed.
Only according to the results of laboratory tests, the pediatrician decides which drugs to treat staphylococcus aureus in this case.
Treatment regimen
There is no general treatment regimen for young children. In the absence of medical contraindications, cephalosporin antibiotics are usually prescribed.  series: "Ceftriaxone", "Cefotaxime", etc. We remind you that the final choice of the drug and the calculation of its dosage should be made by the doctor, and the parents should strictly follow his recommendations!
series: "Ceftriaxone", "Cefotaxime", etc. We remind you that the final choice of the drug and the calculation of its dosage should be made by the doctor, and the parents should strictly follow his recommendations!
In addition, funds are needed to strengthen the immune system: "Immunal", "IRS-19", etc. At the same time, it is desirable to give the child multivitamin preparations that accelerate metabolic processes and strengthen the baby's body. In case of severe intestinal disorders, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Enterosgel will help to correct the situation.... As a last resort, you can give your child activated charcoal.
Chamomile, lime or raspberry tea (without sugar or honey!), Chamomile decoctions, rose water perfectly helps to relieve inflammation of the throat and intestines and quickly remove toxins. Foods containing a large amount of vitamin C are especially useful for the baby during this period: apricots, currants, blueberries. Children over 6 months old can be given puree of them (if there is no diarrhea).
Rinse the spout preferably with a sea salt solution or Aquamaris. Perfectly deals with staphylococcus an oily solution of chlorophyllipt, which needs to gargle and rinse the baby's nose.
Lubricate damaged areas of the skin and mucous membranes 2-3 times a day with brilliant green - perhaps the only antiseptic that can quickly destroy staphylococcus aureus.
Prevention measures
Considering that staphylococcus aureus is a conditionally pathogenic bacterium and is completely harmless for a healthy baby with strong immunity, the main preventive measures should be directed to the general health of the child. Naturally, when the baby is already sick, doing something is not only unnecessary, but also dangerous. But when the treatment is over and repeated tests, which need to be done a month after the end of the course, showed an acceptable amount of staphylococcus, you can start hardening.
 The main preventive measures are as follows:
The main preventive measures are as follows:
- teach the child to follow the basic rules of personal hygiene as early as possible;
- provide him with full-fledged natural food rich in vitamins and microelements;
- strictly observe the sanitary standards for the storage and processing of food;
- monitor the cleanliness, temperature and humidity of the air in the baby's room;
- regularly perform wet cleaning of the room, clean carpets and upholstered furniture with a vacuum cleaner;
- remove from the child's room all substances that irritate the nasal mucosa and possible allergens (household chemicals, perfumes, flowers with a strong odor, etc.);
- if the child is healthy, walk with him daily in the fresh air, dressing him according to the weather;
- stimulate an active lifestyle: outdoor games, sports and gymnastics;
- regularly visit the clinic for preventive examinations.
If the baby is sick and the symptoms raise suspicion of staphylococcus aureus, in no case treat it yourself. This should only be done by a doctor!
It is equally important to strictly adhere to all appointments and bring the treatment to the end. If bacteria remain in the body that have managed to adapt to the antibiotics used, then they will subsequently multiply, and it will no longer be possible to destroy them using the previously tried methods.
When a child falls ill in a family, adults will also have to undergo an examination, and possibly a course of treatment. Otherwise, they will constantly infect the baby again, and the child will never get rid of the tenacious bacteria. Moreover, there is no guarantee that other family members did not become the source of the primary infection.
Staphylococci are conditionally pathogenic microflora. They are constantly present on mucous membranes and skin. With a decrease in the protective functions of the body, they acquire a pathogenic form and cause the development of many diseases. Staphylococcus aureus of all types of staphylococci is considered the most dangerous, especially for children.
Staphylococcus aureus: what is it and how is it dangerous?

Staphylococcus aureus is a dangerous bacterium
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most dangerous bacteria that can cause various serious diseases. This type of staphylococcus has several strains that differ from each other in the set of toxins produced.
Under the microscope, the bacterium appears as round, yellow clusters. Staphylococcus aureus is characterized by high viability, and can remain for about 6 months in a dried state. Bacteria do not die under the influence of direct sunlight, when frozen.
If the infection is not destroyed, then it will actively multiply and affect other organs.
Untimely treatment of staphylococcal infection can cause serious complications:
- Chronic sinusitis
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
- Phlegmon
- Sepsis
If a large number of strains of pathogenic bacteria are detected, treatment should be started in a timely manner in order to prevent the development of serious diseases.
Causes and symptoms

Nasal culture - effective diagnosis of staphylococcal infection
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most dangerous bacteria, as it contributes to the development of serious diseases. It got this name from its color. Most often, it is localized in the nasal cavity, and then penetrates into the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
Infection can occur through airborne droplets, contact-household and oral routes. An infection can get to a child during kissing, sneezing, breastfeeding, through the birth canal, with food. In medical institutions, if sterility is violated during procedures, there is also a high probability of Staphylococcus aureus getting inside.
Staphylococci are conditionally pathogenic microorganisms and are present on the mucous membranes. With concomitant factors, their number exceeds the norm, which leads to an inflammatory process.
The main factors contributing to the penetration of staphylococcal infection into the body:
- Weakening of immunity.
- Improper nutrition.
- Caries.
- Long-term use of vasoconstrictors.
When diagnosing Staphylococcus aureus in children, other family members should be tested. And all members must undergo treatment, as there will be a risk of re-infection.
More information about Staphylococcus aureus can be found in the video:
Staphylococcus aureus is a very insidious infection and can be easily confused with a cold or respiratory illness. Symptoms depend on the number of pathogenic bacteria. The main signs of Staphylococcus aureus in the nose include:
- Mucous nasal discharge.
- Itching and redness of the mucous membrane.
- Temperature increase.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Feeling of a stuffy nose.
- Enlargement of the tonsils and adenoids.
- Crusting in the nasal passages.
- Intoxication.
- Prolonged runny nose.
The symptomatology of adults and children is different. A typical sign of a staphylococcal infection is a skin rash. It is possible to detect Staphylococcus aureus only by laboratory tests - bacterial sowing of mucus from the nasal cavity.
Medication and antibiotics

Correct and effective treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor!
If Staphylococcus aureus is found as a result of nasal swab culture, the sensitivity of the microorganism to antibiotics is assessed. This is an important step in prescribing antibiotic therapy, since various pathogens are resistant to certain drugs.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the nose is aimed at eliminating the cause of its appearance and signs of the inflammatory process. For each child, treatment is prescribed individually. Medication is usually done at home, but more severe cases will require hospitalization.
Treatment features:
- For treatment, antibacterial drugs of a wide spectrum of action are used: Amoxiclav, Oxacillin, Ceftriaxone, Nofloxacin, etc. Antibiotic treatment is 2-3 weeks. If you feel better, it is prohibited to stop using the drug, otherwise antibiotic resistance will develop and the treatment will be delayed.
- From local antibiotics, Mupirocin or Bioparox is used. These drugs are used to lubricate the nasal cavity 2-3 times a day for a week.
- To avoid an allergic reaction to antibiotics, antihistamines are taken. They reduce the amount of discharge and itching. To make wounds and ulcers heal faster, they should be treated with "brilliant green".
- In addition, the ENT may prescribe instillation of Chlorophyllipt into the nose, rinsing with saline.
- The entire period of treatment is recommended to use immunomodulators and multivitamins. After the course of treatment, it is necessary to take a second smear for Staphylococcus aureus to make sure that there is no more infection in the body.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection in the nose should be carried out in a comprehensive manner in compliance with all the doctor's recommendations.
Traditional methods of treatment

We treat staphylococcal infection with linden decoction
Unconventional methods of treating Staphylococcus aureus in children should be approached with caution and should not be chosen as the main treatment. Traditional methods are an auxiliary means of drug therapy.
It should be remembered that Staphylococcus aureus does not die under the influence of alcohol, hydrogen peroxide. Therefore, it makes no sense to use these funds to treat wounds and ulcers. The best remedy that is afraid of staphylococcus is "green".
Popular folk remedies for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus:
- A decoction of echinacea and burdock root. Grind the plants and pour 2 tablespoons of raw materials with 800 ml of hot water. Then boil for 20 minutes and cool. Take orally 3 times a day.
- Garlic compress. Chop the garlic cloves, add warm boiled water and leave for 1.5-2 hours. Next, moisten a cotton cloth and apply to the inflamed areas of the nose. Repeat the procedure every day for about 2 weeks.
- Linden blossom decoction. Pour 2 tablespoons of raw materials into a thermos and pour a glass of boiling water. After 3 hours, drain and use to rinse the nasal cavity.
- Rinsing with eucalyptus essential oil. Take 5 g of salt and 2 drops of oil and dissolve in 1/4 liter of boiled water. It is necessary to rinse immediately after preparation of the solution.
- Propolis. Dissolve 20 g of propolis in 1/2 glass of water and put in a water bath for 2 hours. Give the child 1 tablespoon before meals.
It is strictly forbidden to put warming compresses on the bridge of the nose, forehead area. More fluids should be consumed during the entire treatment. To strengthen the immune system and it is useful to give the child lime, raspberry tea, a decoction of rose hips, chamomile, currant leaves.
Prevention
 Preventive measures against Staphylococcus aureus are aimed at preventing infection from entering the body.
Preventive measures against Staphylococcus aureus are aimed at preventing infection from entering the body.
- Ventilate the room frequently and do wet cleaning.
- Always wash your hands before eating.
- Children's toys and utensils should be kept clean.
- Strengthen the immune system.
- Avoid hypothermia of the body.
- Take immunostimulating drugs during viral infections.
- Products that are not exposed to heat must be handled in soapy water. This will significantly reduce the risk of staphylococcus entering the body through food.
Strengthening the immune system is an important prevention method. Children should be taught to a healthy lifestyle from a young age. It is necessary to do exercises every day, eat right, go for walks, observe the rules of personal hygiene.
It is useful to do hardening, wet rubdown and swim in the pond in the summer.
Staphylococci are conditionally pathogenic microorganisms that live in the mucous membranes of the respiratory system and on the skin. With a sharp increase in the number of microbes in the respiratory tract, various infectious diseases arise - tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, sinusitis, etc.
How can you destroy staphylococcus aureus in a child's throat? Treatment methods depend on what type of bacteria caused inflammation of the mucous membranes of the larynx.
To destroy pathogens, antibiotics, staphylococcal antitoxin, bacteriophage, immunoglobulin and symptomatic drugs are used.
In addition to medicines for the treatment of children, physiotherapy procedures, in particular ultraviolet radiation, can be used.
Features and types of staphylococci
Generally speaking, staphylococci are normal representatives of the microflora of the laryngopharynx, nasal cavity and skin. In small quantities, they live in the body of a healthy person, without causing inflammatory processes and infectious diseases. However, with a decrease in immunity, anaerobic microbes begin to multiply rapidly. Waste products of staphylococci poison the body, causing infectious and allergic reactions.
Clinical manifestations and the severity of the course of ENT diseases largely depends on what kind of bacteria caused the inflammation. When carrying out a bacterial culture in sputum, the following types of staphylococci can be detected:
- golden - provokes purulent inflammation of almost any type of tissue and organs;
- saprophytic - affects mainly the organs of the genitourinary system;
- epidermal - localized in the upper layers of the epidermis, but if untreated, it can affect the nasopharyngeal mucosa;
- hemolytic - one of the most resistant to antimicrobial agents of staphylococci, affecting the respiratory, excretory and cardiovascular systems.
Hemolytic staphylococcus aureus develops rapidly, causing severe complications such as sepsis, meningitis, and pyelonephritis.
It should be noted that Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus aureus in a child's throat multiplies very quickly. Anaerobic bacteria readily adapt to the action of antibacterial agents, in particular to penicillins and cephalosporins.
Therefore, it is rather difficult to find the best medicines for the treatment of staphylococcal diseases in children. In the absence of drug treatment, microbes mutate and cause serious complications, which in rare cases lead to death.
Possible diseases
Decreased immunity, hypothermia, iron deficiency anemia, hypovitaminosis and antibiotic abuse can cause the rapid multiplication of microbes in the respiratory system. Staphylococcal infection leads to the development of a number of bacterial diseases:
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis;
- sphenoiditis;
- sinusitis;
- laryngotracheitis;
- bronchopneumonia;
- otitis media;
- acute tonsillitis.
Each disease has its own distinctive symptoms that need to be considered in more detail. The difficulty lies in the fact that the general clinical manifestations of staphylococcal infection can be easily confused with the symptoms of a viral disease. Many parents believe they can cope with the disease on their own and rely on personal experience. However, inadequate treatment of staphylococci in the throat can lead to disastrous consequences, up to the general damage to the body by bacteria that have penetrated the systemic circulation.
Sore throat symptoms
Staphylococcal angina is a bacterial inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa and palatine tonsils (tonsils). Fever, muscle weakness and sore throat when swallowing are characteristic symptoms of the disease, which appear several hours after infection of the body. Because young children are more susceptible to infections than adults, angina is more severe.
Typical manifestations of streptococcal sore throat include:

Staphylococcal angina in children often develops against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, scarlet fever and chronic rhinitis. Typically, pathogens are localized in the glands and lymphoid tissues at the back of the throat. When characteristic signs appear, it is advisable to examine the child's throat. The presence of white plaque on the root of the tongue and the walls of the pharynx, as well as a slight increase in the palatine tonsils, is 100% confirmation of bacterial inflammation of the respiratory tract.
Laryngitis symptoms
Laryngitis is an acute inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa, which is characterized by hyperemia (redness) and swelling of the larynx. The development of the disease in children is often preceded by chronic rhinitis, tonsillitis, influenza, scarlet fever and overstrain of the vocal cords. Typical manifestations of staphylococcal laryngitis are:
- dry throat;
- pain in the larynx;
- dry or moist cough;
- subfebrile temperature (not higher than 38 degrees);
- separation of sputum with impurities of pus when coughing;
- decrease in the timbre of the voice;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat.
One of the most dangerous manifestations of the disease is laryngospasm. An involuntary contraction of the pharyngeal muscles causes the glottis to close, which can cause loss of consciousness or asphyxiation. Untimely passage of antimicrobial therapy entails the development of sluggish inflammation in the laryngeal mucosa and, accordingly, chronic laryngitis.
Pharyngitis symptoms
Staphylococcus aureus in the throat often causes the development of bacterial pharyngitis in children. Hypothermia, high-carbohydrate food intake, diabetes mellitus, chronic diseases and congenital immunity deficiencies can contribute to the growth of bacteria. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the throat walls, which leads to tissue swelling and difficulty breathing.
The classic symptoms of the development of staphylococcal pharyngitis include:
- sore throat;
- dry cough;
- general malaise;
- hoarseness of voice;
- high fever;
- soreness of the lymph nodes;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- mucus on the walls of the throat.
In frequently ill children with lowered immunity, the risk of developing bacterial pharyngitis is approximately 40-45%.
If the inflammation is left untreated, pathogens can invade the nasal mucosa and Eustachian tube. This can lead to complications such as bacterial rhinitis, rhinosinusitis, or tubo-otitis. In infants, the symptoms of pharyngitis practically do not differ from the manifestations of a cold. The child becomes whiny, refuses to eat and does not sleep well.
Antibacterial therapy
 Staphylococcus aureus is practically immune to antimicrobial agents, therefore, new generation antibiotics are used to treat bacterial inflammation. They contain active substances that prevent the replication of pathogenic DNA and, accordingly, the reproduction of microbes. For the treatment of children, antibiotics are selected that have the least pronounced toxic effect, namely:
Staphylococcus aureus is practically immune to antimicrobial agents, therefore, new generation antibiotics are used to treat bacterial inflammation. They contain active substances that prevent the replication of pathogenic DNA and, accordingly, the reproduction of microbes. For the treatment of children, antibiotics are selected that have the least pronounced toxic effect, namely:
- Rifaximin;
- "Kanamycin";
- Ofloxacin;
- "Amoxiclav".
Pathogenic bacteria that cause the development of tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other ENT pathologies secrete substances that lead to poisoning of the child's body. Therefore, delayed treatment of staphylococcal infection can often provoke the development of toxic shock, leading to the death of the patient.
Etiotropic agents that eliminate pathogens should be taken for at least 7-10 days.
It should be understood that uncontrolled intake of antibiotics can worsen the patient's well-being and even provoke the development of multidrug resistance of microbes, i.e. their insensitivity to most antimicrobial agents.
Antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin
Antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin is an injection drug that contains antibodies to most strains of pathogenic gram-positive microbes. The medicinal solution is obtained from donor blood or serum. The dosage and duration of intramuscular injections depends on the child's age and weight.
Direct indications for the use of the drug are any staphylococcal infections in patients aged 6 months. Typically, antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin is used in conjunction with antibiotics to enhance the action of antimicrobial components. With the help of the drug, it is possible to eliminate even generalized forms of inflammation, up to sepsis.
Advanced forms of purulent tonsillitis and laryngitis are treated with hyperimmune antistaphylococcal plasma. It contains specific antibodies that destroy almost any strains of gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus. The medicinal solution is administered intravenously to children for 2-3 days, after which the symptoms of the disease are smoothed out.
Staphylococcal bacteriophage
Bacteriophages are viruses that literally devour disease-causing bacteria. It should be noted that some types of pathogenic microbes are capable of producing substances that neutralize the action of bacteriophages. For this reason, before using medications, it is necessary to accurately establish the sensitivity of phages to pathogens of bacterial inflammation.
Important! Before use, the bottle with the drug must be shaken to completely dissolve the precipitate.
Staphylococcal bacteriophages are widely used in the treatment of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the throat, trachea, bronchi, nose and gastrointestinal tract. The drug is available in the form of ointments and injection solutions, which are injected directly into the foci of inflammation. The active components of the product almost instantly neutralize pathogenic bacteria, which helps to alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Bacteriophages can be used to treat localized and generalized septic inflammations not only in the airways, but also in the urogenital canals. The medicine is recommended to be used to eliminate staphylococcal infections complicated by otitis media, pneumonia, tracheitis, pleurisy, etc.
Staphylococcal toxoid
Staphylococcal toxoid is an immunocorrecting drug that stimulates the so-called antistaphylococcal immunity in the child's body. Regular use of the drug enhances the production of antibodies that can resist the development of staphylococcal flora in the respiratory tract. Toxoid can cure bacterial inflammation not only in the throat, but also on the skin.
Staphylococcal toxoid can be used to prevent pyoinflammatory infections in immunocompromised patients. The drug is used to treat patients aged 16 and over, since its active ingredients can provoke severe allergic reactions in young children. To achieve the desired results, the solution is injected subcutaneously every two days, gradually increasing the dosage.
Gargling
In addition to specific drugs for the destruction of staphylococci in the throat, antiseptic rinsing solutions are used. Regular sanitation of the oropharynx allows you to clear the mucous membrane from about 50-60% of pathogenic agents that provoke purulent inflammation. The scheme of pediatric therapy for sanitizing procedures includes:
- "Propolis solution" - disinfects and softens the throat, preventing the penetration of microbes deep into the respiratory tract;
- "Ingalipt" - eliminates local manifestations of pharyngitis, tonsillitis, stomatitis and other ENT diseases;
- "Chlorophyllipt" - increases the concentration of oxygen in the tissues, which makes it possible to multiply the effect of antibiotics and accelerate the regeneration processes in the mucous membranes of the throat.
From folk remedies for gargling, decoctions based on echinacea, medicinal chamomile, burdock root and yarrow are used. Phytoreparations gently affect the mucous membrane, helping to eliminate inflammatory processes and flushing out pus from lesions.
However, it should be borne in mind that alternative medicine can cause adverse reactions in children. Therefore, before using decoctions and infusions, it is advisable to consult with a local therapist or pediatrician.
Staphylococci (Staphylococcus) are anaerobic bacteria found in the body of every person. They are located on the skin and mucous membranes. Unfavorable factors provoking an excessive increase in their number can cause various ailments. For example, staphylococcus aureus in a child's throat causes ENT diseases and diseases of the respiratory system.
The most dangerous of the variety of types of staphylococci is golden (aureus), which is found in the nasopharynx. Despite the harmfulness of such bacteria, the disease responds well to treatment.

Features of staphylococcal infection and routes of infection
The active reproduction of staphylococcus occurs primarily in children who do not observe personal hygiene. Bacteria enter the body through household items and airborne droplets.
Other routes of infection:
- through breast milk;
- during childbirth from mother to child;
- through poorly processed foods.
Active multiplication of bacteria on the human body occurs in places where it is humid and warm. For this reason, the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract so often suffer from their activity. Staphylococci are always present in the throat - the norm is 1000 bacteria per 1 ml of medium. If this figure is exceeded, diseases such as pharyngitis, rhinitis, otitis media, tonsillitis, sinusitis and others arise.


Depending on the nature of the course of the disease, it is conventionally divided into 4 degrees:
- the first is characterized by weak growth;
- with the second, growth is observed up to 10 colonies of the same species;
- the third - from 10 to 100 colonies;
- the fourth - more than 100 colonies.
It is possible to talk about the onset of the disease only in the third degree. Staphylococcus aureus 4 degrees (10 to 4) is already considered a pathology.
Once having been ill with an ailment that was provoked by an infection with Staphylococcus, the body forms immunity. When a new infection hits, the immune system tries to resist it.
Staphylococcus aureus is a very tenacious and resistant microorganism. The sun's rays, low and high temperatures (up to 70 ° C) are not afraid of him, only heating up to 100 ° C is destructive for the bacteria. Staphylococcus aureus is very dangerous for young children.
A neglected disease can cause:
- tonsillitis (in acute and chronic form);
- otitis media;
- sinusitis;
- meningitis;
- septic arthritis;
- intracranial phlebitis;
- endocarditis;
- staphylococcal sepsis and other ailments.
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of a disease:

Diagnostics of the Staphylococcus aureus
Diagnosing aureus is not easy. The reason for this is the similarity of the symptoms of the disease with the manifestations of other ENT diseases.
Primary diagnostic methods:
- collection of anamnesis (clarification of complaints, determination of the presence or absence of patient contact with patients, etc.);
- examination of the oral cavity and tonsils;
- palpation of lymph nodes;
- KLA to detect the presence of inflammation.
To identify the bacterial nature of the disease, a swab (bacterial culture) is taken from the child's throat. To detect bacteria in a smear, the Gram method is used (staining microbes) or the culture method, when bacteria are sown on a special base.
Treatment methods
In small quantities, the Staphylococcus bacterium cannot harm the human body. Treatment is necessary if microorganisms provoke chronic or recipient inflammatory processes. The activation of bacteria can occur due to a decrease in immunity, SARS, emotional shock, as well as a lack of vitamins.
It is important to carry out therapy in the early stages of the disease. Then it will be possible to avoid chronic diseases and serious complications.
In the treatment of staphylococcus, the following tasks are pursued:
- suppression of bacterial activity;
- restoration of the integrity of the mucous membranes of the throat and nose;
- stimulation of immunity.
Medicines that suppress staphylococcus aureus include antimicrobial drugs:
- Antibiotics (Cefotaxime, Clindamycin, Amoxiclav) used if the infection is severe.
- Anti-staphylococcal or complex bacteriophage that complements antibiotic therapy. The agent is a virus that destroys staphylococci.
Immunostimulants also play an important role in treatment. The main agent that is allowed to be used for children after 6 months is anti-staphylococcal immunoglobulin. It is also possible to prescribe IRS-19, Ribomunal, Taktivin, Poludan and other drugs.
These medications are prescribed during the acute period of infection. Reception continues for 30 days after the symptoms subside.
Home treatment


Not the last role in the treatment of the ailment in question is assigned to folk methods. However, before using them, you should consult a doctor. If you treat the disease yourself, an even greater increase in the number of bacteria is possible.
Basic folk recipes:
- Rinses with St. John's wort, calendula flowers and eucalyptus leaves (you can use all the components in the complex or each separately). The herb is poured with boiled water (1 tbsp. L. Per glass). Gargle with such an antimicrobial agent three times a day.
- Apricots and black currants. With the daily use of these products in food, it is possible to get rid of germs sooner.
- Decoction of burdock and echinacea roots. Both components are taken in equal proportions and poured with hot water (2 tsp for 400 ml of water), then boiled for 5 minutes over low heat. It is recommended to drink one glass of the prepared broth 3 times a day.
- Rosehip infusion. One glass of berries is poured into a thermos and poured with boiling water. Insist 10 hours. Take ½ glass twice a day.
- A decoction of hop cones, fragrant mint, fireweed, calamus root and dill seeds. All are mixed in equal parts. A liter of boiled water is added to one tablespoon of the mixture, the composition is poured into a thermos and left for 8 hours. Caress the throat with this remedy at least 3 times a day.
Preventive actions
To prevent Staphylococcus aureus requires:
(we recommend reading: symptoms of staphylococcus in children on the skin and photos)
- careful personal hygiene;
- eating only clean fruits and vegetables;
- treatment of wounds and injuries with antiseptics;
- avoid crowded places when walking with a small child;
- do not eat food with damaged packaging or in its absence;
- exclude warming up of the body and taking hot baths;
- hardening, procedures that strengthen the immune system;
- eating only clean dishes;
- regular wet cleaning in the house.
If necessary, you can get vaccinated against staphylococcus. With its help, the baby's immunity is stimulated, which can subsequently fight back the ailment.
The younger the child, the more dangerous a staphylococcal infection is for him. When microorganisms enter the body, they provoke inflammatory processes and destroy the cellular structure of healthy tissue, the products of their vital activity - hemolysins - kill leukocytes and the body is left without protection against the introduction of viruses and bacteria of other types.
In children, staphylococcus aureus causes serious damage to the skin, lymphatic tissue and the nervous system; in a newborn child, the pathogenic flora can cause death.
Types of staphylococcus
The following types of pathogenic flora are most common.
- Saprophytic staphylococcus. It mainly affects the genitourinary system, penetrating into the mucous membranes from the outside;
- Epidermal staphylococcus. Conditionally pathogenic flora is found on the surface of the body and mucous membranes of the nose and internal pharynx. Dangerous for children with a reduced immune status - premature or after surgery. A healthy body can resist the development of microorganisms on its own;
- Staphylococcus aureus. It is still considered the most dangerous of the known cultures of microorganisms. Inhabits the surface of the skin, is sown in feces and urine, throat swab. It destroys phagocytes - immune cells that dissolve infectious agents. A dangerous feature of the disease caused by this culture is increased antibiotic resistance.
Nosocomial infections have already claimed many lives in infants.
The introduction of Staphylococcus aureus into the body
- Staphylococcus aureus in a child's throat most often appears during contact with a respiratory-type infection - a sick person, when talking, coughing and sneezing, releases thousands of pathogens.
- Also, the infection spreads through household items and food.
- Since the role of "gatekeepers" in the body is played by the tonsils - they consist of lymphoid tissue and try to neutralize the penetrating pathogens - the pathogenic flora develops there. With favorable factors for themselves - a decrease in the immune status with hypothermia, constant fatigue, lack of sleep, nervous environment, intoxication, vitamin deficiency - microorganisms begin to multiply actively, reducing overall immunity.
Staphylococcal infection symptoms
Treatment of staphylococcus in the throat is not required for strong children. The body itself will cope with pathogenic microorganisms.
In weak children, the disease takes on a chronic form. On the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, on the edges of the lips and in the nose, pustules, stomatitis, manifestations of conjunctivitis constantly appear. Signs of body intoxication:
- constant weakness;
- lethargy;
- apathy;
- deterioration of the general condition.
When introduced into the body, the temperature rises, sepsis (blood poisoning) may develop, and the digestion process is disrupted.
Staphylococcal sore throat is also difficult to treat because the use of strong antibiotics causes severe diarrhea and intestinal colic in the child. Dysbacteriosis caused by intoxication is exacerbated by the side effect of antibacterial drugs.
Diagnosis of the disease
The presence of a pathogenic culture is detected in the following ways.
- Sowing a bacteriological culture. A throat swab is taken in the acute period - bacteria at this moment are most active and easily detected. During this sowing, at the same time, it becomes clear how to further treat staphylococcus in the nose and throat. To do this, in a test tube, pathogenic microorganisms are combined with antibiotics of various types and research is carried out on which antibacterial drugs can destroy them. At the same time, bacteria are sown from a blood test.
- While microorganisms are in a dormant state, they can be detected by PCR - polymerase chain reaction. Usually this method is used to conduct additional examination. The method is very reliable - even single bacterial DNA can be detected.
- Serological analysis of blood does not emit bacteria, but antibodies to the pathogen of this type.
- In some cases, the baby gets Staphylococcus aureus in breast milk. In this case, he has a general intoxication - not only the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx becomes inflamed, but also digestion processes are disturbed, diarrhea appears, pustules form on the skin. If an infection is suspected during breastfeeding, pathogens are sown from breast milk. But since the baby is already infected, it is not required to switch to artificial nutrition. The mother and baby are given adequate treatment to correct the problem.
With an insignificant amount of bacteria or antibodies to them in the blood test and the normal well-being of the baby, it is not required to treat it.
How to treat Staphylococcus aureus throat
Symptoms of infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus are exactly the same as with any inflammatory process of the nasopharynx:
- swelling of the tonsils and redness;
- the appearance of purulent plaque of various types;
- pain that worsens when swallowing;
- an increase in regional lymph nodes.
A distinctive feature may be the addition of bacterial stomatitis - the appearance of pustules on the mucous membrane and an increase in temperature to 39-40 ° C. After identifying the pathogen, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, which must be drunk completely - even after the signs of inflammation disappear.
Most often, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Oflocacin;
- "Amoxiclav";
- Rifaximin;
- "Nafitsillin";
- Clindamidicin;
- "Neomycin";
- "Tetracycline";
- Vancomycin;
- "Kanamycin".
To reduce the temperature, antipyretic drugs are used, antihistamines must be complemented by treatment - to reduce swelling and weaken the side effects of antibiotics.
The therapeutic regimen necessarily includes local treatment - rinsing the throat and treating the oral cavity with antibacterial agents. From medical devices it is recommended:
- furacilin solution;
- Chlorhexedin;
- "Bioparox";
- Chlorophyllipt;
- gels and sprays containing lidocaine - for example, "Hexoran spray".
Treatment with painkillers helps to cope with a very difficult task - during the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat of a child it is quite difficult to feed him. Because of pain when swallowing, children often refuse to eat, become weak.
Although doctors do not advise to "shove" food into babies during acute periods, it is necessary to give water to a small patient at a high temperature, otherwise dehydration of the body quickly sets in. After treating the larynx with anesthetics, the sore throat and the gag reflex subsides, and it is possible to pour the liquid that he needs into the baby.
Additionally, immunomodulators and immunity stimulants, vitamin therapy are prescribed.
If the condition is extremely serious, the patient is admitted to a hospital.
Traditional medicine cannot cope with the infection completely, but it is possible to cure a small patient faster when using folk remedies. Inflamed tissues of the oral cavity are lubricated with sea buckthorn and rosehip oils, honey - if the baby is not allergic, irrigated with anti-inflammatory infusions - a decoction of chamomile, oak bark, sage, calendula.