Installation of metal structures on high-strength bolts. Recommendations for the supervision and technical operation of mounting joints on high-strength bolts of building structures. Assembly of joints on high-strength bolts, if necessary, complete disassembly of the joints
Chief Engineer of the Institute S.K. Kanevsky
A large number of welds of short length has become a serious obstacle to the mechanization and automation of welding processes at installation. Bolted mounting joints allow, under the conditions of the mounting site, to use hard-welded high strength steels in structures. Bolted connections allow you to work simultaneously on a large number of nodes by unskilled workers. The effectiveness of the use of bolted joints is formed at the design and manufacturing stage of the assembly units. According to the USSR Gosstroy, the estimated volume of the possible use of metal structures on bolts is 60 - 65% of the total steel produced by the industry building structures. However, due to the low technical equipment of a number of metalwork factories, poor design quality and a number of other reasons in the Soviet Union, only 15 - 20% of structures are manufactured with bolted mounting joints.
New materials are filled with plastic hollow spheres to achieve significantly lower densities and present a challenge for mixing and dosing tasks. In the process of increasing automation of modern applications, executed manually, there are special problems for mixing and automation of the material.
Lightweight construction due to application modern technology bonding. Moderation: Mark Biker, Hochschule Landshut, Light cluster, Landshut. The increasing number of different materials creates new problems. Only when the combination of parts from different materials into one component has been made compatible with materials, their beneficial properties can also be used to meet the increased requirements as much as possible. Industrial long-term bonding technologies, such as soldering, welding, riveting or screwing, have their limitations.
The constructions of objects of ferrous metallurgy in recent years (except for sheet ones) are mainly designed with joints on high-strength bolts).
When supervising mounting joints on high-strength bolts, special attention should be paid to the ultra-high-strength bolts supplied by the industry in the 1970s and 1980s. with a temporary resistance of 120, 135 and 155 kg / mm 2. Such bolts are installed in a number of designs of the Cherepovets, Lipetsk metallurgical plants, Magnitogorsk and others. These bolts due to the lack of restrictions on the upper limit of hardness have an increased ability to ZHR (delayed brittle fracture).
Conventional bonding methods have known disadvantages. In the case of thermal processes, such as welding, the material changes its specific properties in the heat-affected zone. Mechanical methods, such as rivets or screws, in turn, provide only point transmission of force; in addition, the holes must also be drilled into workpieces that need to be joined, thus “damaging” the material and, thus, the adhesive technology has an advantage over other joining technologies: this is a low-heat bonding process that does not change or not damages the fittings during the process.
The most dangerous period is the first 1 to 3 years after the start of operation. Bolts "shoot" without a visible application of external load. In all constructions of recent years, attention has been paid to ZHR.
Studies conducted at a number of facilities after years of operation have shown that the drop in bolt tension is negligible. But since in the process of performing installation work, a shortage of bolts is possible, then in the process of operating the structures, a selective check of the tension of the installed bolts is required. The control of bolted mounting joints is much simpler than that of welded joints, since in welded joints there is a greater likelihood of hidden weld defects than in bolted connections. The main way to control bolted connections is visual.
Thanks to bonding technology, all materials can be bonded to each other and to each other for a long time. Especially in light of the fact that the requirements for products from a technological, economic and environmental point of view are steadily growing, and as a result when new materials must be developed and combined with each other, there is a wide scope for adhesive technology, especially in the field of lightweight construction. This is also confirmed by the fact that, within the adhesive bond, the emerging stresses are distributed over the entire area, and thus thinner connectors can be used in the same load compared to other connection methods.
1. GENERAL PROVISIONS
1.1. These Recommendations were developed in accordance with Order No. 759 of 9.XII.1988 according to the USSR Ministry of Industry and Agreement No. P47-6882 concluded between the Central Scientific Research Institute of Steel Construction named after Melnikov Gosstroy of the USSR and the Cherepovets Iron and Steel Works of the Ministry of Industry of the USSR on April 19, 1989 and are the development of section 7 of the industry guidance document ORD 00 00089 “Technical operation steel structures industrial buildings. "
For this reason, adhesive technology in the field of lightweight construction is an integral part of the company and opens up new opportunities and opportunities. Robert Holzer, NDT Research Center, Linz. Non-destructive testing or unbrakable control opens up opportunities for quality assurance, process optimization, and the development or characterization of new materials and processing methods. Also in gluing and joining technology, which in turn is of great importance in the context of lightweight construction.
Tightening High Strength Bolts
The goal is to make these new opportunities available to industry. The manufacturing processes of today's automotive industry cover a wide range of applications. The use of various adhesive technologies includes, inter alia, installing roof hatches, door panels or dashboards for the interior of a vehicle. As a clear market trend and at the same time, innovative drivers are natural fiber reinforced plastics, in particular because of their good mechanical properties and low density, they can reduce weight and bring technical and environmental added value.
1.2. The recommendations cover oversight and technical operation metal structures of buildings and structures of ferrous metallurgy enterprises with connections on high-strength bolts, designed according to the standards of the USSR, operated in areas with an estimated temperature of -65 ° C.
1.3. When accepting structures with connections on high-strength bolts in the acceptance committee, the participation of a service representative is required technical supervision on the operation of buildings and structures of the enterprise.
Moisture cross-linking as well as non-reactive hot-melt adhesives based on polyolefins are characterized, inter alia, by excellent adhesion to low-energy substrates, high heat resistance, low density and without isocyanate. This young hot-melt adhesive technology represents a sustainable alternative to traditional adhesive systems and is already considered the future standard for various applications in the vehicle interior. Due to the production of surface contamination by oils, greases, and refrigerated lubricants, technological factors in a production technological environment increasingly influence factors that affect quality for the functionality of the final product.
1.4. Responsibility for technical condition mounting connections on high-strength bolts, the order for the workshop entrusts the engineering and technical workers of the workshop, who must undergo appropriate theoretical and practical training, are familiar with the rules for making connections on high-strength bolts and have a certificate (Appendix No. 7; 8).
Materials, products and conditions for their use
For example, high purification processes or compounds, such as painting, since even the smallest kinematic impurities lead to a deterioration in product quality. As for the use of components in an industrial environment, quality assurance in production should be decided in the context of technical cleanliness in the process chain before and after processing or accession processes. A preliminary test of technical purity is carried out here using an automated fluorescence laser scanner, and subsequent quality control is carried out using thermography with an active heat flux.
1.5. Direct inspection of installation connections and restoration (repair) should be carried out by specially trained specialists with the appropriate skills and certification. In hard-to-reach places at a height, examinations are carried out with the participation of climbers.
1.6. Specialists in the operation of buildings and structures participating directly in the survey must undergo appropriate training, have a certificate and permission to stay at their best.
Tightening high-strength bolts, with torque control
Lightweight designs in a layered design. Screw connections can carry high workloads and have the clear advantage of solubility. Like alternative joining technologies, further developments are taking place to become more efficient and simpler, for example, a lower ratio of weight to clamping force or even self-loading unit. In addition, the mixture of materials in a lightweight construction creates new problems for the design of the screw, since the classical methods of calculating the screw for connections with light materials are often already insufficient.
The number of specialists is determined at the rate of 1 engineering per 100 thousand high-strength bolts.
1.7. A feature of frictional joints on high-strength bolts is that the forces are perceived not by shear of bolts and crushing of the wall, but by frictional forces arising between the contacting surfaces pulled together by a high-strength bolt. In this regard, the magnitude of the tension of high-strength bolts and the quality of preparation of the friction surfaces of the connected elements is crucial and is controlled during the test. Insufficient tension of high-strength bolts in frictional joints can lead to “slipping” of the elements, while the bolts will work to shear, the elements to collapse. In addition, a geometric shape violation due to the mutual displacement of the elements is possible - the bolts will come into operation unevenly, since the difference in the diameters of the holes and bolts can reach 6 mm in accordance with SNiP III-18-75 table. 4 and there may be cases of successive failure of the bolts.
The lecture emphasizes the importance of this analytic-numerical relationship and shows examples in which expansion through modeling provides valuable new ideas for optimizing connections and working safety. An electric car is not possible without lightweight construction. Therefore, weight optimization is on the agenda of developers. Compared to a conventional metal structure, scientists were able to reduce axle weight by 37 percent, thereby reducing energy consumption. In addition, researchers are considering the possibility of using a fiber-composite material as a replacement for metal components in order to have a positive effect on the rigidity of the structure and dynamics of the vehicle with a skillful choice of fiber matrix properties.
1.8. The studies found that the decisive influence on the reliability of the bolts is exerted by the levels of their mechanical characteristics (temporary tensile strength, elongation and contraction, impact strength), determined by the heat treatment conditions.
The main of these characteristics is the temporary tensile strength, controlled by its upper limit. Excessively strong bolts (marked 135 and 155), which have increased hardness, are prone to delayed brittle fracture and require more careful monitoring and more frequent examination of the joint.
This creates complex, mechanically and three-dimensionally loaded structural elements that can replace realizable metal structures. The main advantages are significant weight loss, a high degree of integration and high quality. This technology allows you to create new system solutions in the industry - for example, for rings, trusses, pipes, heavily loaded parts, complex structural elements and three-dimensional parts of complex shape.
Connection Monitoring
Weight-optimized and supporting lightweight structures are used in almost all industries: aerospace and automotive industries, mechanical engineering and mechanical engineering, sports and leisure industries and wind energy, all of which require the use of lightweight materials and the development of lightweight construction. Aging processes, environmental impacts, as well as unforeseen events such as earthquakes, wind shocks, winds, bird strikes, etc. May damage structures and thereby jeopardize consequences and consequences.
2. MATERIALS, PRODUCTS AND CONDITIONS OF THEIR APPLICATION
2.1. To connect the elements of steel building structures, high-strength bolts, nuts and washers made in accordance with the requirements of GOST 22353-77 are used? 22356-77 or TU 14-4-1345-85 and bolts of normal strength according to GOST 1759-70 (Fig. 1).
2.2. According to GOST 22356-77, the bolts must have the brand of the manufacturer, as well as a marking showing the temporary resistance in kgf / mm 2, and the symbol of the melting number. Bolts of climatic modification of HL are in addition marked.
In the event that damage is detected, measures for mandatory repair or exchange of components can be initiated at an early stage to prevent a complete system failure and avoid indirect costs. Additive process for the production of industrial light construction.
Jörg Welnitz, Technical University Ingolstadt. Generative production processes continue on an increasingly broad path in the industrial world of production. On the one hand, an extremely high degree of freedom in design ignites the imagination of engineers, on the other hand, the presence of custom components in small batches is always a more desirable destination. Whereas in the past, generative manufacturing methods were used mainly for prototyping, testing, and visualization, which claim to be able to create functional components is growing immediately.
2.3. To control the mechanical properties of bolts, nuts and washers at the factory, 5 samples are taken from each batch for each type of test.
Bolts are tested for tearing, tensile specimens, determining toughness (CL), tearing on an oblique washer, determining the twisting coefficient and hardness.
2.4. High strength bolts, nuts and washers are supplied in batches consisting of parts of the same designation made of steel of the same heat, processed in one mode. The mass of a batch of bolts should not exceed 1000 kg, nuts and washers - 500 kg.
Documentation and qualification of products is a much more important role than in the prototype and sample. Almost all generative manufacturing processes, such as the classical method, as well, but have manufacturing approval. Especially with generative plastic components being manufactured, while the production and documentation of dimensional accuracy and dimensional stability of components is of great importance in addition to the microstructure. The presentation demonstrates the ability to implement an optimization chain for the production of dimensionally stable and functional components in the manufacturing process of additives using industrial computed tomography.
2.5. Each batch of hardware should be provided with a certificate stating:
Certificate Number name of the manufacturer; name, type and size of products; steel grade; batch number; heat number; test results; Net weight.
In addition, there is a need to be able to produce small batches with individual geometries of said original materials. The presentation will focus on the current capabilities and limitations of new manufacturing additive processes using original materials, compared to the classic snap-in template technology.
Selective laser metal melting with powder source material is an innovative manufacturing process for the manufacture of metal components of all kinds - but especially for the production of very complex geometries. Since the components are “from the bottom to the top”, it opens up completely new opportunities in the production of products. Of particular note is the creative freedom for the designer, which is significantly higher than other manufactures due to restrictions on access to cutting tools or the release of such a mold.
2.6. For structures with a design temperature below minus 40 ° C and up to minus 65 ° C, high-strength CL bolts should be used. On the head of these bolts there is a sign "CL".
2.7. The strength class of bolts of normal strength is indicated by two numbers. The first number, multiplied by 10, determines the value of the minimum tensile strength in kgf / mm 2, the second number, multiplied by 10, determines the ratio of the yield strength to tensile strength in percent. The product of numbers determines the yield strength. This type includes bolts marked 10.9; 8.8; 5.8 (Fig. 1).
B. from casting tools omitted. This allows you to integrate additional features into the component design and optimized lightweight with precisely adapted to the power characteristics of the wall thickness. realization of internal cavities and optimized loading of internal ribs of structures is also possible. This led to second generation duplex steels known for their improved properties such as mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. Cordless drills and battery drills are available for various applications with 12 or 18 volts. Accessories that have been available since January are fully functional in the system with new generators. The project began at the end of 70% of the total flow to the new technological technology for the production of ferrite. Today, a Swabian traditional company around the world is engaged in professional application solutions and high quality - not just for drilling. The new automatic bending machine with several hydraulic press brakes provides universal production of profiles with a wide range of different sizes. High demands on quality, technological problems, resource efficiency and price pressure are the dominant topics in engineering and engineering. Renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly important as a substitute for fossil and nuclear energy sources. The industrial leather industry is a complex business that must combine frequent model changes and increasingly shorter production times with quality and profitability. The maximum accuracy and efficiency of processing processes are a prerequisite for insisting on the market. The requirements for reliability and process performance of the machines used for this are correspondingly high. The requirements for the process and product quality in the production of cut openings are huge, their trend is increasing. The latest new acquisition under the auspices of the family business is a high-precision long-distance communication system. It shares a width of not more than 700 millimeters and stainless steel strips with a thickness of 0, 2 - 3, 0 mm. Thanks to its special design, the system is ideally suited for the gentle processing of high-quality or extremely sensitive tape surfaces. Using a flat, tool-free swivel machine, fillet welds on metal structures can be processed quickly and economically without damaging adjacent components, even at sharp angles. It is unlikely that any topic is currently being discussed as intensively as a way out of nuclear energy and the transition to renewable energy sources. At a time when Renewable Energy was still a big unknown to many. The facade of the skyscraper is particularly emphasized by a stainless steel frame. The 90 t drawing stand is based on an innovative concept that allows you to save energy and material when drawing steel rods. The second-generation family business has made a name for itself as a manufacturer of fastening systems, as well as a provider of metal processing services. Glamor, shine, palm trees. It is unlikely that any other city comes down to a stereotype as a Mecca of the rich and rich than Miami. Original, good building fabric should be used as little as possible for cost reasons. Stainless steel sheet metal processors, which are important for time and money, now rely on finished sheet metal workpieces. As a result of this, costly separation methods can be avoided, and furthermore, waste can be significantly minimized. Mozart, Haydn, Mahler, Strauss, Lehar or Franz von Suppe: in Austria there is music in the blood. The history of the country is characterized by musical diversity, which is unparalleled. The notorious Spanish serenity is in Madrid. Its particularly beautiful location directly on the Atlantic also places particularly high demands on the corrosion resistance of building fabric. After only 15 years, significant damage to concrete and reinforced concrete reinforcement occurred on the external walls and boom arrows due to salt air and swelling. For the necessary repairs, it is now necessary to ensure a service life of 100 years. Permissible loads for traction and diagonal traction, as well as transverse traction and diagonal traction, vary from 2, 0 to 25 kN and cover all the basic requirements of architects and planners. As one of the cultural and industrial centers of the old continent, Milan is a daily destination for thousands of tourists and business people from all over the world. When stainless steel profiles are used in external and internal architecture, for example, as facades or tile strips, they must be provided with self-adhesive films to protect their surfaces. With partially coated film, only visible surfaces of a later profile are protected very purposefully. Be round, oval or polygonal: each pipe, also in a small or medium series, is made of precise boards in accordance with individual customer requirements. The times when the facades of darkness caused a shadow death have long passed. Istanbul, the largest city in Turkey and the only metropolis in the world on two continents, looks back at the turbulent past. Quality made in Germany also in West Africa: for two new government buildings in the Nigerian capital Abuja, a Westfalia stainless steel specialist Moderson supplied brackets for facade cladding. Higher, more expensive, more impressive: the rules for successful construction in the highly dynamic cities of the Persian Gulf are unmistakable. Weaving in Duren is a world leading manufacturer of woven materials made of metals, plastics and fibers. A variety of decorative surface finishes makes stainless steel a fashionable material in designer architecture. The rolling cage is called a metal structure, which is usually installed on cars used in motorsport.
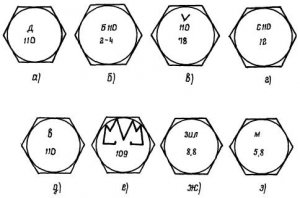
Fig. 1 Marking of bolts of various strength classes, including high-strength ones.
a. High-strength bolt of the Druzhkovsky plant; b. High-strength bolt of the Magnitogorsk plant; c. High-strength bolt of the Shchelkovo plant; D. High-strength bolt of the Voronezh plant; e. Bolt strength class 10.9 Magnitogorsk plant; g. Bolt strength class 8.8 Automobile them. Likhachev; h. Bolt strength class 5.8 Magnitogorsk plant.
For example, a bolt strength class of 5.8 indicates that the minimum tensile strength of the metal? c, from which the bolt is made, is 5 × 10 \u003d 50 kgf / mm 2, and the ratio of yield strength? t to temporary resistance? in percent it is equal 8? 10 \u003d 80%. The first number of marking, multiplied by the second, determines the yield strength
T \u003d 5? 8 \u003d 40 kgf / mm 2
2.8. High-strength bolts are marked 110, which indicates the minimum temporary resistance in kgf / mm 2 of the material of the bolt.
2.9. In the absence of bolts specified in the project, replacement of bolts of strength class 5.8 with bolts of 8.8 is permitted; 10.9 and high strength. Bolts 8.8 can be replaced by 10.9 and high strength. Bolts 10.9 - for high strength. Reverse replacement without appropriate recounting of structures is prohibited.
3. SUPERVISION OF THE CONDITION OF THE CONNECTIONS
3.1. Supervision of the condition of the connections is carried out by the workshop service for the technical operation of steel structures of industrial buildings through ongoing inspections.
3.2. Routine inspections of compounds are carried out selectively once every six months in flight converter, open-hearth and other shops, whose designs are subject to dynamic effects. In other workshops, departments and spans at least once a year.
Inspection of nodes on high-strength bolts, as a rule, is carried out in conjunction with the examination of steel building structures in the time provided by the ARD 00 000-89.
3.3. The condition of high-strength bolts and connected elements is monitored visually and consists in checking the presence of bolts in the nodes, as well as in randomly checking their tension and safety (absence of cracks, gusts) of the connected elements. The bolts are checked in accordance with table. 3 in every tenth node (10% of nodes). Subsequent checks verify previously unverified nodes.
Particular attention should be paid to the identification of defects in accordance with table. 1.
|
Defect name |
Remedy |
||
|
non-emergency |
emergency * |
||
|
No bolts less than 10% in the joint |
More than 10% of bolts in the connection are missing |
Install new bolts, tighten the design effort with a control wrench |
|
|
Less than 10% of bolts are not tightened on design effort |
More than 10% of bolts are not tightened on design effort |
Retighten bolts with a control key |
|
|
When controlling tension, bolts with nuts turn |
Install new bolts. Tighten the bolts to the design effort with a control wrench |
||
|
Probe 0.3 mm passes into the gap between the connected elements |
Check the tension of the bolts in the assembly. Tighten bolts to design effort. Paint joints along the contour |
||
|
Cracks in the body of less than 10% of bolts, nuts or washers in the joint |
Cracks in the body of more than 10% of bolts, nuts or washers in the joint |
Replace damaged bolts, nuts, or washers. Tighten the bolts to the design effort with a control key |
|
|
Crack in connectable structures detected |
Strengthen or replace an element in accordance with the decision of the authors of the project |
||
3.4. In case of defect detection emergencywhen more than 10% of the bolts are loosened in the joint, defects are detected or more than 10% of the bolts are missing, cracks or gusts in the connected structures are detected, immediate measures must be taken to eliminate them.
3.5. In the first two to three years of operation of buildings or structures, a selective instrumental check is carried out in accordance with Section 4, in order to identify possible defects made during installation work.
Table 1
List of possible defects in joints with high-strength bolts
* - The emergency nature of the defect is determined conditionally, the final decision on the nature of the influence of the defect on the bearing capacity and integrity of the structures is determined by the author of the project.
3.6. In the process of instrumental testing, the tension of the bolts is controlled (table. 2).
3.7. Bolt tension control is carried out at the time of tightening with torque wrenches. The tightening torque applied to the nut or bolt head must be at least the value indicated in the table. 2.
3.8. The results of checking joints on high-strength bolts are recorded in the log of technical inspections of joints, if necessary, the outer surfaces of the joints are primed with the most common soil GF-020, FL-03K or others that do not contain oil.
3.9. Work to eliminate defects associated with the installation of new bolts is carried out in accordance with the technological process of assembling joints on high-strength bolts (section 4).
3.10. If it is necessary to check the quality of surface preparation or to determine the strength class of bolts and study working drawings, one should be guided by the documents (Appendix 3) stored at the factory with the certificate of completion of the structures.
3.11. When checking mounting connections on bolts, particular attention should be paid to the following components:
(Appendix 9)
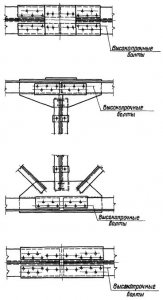
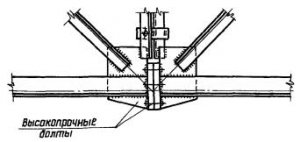
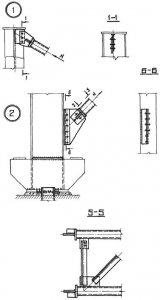
Mounting points for ties in columns (for bolts); fig. 5, 7 (nodes 1, 2, 3, 5);
Attachment points for crane beams (for bolts and possible loosening of their tension) fig. 6, fig. 7 (node \u200b\u200b6);
Knots of PPF (crane-girder trusses), truss and truss trusses of large spans (the presence of bolts and selective control of their tension) Fig. 12;
Knots of beam cells (the presence of bolts and selective control of their tension), Fig. 3;
Joint of columns (presence of bolts and selective control of their tension), fig. 4.
3.12. If it is necessary to establish the causes of defects and develop measures to eliminate them, as well as to examine compounds, specialists of research and design organizations may be contracted.
4. TECHNOLOGY OF RESTORING THE CONNECTION
The restoration of joints on high-strength bolts and their acceptance should be carried out under the direction of the person designated as responsible for the implementation of this type of joints by order of the organization performing these works.
To make connections on high-strength bolts, personnel who have undergone appropriate training and have a certificate of admission to these works are allowed.
Technological process making connections on high-strength bolts when restoring nodes without completely disassembling them includes the following operations:
Preparation of high-strength bolts, nuts and washers;
Assembly of connections;
Tension;
Acceptance and sealing of joints.
The resulting bolts must have a marking showing the temporary resistance in kgf / mm 2 and the brand of the manufacturer.
Each batch of bolts must be equipped with a certificate stating:
Certificate Number
Name of the manufacturer;
Product designation with symbol melting and batch numbers;
Test results;
Spin factors;
Net weight.
4.1. Preparation of high strength bolts, nuts and washers
4.1.1. The technological process for the preparation of hardware includes de-preservation, cleaning of dirt and rust, threading of discarded bolts and nuts, and lubrication.
4.1.2. There are two ways to handle hardware. Hardware in lattice containers (for small volumes - in a bucket with punched holes); in a clean barrel, water is boiled, if possible, with a washing solution or household washing powder. A bucket is dipped in water and boiled for 10 - 15 minutes. After that, when the water merges, the hardware is lowered for 1 - 2 minutes into a container with a mixture of gasoline (85%) and mineral oil of the Avtol type (15%), then removed. From heated hardware, gasoline quickly evaporates, and oil in the form of a thin film remains on the surface. This method provides equalization of the coefficient of twist to 0.18.
4.1.3. A reduction in the coefficient of twisting to 0.12 and its stabilization is done by waxing the nuts. After cleaning the hardware using the aforementioned technology, only nuts are lowered into the bath with molten paraffin (they are kept for 10-15 minutes), the nuts are removed and allowed to drain excess paraffin and cooled to ambient temperature.
4.2. Assembly of joints on high-strength bolts, if necessary, complete disassembly of joints
If it is necessary to completely disassemble the connections, the design load should be removed according to a specially developed project and the unit restored using the following technology:
4.2.1. The assembly assembly process includes:
Inspection of structures and verification of their compliance with the requirements of the project and chapter SNiP III-18-75 (in terms of accuracy of manufacturing structures);
Alignment of holes and fixing in the design position of the elements and parts of the connection using mounting plugs (10% of the number of holes, but not less than 2 pcs.);
Installation of high-strength bolts in plug-free holes;
Checking the geometric dimensions of assembled structures;
Tight screed package;
The tension of the delivered high-strength bolts to the force provided by the project;
Removing plugs, placing high-strength bolts in the released holes and tensioning them to the design effort.
4.2.2. The difference in the thicknesses of the elements overlapped by the overlays, determined before setting the overlays with a ruler and probe, shall not exceed 0.5 mm.
4.2.3. When the difference in the planes of the parts to be joined is from 0.5 to 3 mm, to ensure a smooth bending of the lining, the edge of the protruding part must be smoothed with an emery stone at a distance of up to 30 mm from the edge of the part, with a slope not steeper than 1:10. In case of a plane difference of more than 3 mm, gaskets should be used. The use of gaskets must be agreed with the design organization.
4.2.4. The lengths of the bolts used are selected depending on the thickness of the bag (Appendix 2).
4.2.5. When drilling holes in elements with machined surfaces, coolants containing oil should not be used.
4.2.6. The assembly of joints should be carried out immediately on high-strength bolts and plugs. The use of other bolts as assembly is prohibited.
4.2.7. Each bolt is installed in connection with two high-strength washers (one is placed under the head of the bolt, the other under the nut).
4.2.8. Nuts tightened to the design effort are not further secured.
4.2.9. At the time of installation of high-strength bolts, the nuts should turn freely (by hand) on the thread. Otherwise, the nut or bolt should be replaced, and the rejected bolts and nuts should be sent for re-training.
4.3. Tightening high-strength bolts, with torque control
4.3.1. The specified method is based on measuring the twisting moment applied to the nut or bolt head when the design axial force is reached in the bolt shaft. The required value of the twisting moment is determined by the formula
M \u003d P · d · K,
where P is a given bolt tension force, kgf;
d is the nominal diameter of the bolt, m;
K is the twisting coefficient, taken equal to 0.18 for all types of bolts supplied in accordance with GOST 22353-77 - GOST 22356-77 and processed according to the proposed technology in clause 3.1.3 and equal to 0.12 when processing in accordance with clause 3.1.3. The twisting coefficient for the certificate is not taken into account in the calculations.
4.3.2. With the number of bolts in the assembly up to 10 - 15 pcs. and in hard-to-reach places, the tension of the bolts is allowed to be performed with torque wrenches in one go (dash key. Appendix 6).
4.3.3. The tightening torque transmitted by the key should be recorded while the key is moving in a direction that increases tension. Tighten smoothly without jerking.
4.3.4. Torque wrenches must be numbered and calibrated.
Keys can be made either at a specialized factory or on their own. Calibration should be carried out at the beginning of the shift.
4.3.5. The deviation of the actual tightening torque from the calculated one should not exceed 20%.
4.3.6. Shortage of bolts is prohibited.
table 2
4.4. Torque wrench calibration
4.4.1. Torque wrenches are calibrated by hanging a specified amount of cargo to the handle of the wrench or using special calibration stands.
4.4.2. According to the first method, calibration should be performed in the following order:
hang a torque wrench on a hexagonal mandrel or on a tightened high-strength bolt so that its handle occupies a horizontal position (Fig. 2). At a fixed point on the end of the key, hang a weight of P (kg)
![]()
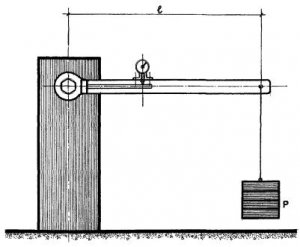
Fig. 2 Calibration torque wrenches
where l - the distance from the center of gravity of the load to the axis of the mandrel or bolt;
M s - estimated torque;
M s - the moment of twisting of the mass of the key, equal to the product of the mass of the key at a distance from its center of gravity to the axis of the mandrel or bolt.
When the load is suspended, the countdown is taken on the key registering device. Repeat the measurement 2 to 3 times until a stable result is obtained. Log calibration results.
4.5. Acceptance and sealing of joints subject to complete disassembly
4.5.1. Regardless of the method of tension, the controller should first of all conduct an external inspection of all supplied high-strength bolts and make sure that all bolts are marked, all washers are placed under all heads and nuts; the parts of the bolts protruding beyond the nut have at least one thread turn over the nut and two under the nut; on the assembled unit there is a stamp of the team that performed these works (Fig. 3).
4.5.2. The number of bolts in the assembly to be monitored is indicated in the table. 3.
Table 3
4.5.3. If the results of the control do not meet the requirements of clause 3.5.1, for at least one bolt, a double number of bolts is controlled. If, in this case, a defective bolt is detected, all the bolts of this connection are monitored.

4.5.4. The control results, regardless of the method of tension, should be entered in a special journal (Appendix No. 1).
4.5.5. Responsibility for the quality of the bolts is the manufacturer of the work.
4.5.6. The density of the package tie is checked with a 0.3 mm thick probe against the tightened bolt in the area bounded by the washer. The probe should not pass between the assembled parts into the area bounded by the washer (hereinafter formed washer).
4.5.7. On each connection, as a rule, the core is stamped with the team that performed the connection and the person who made the control. The stigma number is assigned by order of the unit performing the connections. If the bolts are prepared by waxing, the letter “P” is placed next to the stigma.
4.5.8. After accepting the connection by the controller, all joints along the contour should be primed. If there is no primer mark in the project design, the use of primers FL-03K, GF-021 with the addition of dry pigment to a consistency that excludes the primer from flowing inside the package is allowed.
4.5.9. The tool for tightening bolts and preparing surfaces is adopted in accordance with the “Guidelines for the use of a tool kit for setting high-strength bolts”. MMSS USSR Moscow 1985 (Appendix No. 10).
4.6. Bolt tension on the angle of rotation of the nut
4.6.1. For small volumes of work, the adjustment of the tension of the bolts by the angle of rotation of the nut can be performed with a hand tool for bolts with a diameter of 20, 22 and 24 mm, with a thickness of the bag up to 140 mm and the number of bodies in the bag up to 7.
4.6.2. The tension of the bolts is carried out in the following order:
Tighten all installed bolts to failure with a wrench with a handle length of 300 mm; (Starting position);
Risks are applied to nuts and protruding parts of bolts with paint or chalk;
Nuts tightened to the initial position of the bolts are rotated through an angle of 180 ° ± 30 °;
Tensioning can be done with any available wrench.
4.6.3. Tension control is performed only at the time of twisting.

TIGHTEN THE BOLT UNLOCKING WITH A KEY WITH HANDLE LENGTH 0.3 m. GUIDANCE ONLY ~ 20 kg · m.

EXPOSURE RISKS TO THE SPEED OF THE BOLT AND THE NUT. INSTALL A KEY WITH HANDLE 1.8 M LENGTH IN THE ORIGINAL POSITION.
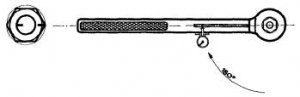
Gently rotate the NUT WRENCH with a 180? WRENCH, MONITORING THE TURN ANGLE ON THE RISK MOVEMENT ON THE NUT.
Fig. 4 Tighten the bolts along the angle of rotation of the nut
5. TECHNOLOGY OF RESTORING INSTALLATION COMPOUNDS OF METAL STRUCTURES PERFORMED ON RIVETS, FEATURES OF PERFORMANCE OF BOLT-RIPPED COMPOUNDS
5.1. Bolt-riveted joints are not an independent type of mounting joints, but are introduced in the process of replacing defective rivets with high-strength bolts during repair or in order to increase the endurance of joints of riveted steel building structures.
5.2. The diameters of high-strength bolts should be taken according to the table. 4.
Table 4
5.3. When replacing defective rivets, it is unacceptable to create such mixed bolt joints in which the bolts are located only on one side of the longitudinal axis of symmetry of the structural element. Therefore, at the same time as defective ones, it is necessary to replace symmetrically located non-defective rivets.
5.4. Removing the rivet heads and knocking out the rod is performed in the following sequence (Fig. 5):
Mutually perpendicular slots are made on the rivet head to be removed, with a quadrangle being formed in the center of the head of a diagonal smaller than the diameter of the rod. The depth of the slot is less than the height of the head by 1 - 2 mm;
After the formation of slots on the rivet head, the rod, together with a part of the head in the form of a quadrangle, is knocked out of the opening of the packet.
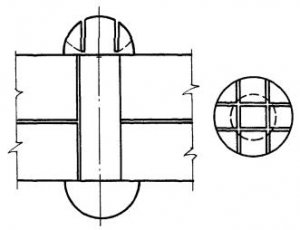
Fig. 5 Rivet removal method
5.5. The rivet rods are knocked out with heat-treated (40 - 45 units) conical mandrels with a diameter of 0.5 mm less than the diameter of the holes.
5.6. Removable rivets should be dispersed across the joint field. The simultaneous removal of two or more adjacent rivets is prohibited. There must be at least two rivets between the holes (these include high-strength bolts that are tightened to the design force).
5.7. If there are burrs, the holes are cleaned with a drill with a diameter equal to the diameter of the rivets. When drilling holes, coolants must not be used.
5.8. The burrs around the holes are removed with an emery stone attached to the shaft of a pneumatic or electric machine.
5.9. Preparation of high-strength bolts, their installation in the structure and tension should be performed, as with the device friction joints.
5.10. Other rivet removal methods are allowed to ensure structural integrity and their fixation when replacing rivets with bolts.
Annex 1
INSPECTION MAGAZINE
metalwork joints on high-strength bolts
Appendix 2
Bolt lengths depending on the thickness of the bag being pulled together
|
Bolt length mm |
The thickness of the package in the connection on high-strength bolts with a diameter, mm |
||||||||
Appendix 3
LIST OF DOCUMENTS PRESENTED AT DELIVERY OF MOUNTED METAL STRUCTURES WITH CONNECTIONS ON HIGH-STRENGTH BOLTS (INTERMEDIATE RECEPTION)
1. The certificate of acceptance of metal structures.
2. Journal of installation work.
3. The magazine staging high-strength bolts.
4. Calibration log of wrenches and torque wrenches.
5. The journal for the preparation of high-strength bolts (or an entry in the journal for the production of high-strength bolts) about the methods for preparing hardware with an indication of the adopted twisting coefficient.
6. A copy of the order of the installation organization on the appointment of responsible performers for making connections on high-strength bolts and controllers, indicating the number of brands assigned to performers and controllers.
7. A set of drawings of KM with all corrections and changes made by the design organization.
8. A set of KMD drawings with the stamp “Executive Drawing” and the signature of the chief engineer of the mounting organization.
9. Certificate for completed metalwork.
10. A copy of the certificate for high-strength bolts, nuts and washers.
Appendix 4
LIST OF TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION OF THE OPERATIONAL PERIOD
1. Act of technical change.
2. Certificates for structures, bolts, welding consumables, etc.
3. Executive drawings KM and KMD.
5. The log of inspections of metal structures on high-strength bolts (Appendix 1).
Appendix 5
LIST OF MATERIALS, TOOLS AND ACCESSORIES REQUIRED WHEN CHECKING THE CONDITION OF MOUNTING CONNECTIONS ON HIGH-STRENGTH BOLTS
1. Torque wrench KTR-3 with a set of control loads weighing 10 - 20 kg in an amount of 3 - 6 pieces.
2. A set of probes (0.1 mm; 0.3 mm; 1 mm).
3. Chisel, sledgehammer.
4. A hacksaw for metal with blades (to replace defective rivets) or a grinder.
5. Assembly mandrels.
6. A control hammer of 0.3 - 0.4 kg with a handle of 600 mm.
7. A set of mounting keys.
8. A set of bolts with nuts and washers.
9. Lattice containers and containers for the preparation of hardware.
10. Brush, paint.
11. The binoculars.
12. Magnifying glass.
13. Safety belt.
14. Protective helmet.
15. Overalls.
Appendix 6
![]()
Torque wrench KTR-3 (control)
1 - lever head; 2 - bar; 3 - tongue welded to the bar; 4 - handle; 5 - bracket for mounting the indicator; 6 - indicator of the sentry type ICh-10 GOST 577-60.
Note
Lever pos. No. 1 may be made of steel of grades: 09G2S; 10G2S1D; 13x SND; 14G2. All items are shown in table 1.
Welding assembly drawing
Table 1
Certification
|
Designation |
Name |
|||||
|
Welding assembly |
||||||
|
Key lever |
||||||
|
Boss 40? 20? 20 |
||||||
|
M6 bolt? 14 with a washer |
GOST 7798-62 |
|||||
|
Indicator 0 - 10 mm |
||||||
|
Bracket |
||||||
|
M6 bolt? 25 with nut |
GOST 7798-62 |
|||||
|
Sleeve? 12? 6 under the screw M6 |
||||||
|
GOST 1490-62 |
||||||
|
End nozzle |
||||||
Notes:
The length of the nozzle, depending on the height of the protruding parts of the connected elements, is allowed within l \u003d 100? 250 mm
2. Heat treatment:
Hardening, vacation up to 30 ~ 40 units. HRC
End nozzle pos. eleven
Appendix 7
SAMPLE IDENTIFICATION
Certificate No. 336
Issued to KISELEV, Ivan Petrovich
Profession: Overseer Engineer
Passed a TRAINING on surface preparation, control and installation of high-strength bolts in a 40-hour program.
M.P. Deputy chief engineer
combine (Petrov)
Appendix 8
AN EXAMPLE 40 HOUR TRAINING PROGRAM
1. Types of joints of steel structures, features of the work of shear-resistant joints on high-strength bolts - 3 hours.
2. Materials, products, conditions for their use - 3 hours.
3. The technology of connection with high-strength bolts
theoretical classes - 10 hours
practical exercises - 12 hours
4. Tools and fixtures - 3 hours.
5. Acceptance and sealing of joints - 2 hours.
6. Technical executive documentation - 2 hours.
7. Safety measures - 5 hours.
Appendix 9
Mounting joint of trusses on high-strength bolts
Flange connection of the lower belt of trusses

Vyborg Electric Power Plant
Pneumatic drives of metal brushes
Konakovo Power Tool Plant
Noginsky experimental assembly plant
II. TOOL FOR TENSIONING HIGH STRENGTH BOLTS
|
Name |
Ultimate moment kgf · m |
Manufacturing plant |
||
|
Pneumatic Wrenches |
Sverdlovsk P / O "Pneumostroy machine" of the USSR Ministry of construction and economy |
|||
|
Electric Wrenches |
Rostov P / O "Power Tools" of the USSR Ministry of Construction and Economy |
|||
|
Vyborg Electric Tool Plant of the USSR Ministry of Construction and Construction |
||||
|
Manual control key |
Kropotkinsk plant of installation and special construction equipment of the Heads of the SCP of the USSR Ministry of Construction and Special Construction |
III. CONTROL TOOL FOR TARGING THE WRENCHES AND DETERMINING THE TURNING COEFFICIENT OF HIGH-STRENGTH BOLTS
Appendix 11
HIGH-STRENGTH BOLT MANUFACTURING PLANTS
1. Hardware and metallurgical plant.
455031, Magnitogorsk, Chelyabinsk Region releases bolts M16 M20 and M24.
2. Druzhkovsky hardware plant
343260, Druzhkovka, Donetsk region, st. Lenin, 3 releases bolts M22, M24, M27
3. Plant of bridge metal structures. E.F. Kozhevnikova
670007, Ulan-Ude produces M22 bolts
4. Voronezh bridge factory
voronezh, 2nd Post Office produces bolts M22 and M24
5. Schelkovsky factory of special installation products “Special installation product”
141100, the city of Schelkovo-2, Moscow region releases bolts M20, M22 and M24
|
1. General Provisions. 2 2. Materials, products and conditions for their use. 3 3. Monitoring the status of connections. 4 4. Connection recovery technology. 6 4.1. Preparation of high strength bolts, nuts and washers. 6 4.2. Assembly of joints on high-strength bolts if necessary, complete disassembly of joints. 7 4.3. Tensioning of high-strength bolts, with adjustment of efforts at the moment of twisting. 7 4.4. Calibration of torque wrenches. 8 4.5. Acceptance and sealing of joints subject to complete disassembly. 9 4.6. Bolt tension in the angle of rotation of the nut. 10 5. Technology for the restoration of mounting joints of metal structures made on rivets, especially the performance of bolt-riveted joints. eleven Appendix 1. The log of inspections of metal structures on high-strength bolts. 12 Appendix 2. The length of the bolts depending on the thickness of the pulled package. 12 Appendix 3. List of documents required for delivery of assembled metal structures with connection on high-strength bolts (intermediate acceptance) 12 Appendix 4. The list of technical documentation for the operational period. thirteen Appendix 5. The list of materials, tools and devices necessary for checking the condition of mounting joints on high-strength bolts. thirteen Appendix 6. Working drawings of the key KTR-3. thirteen Appendix 7. Sample certificate. fifteen Appendix 8. Approximate 40-hour training program. 16 Appendix 9. The use of high-strength bolts in standard designs of industrial buildings. 17 Appendix 10. Tool for cleaning surfaces of friction joints. Tool for tensioning high strength bolts. A control tool for calibrating wrenches and determining the twisting coefficient of high-strength bolts. 24 Appendix 11. Manufacturers of high-strength bolts. 25 |
ON SUPERVISION AND TECHNICAL OPERATION OF MOUNTING CONNECTIONS ON HIGH-STRENGTH BOLTS OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION STRUCTURES OF BUILDINGS AND STRUCTURES OF THE USSR MINISTRY OF METALLURGY
Moscow, 1989
1. GENERAL PROVISIONS
2. MATERIALS, PRODUCTS AND CONDITIONS OF THEIR APPLICATION
3. SUPERVISION OF THE CONDITION OF THE CONNECTIONS
4. CONNECTION TECHNOLOGY
4.1. Preparation of high strength bolts, nuts and washers
4.2. Assembly of joints on high-strength bolts, if necessary, complete disassembly of joints
4.3. Tightening high-strength bolts, with torque control
4.4. Torque wrench calibration
4.5. Acceptance and sealing of joints subject to complete disassembly
4.6. Bolt tension on the angle of rotation of the nut
5. the technology of RESTORATION OF INSTALLATION COMPOUNDS OF METAL STRUCTURES RUNNED ON RIVETS. FEATURES OF CARRYING OUT THE BOLT-RIVET COMPOUNDS
Appendix 1 The log of inspections of metal structures on high-strength bolts
Appendix 2 Bolt lengths depending on the thickness of the bag being pulled together
Appendix 3 LIST OF DOCUMENTS PRESENTED AT DELIVERY OF MOUNTED METAL CONSTRUCTIONS WITH CONNECTIONS ON HIGH-STRENGTH BOLTS (INTERMEDIATE ACCEPTANCE)
Appendix 4 LIST tECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION OPERATING PERIOD.
Appendix 5 LIST OF MATERIALS, TOOLS AND ACCESSORIES REQUIRED WHEN CHECKING THE CONDITION OF MOUNTING CONNECTIONS ON HIGH-STRENGTH BOLTS
Appendix 6 Working drawings of the key KTR-3
Annex 7 SAMPLE IDENTIFICATION
Appendix No. 8 EXAMPLE 40-HOUR TRAINING PROGRAM
Appendix 9 Application of high-strength bolts in standard designs industrial buildings
Appendices 10 Tool for cleaning surfaces of friction joints. Tool for tensioning high strength bolts. A control tool for calibrating wrenches and determining the twisting coefficient of high-strength bolts.
Appendix 11 PLANT MANUFACTURERS OF HIGH-STRENGTH BOLTS
In recent years, significant changes have occurred in the design and installation of metal structures. In addition to the use of new rolled profiles, high-strength steels and improved calculation, there has been a tendency to increase the volume of metal structures with mounting joints on bolts of various strength classes, including high-strength ones.
A large number of welds of short length has become a serious obstacle to mechanization and automation, welding processes at installation. Bolted mounting joints allow, under the conditions of the mounting site, to use hard-welded high strength steels in structures. Bolted connections allow you to work simultaneously on a large number of nodes by unskilled workers. The effectiveness of the use of bolted joints is formed at the design and manufacturing stage of the assembly units. According to the Gosstroy of the USSR, the estimated volume of the possible use of metal structures on bolts is 60-65% of the total volume of steel building structures manufactured by the industry. However, due to the low technical equipment of a number of metalwork factories, poor design quality, and a number of other reasons in the Soviet Union, only 15-20% of structures are manufactured with bolted mounting joints.
The constructions of objects of ferrous metallurgy in recent years (except for sheet ones) are mainly designed with connections on high-strength bolts.
When supervising mounting joints on high-strength bolts, particular attention should be paid to the ultra-high-strength bolts supplied by the industry in 1970-80. with a temporary resistance of 120, 135 and 155 kg / mm 2. Such bolts are installed in a number of designs of the Cherepovets, Lipetsk metallurgical plants, Magnitogorsk and others. These bolts due to the lack of restrictions on the upper limit of hardness have an increased ability to ZHR (delayed brittle fracture).
The most dangerous period is the first 1-3 years after the start of operation. Bolts "shoot" without a visible external load. In all constructions of recent years, attention has been paid to ZHR.
Studies conducted at a number of facilities after years of operation have shown that the drop in bolt tension is negligible. But since in the process of performing installation work, a shortage of bolts is possible, then in the process of operating structures, a selective check of the tension of the installed bolts is required. The control of bolted mounting joints is much simpler than that of welded joints, since in welded joints there is a greater likelihood of hidden weld defects than in bolted joints. The main way to control bolted connections is visual.
1. GENERAL PROVISIONS
1.1. These Recommendations were developed in accordance with Order III 759 of 9.XII.1988, according to the USSR Ministry of Industry and Agreement No. P47-6882, concluded between the Central Research Institute of Steel Project named after Melnikov Gosstroy of the USSR and the Cherepovets Iron and Steel Works of the Ministry of Industry of the USSR on April 19, 1989 and are the development of section 7 of the industry guidance document ORD 00 00089 "Technical operation of steel structures of industrial buildings".
1.2. The recommendations apply to the supervision and technical operation of the metal structures of buildings and structures of ferrous metallurgy enterprises with connections on high-strength bolts designed according to the standards of the USSR, operated in areas with a design temperature of -65 ° С.
1.3. When accepting structures with connections on high-strength bolts in the acceptance commission, the participation of a representative of the technical supervision service for the operation of buildings and structures of the enterprise is mandatory.
1.4. Responsibility for the technical condition of mounting joints on high-strength bolts by the order of the workshop rests with the engineering and technical workers of the workshop, who must undergo appropriate theoretical and practical training, are familiar with the rules for making connections on high-strength bolts and have a certificate (Appendices No. 7; 8).
1.5. Direct inspection of installation connections and restoration (repair) should be carried out by specially trained specialists with the appropriate skills and certification. In hard-to-reach places at a height, examinations are carried out with the participation of climbers.
1.6. Specialists in the operation of buildings and structures participating directly in the survey must undergo appropriate training, have a certificate and permission to stay at their best.
The number of specialists is determined at the rate of 1 engineering per 100 thousand high-strength bolts.
1.7. A feature of friction joints on high-strength bolts is that the forces are perceived not by shear of bolts and crushing of the wall, but by friction forces arising between the contacting surfaces, tightened by a high-strength bolt. In this regard, the magnitude of the tension of high-strength bolts and the quality of preparation of the friction surfaces of the connected elements is crucial and is controlled during the test. Insufficient tension of high-strength bolts in friction joints can lead to “slipping” of the elements, while the bolts will work for shearing, the elements for shearing. In addition, a geometric shape violation due to the mutual displacement of the elements is possible - the bolts will come into operation unevenly, since the difference in the diameters of the holes and bolts can reach 6 mm in accordance with SNiP III-18-75 table. 4 and there may be cases of successive failure of the bolts.
1.8. The studies found that the decisive influence on the reliability of the bolts is exerted by the levels of their mechanical characteristics (temporary tensile strength, elongation and contraction, impact strength), determined by the heat treatment conditions.
The main of these characteristics is the temporary tensile strength, controlled by its upper limit. Excessively strong bolts (marked 135 and 155), which have increased hardness, are prone to delayed brittle fracture and require more careful monitoring and more frequent examination of the compound.