Tension force of high strength bolts. High strength bolts
Bolt tightening torque - this is the force that is applied to the nut when screwing it onto the threaded rod of the bolt. It is very important to calculate it correctly. If it is too small, then the impact of the loads will lead to unscrewing the nut. With a strong tightening, the destruction of the hardware and, accordingly, the entire structure will occur.
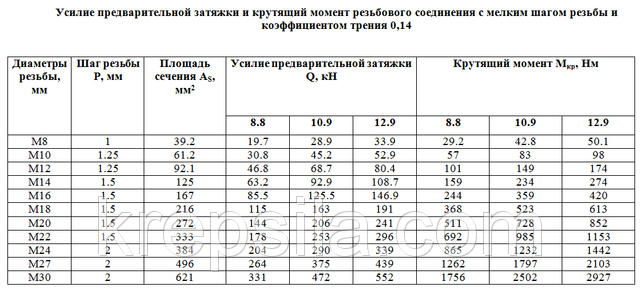
Nowadays, the torque values \u200b\u200bfor threaded steels are calculated and listed in various reference books. To facilitate your search, the following tables provide reference values \u200b\u200bfor torque and preliminary tightening forces for high-strength bolts with normal (large) and small thread pitch.
Exist two bolt tightening methods:
1. Uncontrolled- this method uses equipment or operations in which the forces applied to the fasteners cannot be measured. The load acting on the mount is ensured with a hammer and a wrench.
2. Controlled tightening method - it is ensured through the use of calibrated and / or measured equipment, compliance with prescribed operations. This method can be implemented in two ways:
- Tightening with a torque tool - the load on the mounting pair is achieved using the controlled use of the tool.
- Bolt tension - the necessary load on the fasteners is achieved by tensioning the bolt in the axial direction using special tools.
The controlled tightening method has several advantages over uncontrolled:
- the use of tools to allow the use of more significant efforts without fear of destruction of the fasteners.2) load uniformity- the uniformity of the forces is very important for nodes in which gaskets are used, since they require uniform compression.
3) Work safety- the use of tools allows to reduce the risk of injuries, as workers must have appropriate training before working with equipment.
4) Increase productivity- the execution time of the puff using the tool is much shorter than by hand, respectively, fatigue of workers decreases and productivity increases.
5) Achieving the desired result the first time.
1.126. Fire processing is allowed with a metal thickness of at least 5 mm.
Overheating of metal during firing is not allowed.
After firing, lagging scale and combustion products (slag) must be removed.
Until the joints are fully fixed with high-strength bolts, they should be protected from oil and, as a rule, moisture.
From surfaces to be treated steel brushes, you must first remove the grease. The surface condition after processing and before assembly should be monitored.
1.127. The difference in surfaces (deplanation) of the parts to be joined must not exceed 0.5 mm. The magnitude of the difference is determined before the installation of parts that overlap the connection, using a ruler and probe in the area of \u200b\u200bthe first row of holes from the junction.
In the event of a difference in the planes of the joined parts from 0.5 to 3 mm, a bevel with a slope of 1:10 should be made on the protruding part. Oblique formation by oxygen and air arc cutting is prohibited.
For differences exceeding 3 mm, it is necessary to use gaskets made of steel of the same grade as structures processed on both sides in the same way that the details of the connection were processed.
1.128. The assembly of joints on high-strength bolts should be carried out immediately on permanent bolts with the installation of plugs in the amount of 10% of the number of holes. The installation of temporary bolts is prohibited.
1.129. Assemblers engaged in setting high-strength bolts must have a certificate of admission to work on making connections on high-strength bolts.
1.130. High strength bolts, nuts and washers must be cleaned from dirt, preserving lubricant and prepared in such a way that standard values \u200b\u200bof twisting coefficients are ensured during tension and contact surfaces are not contaminated when tensioned.
1.131. The bolt tension specified by the project should be ensured by tightening the nut with a torque wrench to the rated torque, or by turning the nut through a certain angle according to special instructions. Torque wrenches for tensioning high-strength bolts, incorporating a hydraulic or mechanical device, must be calibrated 2 times per shift (before and in the middle of the shift).
1.132. The order of tension of high-strength bolts in the joints should exclude the formation of leaks in tightened bags.
1.133. The magnitude of the torque (MKR) required for tensioning high-strength bolts is determined by the formula
where k is the twisting coefficient established by the standards or specifications for the bolts;
P is a given bolt tension force;
d is the nominal diameter of the bolt.
The deviation of the actual torque from the moment determined by the formula (1) should not exceed 0; + 20%.
1.134. Heat-treated washers must be placed under the heads and nuts of high-strength bolts - one washer for each head and nut.
1.135. Nuts that are tightened to a torque determined in accordance with the requirements of Clause 1.133 of this chapter, or by turning a certain angle, are not additionally fixed.
1.136. In joints in which the project, along with the installation of high-strength bolts, provides for the welding of parts by roller seams, welding should be done after setting all the high-strength bolts and tightening them to a given force.
After welding, it is necessary to carry out a control check of the tension of all high-strength bolts.
1.137. After the final tightening of all bolts in the joint to the specified force, the assembler must affix the number or sign assigned to him in the intended place.
1.138. The tension of the bolts should be controlled by spot checking: with the number of bolts in the connection up to 5 pcs. 100% of bolts are controlled, with the number of bolts from 6 to 20 pcs. - not less than 5 pcs. and with more - at least 25% of the bolts in the connection; if during inspection at least one bolt is found whose tension does not meet the requirements of Clause 1.133 of this chapter, then 100% of the bolts in the joint are subject to control. In this case, the tension of the bolts should be brought to the required value.
After inspection, the bolt heads must be painted. The entire connection should be putty along the contour.
Work should be recorded in the logs for monitoring the preparation of joints and the installation of high-strength bolts.
At the beginning of my career, I did not delve into the brands of bolts, their strength was the priority of the size of the bolts and nuts, but of course in the applications I indicated the bolts with the characteristics from the project. As it turned out, this was not correct, and in addition to the dimensions, it is necessary to pay attention to the characteristics of the bolts.
Technical literature like this one, “Supervision and technical operation mounting connections on high strength steel bolts building structures buildings and structures of the USSR Ministry of Metallurgy "or" GOST R 52644-2006 High-strength bolts with a hexagonal head with an increased turnkey size "I did not read, if I read at the institute, I don’t remember.
Let's see what is so unusual in high-strength bolts. This group includes products in which the resistance to temporary loads is 800 MPa. Strength class starts with 8.8 for bolts and 8 for nuts.
What do the numbers 8.8 mean? The first number multiplied by 10 indicates the value of the minimum tensile strength in kgf / mm2, the second number also multiplied by 10 indicates the ratio of the yield strength to tensile strength in percent.
For example, the first digit 8x10 \u003d 80 kgf / mm2 is the value of the minimum temporary metal resistance σ inyield strength ratio σ t to temporary resistance σ in the percentage is 8 × 10 \u003d 80%.
The yield strength is calculated by multiplying the first digit of the marking by the second 8x8 \u003d 64 kgf / mm2.
On our bolts connecting the beam there is a designation:
- D15.3 bolt of the Shchelkovo factory.
- 10.9 - the minimum temporary resistance of the bolt is 10.9 kgf / mm2
- SXL - S denotes the increased size of the turnkey hex head, HL - indicates that these bolts can be used in areas with a temperature dropping from -40 to -65 degrees.
If you could not find the bolts with the specified characteristics for the project, then they can be replaced upwards, for example, instead of 8.8, use bolts 10.9.
A feature of the joints of high-strength bolts is that the forces are perceived not by shear of the bolts and crushing of the wall, but by the forces of friction between the connected surfaces. Based on this, great attention must be paid to the surfaces of the joints to remove rust and dirt.
Insufficient tension of the bolts will lead to “slipping” of the elements and the bolts will work to shear, and the elements to collapse, which will lead to deformation of the structure and destruction of the bolts.
Preparation of high strength bolts, nuts and washers
Having worked at the facilities for the assembly of metal structures, no one prepared high-strength bolts before installation. The bolts were brought to the facility with factory lubrication and they were immediately put into operation. It turns out that this was not right and the way they were prepared surprise me, not much.
What you need to do with high-strength bolts before installing them and after. Who will work with high-strength bolts for the first time, without reading the recommendations, will never guess that before use they should be boiled in water with household washing powder or detergent.
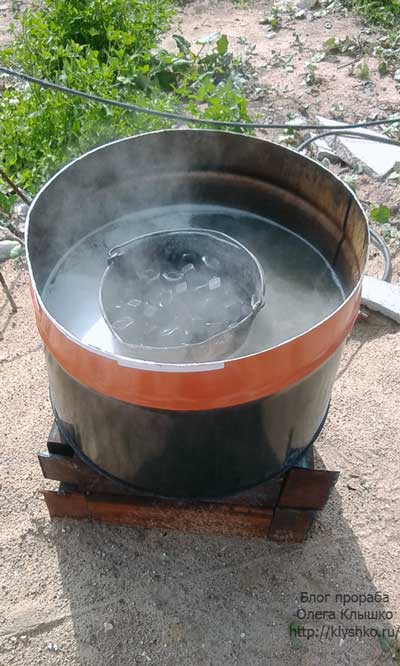

High Strength Bolt Preparation
This is done in order to remove factory oil, scale, dirt, to visually inspect the bolts for cracks, to run the rejected bolts and nuts.
Preparation of high strength bolts, nuts and washers
4.1.1. The technological process for the preparation of hardware includes de-preservation, cleaning of dirt and rust, threading of discarded bolts and nuts, and lubrication.
4.1.2. There are two ways to handle hardware. Hardware in lattice containers (for small volumes - in a bucket with punched holes); in a clean barrel, water is boiled, if possible, with a washing solution or household washing powder. The bucket is dipped in water and boiled for 10-15 minutes. After that, when the water merges, the hardware is lowered for 1-2 minutes into a container with a mixture of gasoline (85%) and mineral oil of the Avtol type (15%), then removed. From heated hardware, gasoline quickly evaporates, and oil in the form of a thin film remains on the surface. This method provides equalization of the coefficient of twist to 0.18.
Before installation in the structure, the threaded part is lubricated with oil. In the recommendations prescribed after boiling, dip the bolts in a mixture of gasoline with oil.
The high-strength bolt is installed with two washers, one on the side of the bolt, the second on the side of the nut.
Tightening High Strength Bolts

According to the project in Mytishchi flange connections beams are tightened with high-strength bolts from steel 40X "select" with a standard temporary resistance of 11 tf / cm2. The pre-tension of the M24 bolts is 24.4 tf.
How to create such an effort when tightening the bolts? To do this, use special torque wrenches. These keys show the tension force. The video below shows how to tighten the bolts with a torque wrench. Upon receipt of a predetermined force, the key handle "breaks".
In addition, the quality of the design tightening is checked with a 0.1 mm thick probe in the radius zone from the axis of the bolt 40 mm, the probe should not pass.
After accepting the connections by an ITR worker, the joints along the contour are primed with FL-03L GF-021 with the addition of dry pigment to a consistency that excludes the leakage of primer into the compound or the joints are putty.
How to fill in a production magazine high strength joints we read and see examples in this.
We leave comments on this article high-strength bolts.
In order to ensure the necessary degree of tension of high-strength bolts, the tightening of the nut cannot be carried out in accordance with the angle of rotation. Tension should only occur in torque.
Usually the bolts are tightened in two passes. First, using a wrench, the bolt is tightened by an amount from 50% to 90% of the design force, which should provide the necessary tightness of abutment of the joined elements. By the second approach, the bolts reach the required tension value, for this they use special torque wrenches, which allow you to control the bolt tension by torque. At the same time, dynamic action tools cannot be used in the second approach, i.e. rare impact and impact-impulse wrenches cannot be used.
It is worth noting that the initial tension of the bolts occurs at the time of installation of the joints and for this, pulse-impact wrenches are used.
When tensioning the bolt, it is necessary to keep its head from turning, which should stop as the bolt is pulled, if this does not happen, then both the bolt and the nut must be replaced.
The bolts are drawn to the calculated tension value after checking the geometry of the structure or its specific part, which occurs in accordance withSNiP 3.06.04-91, in addition, the compression density of the entire packet is checked. The accuracy accuracy of creating torque should never be more than 15%.
It is recommended to use special keys for tightening, more precisely, KLTs hydrodynamic keys. The use of wrenches of this type provides registration of the magnitude of the torque with an error of not more than 4%. In addition, it is possible to use manual dynamic keys of lever type.
At the same time, the tension of the bolts using multiplier wrenches, which are characterized by misaligned shaft rotation is unacceptable.
To determine the magnitude of the applied torque, use the following formula:
M cr= Kpd
Here K is the twisting coefficient;
P - indicates the magnitude of the controlled tension, which does not take into account the loss of relaxation, kN;
d - indicates the thread diameter of the bolt used in mm.
Values \u200b\u200bof P and M cr you can find out characteristic for high-strength bolts produced by the Voronezh, Kurgan plants and the plant in Ulan-Ude by reading the table2 , bolts matchGOST 22353 - GOST 22356.
Table 2
|
dmm |
RkN |
M crNm |
|
1084 |
||
|
1578 |
||
|
Note . The value of the temporary resistance of the materials used in the manufacture of bolts is1078 MPa; climatic modification At and HL. |
||
If the bolt was tensioned by twisting the head, the value of the torque itself should be increased by 5%.
If bolts made in accordance with GOST 22353 were used -GOST 22356 production of other plants or they have a special anti-corrosion coating then the twisting coefficient is determined separately for each specific case according to GOST 22356 either application A this STP. In this case, the obtained values \u200b\u200bshould not go beyond certainclause 1.9 of GOST 22356, and these are values \u200b\u200branging from a minimum of 0.14 to a maximum of 0.2.
The tension of the bolts should begin from the places where the closest fit of the mating elements is observed, and continue in the direction of the less tight fit. Bolt retraction occurs from the center of the structure to its edges. In this case, the bolts that are in close proximity to the mounting plugs must be reached after removing the latter.
All torque wrenches must undergo periodic calibration, which is carried out according to the applicationTO . Calibration results are necessarily recorded in the appropriate journal, designed to account for all completed connections with controlled bolt tension.
The kit designed for tensioning high-strength bolts, the diameter of which is 22, 24 or 27 mm, includes KLC keys. Set of equipment as perapplications And includes KLTs-110 hydrodynamic keys, there are two of them and one KLTs-160 key. Also included is a pneumohydro pump NPG-250 and a calibration device such as UT-1.
It is worth noting that only specially trained workers can work on the tensioning of bolts, who must study the characteristics and principle of operation of the equipment, learn the rules for operating the equipment and the tensioning technology and pass the exam for the right of admission to such work. For the training of workers, the requirements of STP and the relevant operating instructions for the equipment used are used.
All technological processesnamely, the preparation of the tool for operation, its storage and maintenance, the direct tension of the bolts must take place in full accordance with the relevant instructions for their use.
Calibration of KLZ keys is carried out immediately before their first use and then after tensioning 1000 and 2000 bolts. After this, taring must be carried out each time after tensioning the 5000 bolts or in case of replacement of such key components as a hydraulic cylinder or chain drum.
Manual keys must be calibrated every 4 hours of continuous operation, but at least two times per shift. For this, a control load suspension method is used. In any case, only trained personnel are allowed to tare, and it must be carried out with the direct presence of the person in charge.
When taring, the torque error should be no more than 5%. If the error exceeds the permissible values, the key itself, as well as the calibration device, are inspected and all detected malfunctions are eliminated. If after this the error goes beyond the norm, the keys must be processed and subsequently repaired.
In the process of tensioning high-strength bolts, the application of the torque calculated by the above formula to the bolt must be ensured. In this case, the magnitude of the generated torque should be monitored at the moment of turning the key. It should be noted that the tightening of the bolts should occur smoothly without any jerking. As soon as the torque reaches the required value, the tension stops.
To ensure the operation of keys such as keys KLTs-110 and KLTs-160 in a limited space, the kit provides for the presence of torque stops, applicationI. p. I.1.1.
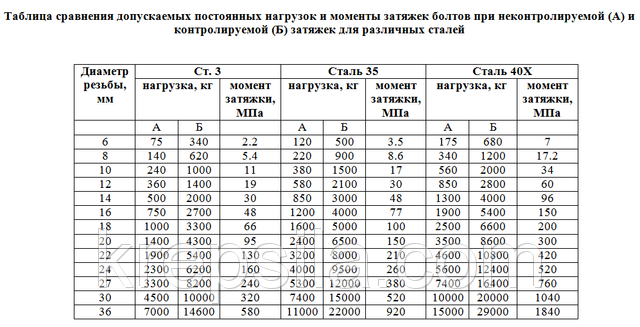
6.1. To ensure the necessary strength of the joint, high-strength bolts must be given the tension specified for bolts made of steel grade 40X in table. 3.
Table 3
Bolt Tension
6.2. The tension of high-strength bolts is achieved by applying to the nuts their torque M, determined by the formula
where N is the tension force of the bolt, determined in accordance with paragraph 6.1, hardware; d is the nominal diameter of the bolt, mm;
K is the coefficient of twisting, taken equal to 0.17. The values \u200b\u200bof the torques calculated by the formula (1) for the calculated efforts of the tension of the bolts are given in table. 4.
Table 4
Bolt tension and value of corresponding torques
6.3. High-strength bolts can be tensioned to rated forces using manual torque wrenches, pneumatic wrenches, or by turning the nut a certain angle according to special instructions.
6.4. The sequence of setting and tightening the bolts is set when developing the technology of repair work. The bolts are tightened within the joint or attachment from the middle of the joint to the edges.
After tightening the last bolt, the previously tightened bolts of the connection should be checked and, if necessary, tightened by a predetermined amount of torque.
The results of the tension of the bolts are entered in the register of the bolts (table. 5).
6.5. Tightening high-strength bolts is recommended in two steps: first, with pneumatic wrenches, 0.5-0.8 of the calculated tension, then torque wrenches to the calculated tension with control of the magnitude of the torque.
Tighten bolts with torque wrenches should be performed smoothly, without jerking. Torque is recorded while the wrench is moving in the direction of tension.
6.6. Each bolt tightened for standard force must be marked with paint.
6.7. Tightening high-strength bolts should be done with wrenches having a torque control device with an accuracy of 5%.
The key reading of the amount of torque required to tighten the nut of the bolt should be made at the moment of rotation of the nut.
6.8. The keys must be numbered, and a check calibration must be performed before starting work.
The results of the calibration of the keys are entered in the register of bolts (table. 5).
Table 5
High Strength Bolt Magazine
Gantry crane _________________
Inv. No. _________________________
Calibration of the keys is recorded in the log across the graph indicating the calibration date, key number, value of the calibrated torque and the corresponding dynamometer reading. The record is signed by the calibrator.