Installation as a type of construction work. What are the types of construction work? Types of construction works and their interconnection
Types of work in construction - this is a list of construction work, for the legal implementation of which the company is obliged to join the SRO. The list was approved by the Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation, but was repeatedly changed, adopted in a new edition. The list was approved by the order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2009 No. 624, and the changes were made by order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated June 23, 2010 No. 294.
The classifier of types of work in construction, design, engineering surveys will help you determine the types of activities for which you need to obtain an SRO permit. If you did not find certain types of work in the classifier, and you have any doubts about the need to obtain permission, be sure to contact our specialists for a free consultation! The lack of admission of the SRO for certain types of work may be fraught with penalties for the enterprise. A timely and complete consultation of an expert in the field of SRO will protect you from these and other undesirable moments.
- 1. Geodetic work performed on construction sites
- 1.1. Marking work in the construction process
- 1.2. Geodetic control of the accuracy of the geometric parameters of buildings and structures *
- 2. Preparatory work
- 2.1. Dismantling (dismantling) of buildings and structures, walls, ceilings, flights of stairs and other structural and related elements or parts thereof *
- 2.2. Construction of temporary: roads; sites; engineering networks and structures *
- 2.3. Installation of rail crane tracks and foundations (supports) of stationary cranes
- 2.4. Installation and dismantling of inventory external and internal scaffolding, technological garbage chutes*
- 3. Earthworks
- 3.1. Mechanized excavation *
- 3.2. Soil excavation and drainage arrangement in water management construction
- 3.3. Soil development by hydromechanization
- 3.4. Works on artificial freezing of soils
- 3.5. Soil compaction with rollers, compactors or heavy rammers *
- 3.6. Mechanized loosening and development of permafrost soils
- 3.7. Works on dewatering, organization of surface runoff and drainage
- 4. Construction of wells
- 4.1. Drilling, construction and installation of oil and gas wells
- 4.2. Drilling and construction of wells (except for oil and gas wells)
- 4.3. Fixing wells with pipes, extracting pipes, free lowering or lifting pipes from wells
- 4.4. Plugging works
- 4.5. Construction of mine wells
- 5. Pile work. Soil stabilization
- 5.1. Pile work performed from the ground, including in sea and river conditions
- 5.2. Pile work performed in frozen and permafrost soils
- 5.3. Grillage device
- 5.4. Installation of driven and bored piles
- 5.5. Thermal strengthening of soils
- 5.6. Cementation of soil bases with driving injectors
- 5.7. Silicization and resinization of soils
- 5.8. Works on the construction of structures using the "wall in the ground" method
- 5.9. Driving and lifting steel and sheet piles
- 6. Installation of concrete and reinforced concrete monolithic structures
- 6.1. Formwork
- 6.2. Reinforcing works
- 6.3. Installation of monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete structures
- 7. Installation of prefabricated concrete and reinforced concrete structures
- 7.1. Installation of foundations and structures of the underground part of buildings and structures
- 7.2. Installation of structural elements of the above-ground part of buildings and structures, including columns, frames, crossbars, trusses, beams, slabs, belts, wall panels and partitions
- 7.3. Installation of volumetric units, including ventilation units, elevator shafts and garbage chutes, sanitary cabins
- 8. Drilling and blasting during construction
- 9. Works on the device of stone structures
- 9.1. Arrangement of structures of buildings and structures made of natural and artificial stones, including those with cladding *
- 9.2. Installation of brick structures, including those with cladding *
- 9.3. Arrangement of heating furnaces and hearths *
- 10. Installation of metal structures
- 10.1. Installation, strengthening and dismantling of structural elements and enclosing structures of buildings and structures
- 10.2. Installation, reinforcement and dismantling of structures of transport galleries
- 10.3. Installation, reinforcement and dismantling of tank structures
- 10.4. Installation, strengthening and dismantling of mast structures, towers, exhaust pipes
- 10.5. Installation, reinforcement and dismantling of technological structures
- 10.6. Installation and dismantling of cable supporting structures (stretch marks, cable-stayed structures, etc.)
- 11. Installation of wooden structures
- 11.1. Installation, strengthening and dismantling of structural elements and enclosing structures of buildings and structures, including those made of glued structures *
- 11.2. Assembly of residential and public buildings from prefabricated parts of a complete delivery *
- 12. Protection of building structures, pipelines and equipment (except for main and field pipelines)
- 12.1. Lining works
- 12.2. Masonry made of acid-resistant bricks and shaped acid-resistant ceramic products
- 12.3. Protective coating with paintwork materials *
- 12.4. Gumming (lining with sheet rubber and liquid rubber compounds)
- 12.5. Glue insulation device
- 12.6. The device of metallization coatings
- 12.7. Application of a front coating when installing a monolithic floor in rooms with aggressive environments
- 12.8. Antiseptic treatment of wooden structures
- 12.9. Waterproofing of building structures
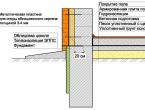
- 12.10. Works on thermal insulation of buildings, building structures and equipment
- 12.11. Works on thermal insulation of pipelines *
- 12.12. Works on fire protection of building structures and equipment
- 13. Roofing
- 13.1. Installation of roofs from piece and sheet materials *
- 13.2. Roofing from rolled materials *
- 13.3. Liquid roofing device *
- 14. Facade works
- 14.1. Surface cladding with natural and artificial stones and linear shaped stones *
- 14.2. Installation of ventilated facades *
- 15. Arrangement of internal engineering systems and equipment of buildings and structures
- 15.1. Installation and dismantling of the water supply and sewerage system *
- 15.2. Installation and dismantling of the heating system *
- 15.3. Installation and dismantling of the gas supply system
- 15.4. Installation and dismantling of the ventilation and air conditioning system *
- 15.5. The device of the power supply system *
- 15.6. Arrangement of electrical and other control networks for life support systems of buildings and structures *
- 16. Installation of external water supply networks
- 16.1. Laying of water pipelines
- 16.2. Installation and dismantling of shut-off valves and equipment for water supply networks
- 16.3. Installation of water wells, caps, catchment dampers
- 16.4. Cavity cleaning and testing of water pipelines
- 17. Construction of external sewer networks
- 17.1. Laying of non-pressure sewer pipelines
- 17.2. Laying sewer pressure pipelines
- 17.3. Installation and dismantling of shut-off valves and equipment of sewer networks
- 17.4. Installation of sewer and drain wells
- 17.5. Arrangement of a filtering base for silt pads and filtration fields
- 17.6. Laying drainage pipes on sludge beds
- 17.7. Cavity cleaning and testing of sewer pipelines
- 18. Construction of external heat supply networks
- 18.1. Laying of heat supply pipelines with a coolant temperature of up to 115 degrees Celsius
- 18.2. Laying of heat supply pipelines with a coolant temperature of 115 degrees Celsius and above
- 18.3. Installation and dismantling of shutoff valves and equipment of heat supply networks
- 18.4. Arrangement of wells and chambers of heat supply networks
- 18.5. Cavity cleaning and testing of heating pipelines
- 19. The device of external gas supply networks, except for the main
- 19.1. Laying of gas pipelines with working pressure up to 0.005 MPa inclusive
- 19.2. Laying of gas pipelines with working pressure from 0.005 MPa to 0.3 MPa inclusive
- 19.3. Laying of gas pipelines with working pressure from 0.3 MPa to 1.2 MPa inclusive (for natural gas), up to 1.6 MPa inclusive (for liquefied hydrocarbon gas)
- 19.4. Installation of condensate collectors for hydraulic seals and compensators on gas pipelines
- 19.5. Installation and dismantling of gas control points and installations
- 19.6. Installation and dismantling of tank and group cylinder installations of liquefied gas
- 19.7. Entering the gas pipeline into buildings and structures
- 19.8. Installation and dismantling of gas equipment for consumers using natural and liquefied gas
- 19.9. Tapping under pressure into existing gas pipelines, disconnection and plugging under pressure of existing gas pipelines
- 19.10. Cavity cleaning and testing of gas pipelines
- 20. The device of external electrical networks and communication lines
- 20.1. Arrangement of power supply networks with voltage up to 1 kV inclusive *
- 20.2. Arrangement of power supply networks with voltage up to 35 kV inclusive
- 20.3. Arrangement of power supply networks with voltage up to 330 kV inclusive
- 20.4. Construction of power supply networks with voltage over 330 kV
- 20.5. Installation and dismantling of supports for overhead power lines with voltage up to 35 kV
- 20.6. Installation and dismantling of supports for overhead power lines with voltage up to 500 kV
- 20.7. Installation and dismantling of supports for overhead power lines with a voltage of more than 500 kV
- 20.8. Installation and dismantling of wires and lightning protection cables of overhead power lines with voltage up to 35 kV inclusive
- 20.9. Installation and dismantling of wires and lightning protection cables of overhead power lines with voltage over 35 kV
- 20.10. Installation and dismantling of transformer substations and linear electrical equipment with voltage up to 35 kV inclusive
- 20.11. Installation and dismantling of transformer substations and linear electrical equipment with voltage over 35 kV
- 20.12. Installation of distribution devices, switching equipment, protection devices
- 20.13. Arrangement of external communication lines, including telephone, radio and television *
- 21. Arrangement of nuclear facilities
- 21.1. Works on the construction of facilities with nuclear installations
- 21.2. Works on the construction of nuclear weapons complex facilities
- 21.3. Works on the construction of elementary particle accelerators and hot chambers
- 21.4. Works on the construction of storage facilities for nuclear materials and radioactive substances, storage facilities for radioactive waste
- 21.5. Works on the construction of nuclear fuel cycle facilities
- 21.6. Works on the construction of facilities for the extraction and processing of uranium
- 21.7. Works on decommissioning of nuclear facilities
- 22. Arrangement of oil and gas industry facilities
- 22.1. Installation of main and field pipelines
- 22.2. Works on the arrangement of facilities for preparing oil and gas for transport
- 22.3. Arrangement of oil depots and gas storage facilities
- 22.4. Installation of crossing structures under linear objects (roads and railways) and other obstacles of natural and artificial origin
- 22.5. Works on the construction of crossings by the method of directional drilling
- 22.6. Device for electrochemical protection of pipelines
- 22.7. Tapping under pressure into existing main and field pipelines, disconnection and plugging under pressure of existing main and field pipelines
- 22.8. Performance of anti-corrosion protection and insulation works in relation to main and field pipelines
- 22.9. Works on the development of oil and gas fields offshore
- 22.10. Works on the construction of gas filling compressor stations
- 22.11. Quality control of welded joints and their isolation
- 22.12. Cavity cleaning and testing of main and field pipelines
- 23. Installation work
- 23.1. Installation of handling equipment
- 23.2. Elevator installation
- 23.3. Installation of equipment for thermal power plants
- 23.4. Installation of boiler room equipment
- 23.5. Installation of compressor units, pumps and fans *
- 23.6. Installation of electrical installations, equipment, automation and alarm systems *
- 23.7. Installation of equipment for nuclear facilities
- 23.8. Installation of equipment for cleaning and preparation for the transportation of gas and oil
- 23.9. Installation of equipment for oil and gas pumping stations and for other product pipelines
- 23.10. Installation of natural gas liquefaction equipment
- 23.11. Installation of gas station equipment
- 23.12. Installation of equipment for ferrous metallurgy enterprises
- 23.13. Installation of equipment for non-ferrous metallurgy enterprises
- 23.14. Installation of equipment for the chemical and oil refining industries
- 23.15. Installation of mining and ore-dressing equipment
- 23.16. Installation of equipment for railway infrastructure facilities
- 23.17. Installation of subway and tunnel equipment
- 23.18. Installation of equipment for hydroelectric stations and other hydraulic structures
- 23.19. Installation of equipment for electrical industry enterprises
- 23.20. Installation of equipment for enterprises in the building materials industry
- 23.21. Installation of equipment for the pulp and paper industry
- 23.22. Installation of equipment for textile industry enterprises
- 23.23. Installation of equipment for printing industry enterprises
- 23.24. Installation of equipment for food industry enterprises *
- 23.25. Installation of equipment for theater and entertainment enterprises
- 23.26. Installation of equipment for granaries and grain processing enterprises
- 23.27. Installation of equipment for cinematography enterprises *
- 23.28. Installation of equipment for electronics and communications industries *
- 23.29. Installation of equipment for healthcare institutions and medical industry enterprises *
- 23.30. Installation of equipment for agricultural production, including fish processing and fish storage *
- 23.31. Installation of equipment for consumer services and public utilities *
- 23.32. Installation of water intake equipment, sewerage and treatment facilities
- 23.33. Installation of equipment for communication facilities *
- 23.34. Installation of equipment for space infrastructure facilities
- 23.35. Installation of airport equipment and other aviation infrastructure facilities
- 23.36. Installation of equipment for sea and river ports
- 24. Commissioning
- 24.1. Commissioning of lifting and transport equipment
- 24.2. Commissioning of elevators
- 24.3. Commissioning of synchronous generators and excitation systems
- 24.4. Commissioning of power and instrument transformers
- 24.5. Commissioning of switching devices
- 24.6. Commissioning of relay protection devices
- 24.7. Commissioning of automation in power supply *
- 24.8. Commissioning of voltage and control current systems
- 24.9. Commissioning of electrical machines and electric drives
- 24.10. Commissioning of automation systems, alarm systems and related devices *
- 24.11. Commissioning of stand-alone system debugging *
- 24.12. Commissioning works of complex adjustment of systems *
- 24.13. Commissioning of telemechanics *
- 24.14. Adjustment of ventilation and air conditioning systems *
- 24.15. Commissioning of automatic machine lines
- 24.16. Commissioning of multi-purpose metal-cutting machines with CNC
- 24.17. Commissioning of unique metal-cutting machines weighing over 100 tons
- 24.18. Commissioning of refrigeration units *
- 24.19. Commissioning of compressor units
- 24.20. Commissioning of steam boilers
- 24.21. Commissioning of hot water boilers *
- 24.22. Commissioning of auxiliary boiler equipment *
- 24.23. Commissioning of water treatment equipment and chemical water treatment equipment
- 24.24. Start-up and adjustment works of technological installations of the fuel economy
- 24.25. Commissioning of the gas-air path
- 24.26. Commissioning of general boiler systems and utilities
- 24.27. Commissioning of equipment for processing and finishing wood
- 24.28. Commissioning of drying plants
- 24.29. Commissioning works of water supply facilities
- 24.30. Commissioning works of sewerage facilities
- 24.31. Commissioning works at the facilities of the oil and gas complex
- 24.32. Commissioning works at nuclear facilities
- 25. Construction of roads and airfields
- 25.1. Works on the construction of subgrade for highways, airport platforms, runways, taxiways
- 25.2. The device of the bases of highways
- 25.3. Arrangement of foundations for airport aprons, runways, taxiways
- 25.4. Road pavement devices, including those reinforced with binders
- 25.5. Devices for covering airport aprons, runways, taxiways
- 25.6. Installation of drainage, catchment, culvert, spillway devices
- 25.7. Installation of protective fences and elements of arrangement of highways
- 25.8. Road marking device
- 26. Arrangement of railway and tram tracks
- 26.1. Works on the construction of subgrade for railway tracks
- 26.2. Works on the construction of subgrade for tram tracks
- 26.3. The device of the upper structure of the railway track
- 26.4. Arrangement of drainage and protective structures of the subgrade of the railway track
- 26.5. Installation of signaling, centralization and blocking of railways
- 26.6. Railway electrification
- 26.7. Stabilization of soils in the right of way of the railway
- 26.8. Construction of railway crossings
- 27. Construction of tunnels, subways
- 27.1. Sinking of tunnels and subways without the use of special methods of tunneling
- 27.2. Excavation of tunnels and subways using artificial freezing
- 27.3. Sinking of tunnels and subways using grouting
- 27.4. Sinking of tunnels and subways with the use of electrochemical fastening
- 27.5. Sinking of tunnels and subways with the use of lowering support
- 27.6. Arrangement of internal structures of tunnels and subways
- 27.7. Subway track arrangement
- 28. Installation of mine structures
- 28.1. Sinking of the development of mine structures without the use of special methods of sinking
- 28.2. Sinking of the development of mine structures using artificial freezing
- 28.3. Sinking of the development of mine structures with the use of grouting
- 28.4. Sinking of the development of mine structures with the use of electrochemical fastening
- 28.5. Sinking of the development of mine structures with the use of lowering lining
- 29. Arrangement of bridges, overpasses and overpasses
- 29.1. Installation of monolithic reinforced concrete and concrete structures of bridges, flyovers and overpasses
- 29.2. Arrangement of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures of bridges, flyovers and overpasses
- 29.3. Construction of pedestrian bridges
- 29.4. Installation of steel superstructures of bridges, flyovers and overpasses
- 29.5. Installation of wooden bridges, flyovers and overpasses
- 29.6. Installation of stone bridges, flyovers and overpasses
- 29.7. Laying of culvert pipes on finished foundations (bases) and drainage trays
- 30. Hydraulic works, diving works
- 30.1. Development and movement of soil by jet and floating dredgers
- 30.2. Loosening and development of soils under water in a mechanized way and issuance to a dump or floating facilities
- 30.3. Drilling and construction of wells under water
- 30.4. Piling work performed in marine conditions from floating facilities, including the installation of shell piles
- 30.5. Pile work performed in river conditions from floating facilities, including the installation of shell piles
- 30.6. Construction of structures in sea and river conditions from natural and artificial massifs
- 30.7. Construction of dams
- 30.8. Installation, dismantling of building structures in underwater conditions
- 30.9. Laying pipelines in underwater conditions
- 30.10. Laying cables in underwater conditions, including electrical and communication
- 30.11. Diving (underwater construction) works, including quality control of hydrotechnical works under water
- 31. Industrial furnaces and chimneys
- 31.1. Blast furnace masonry
- 31.2. Masonry of the upper structure of glass melting furnaces
- 31.3. Installation of furnaces from prefabricated elements of increased factory readiness
- 31.4. Electrolyzers for the aluminum industry
- 31.5. Lining of industrial flue and ventilation furnaces and pipes
- 32. Works on the implementation of construction control by the involved developer or customer on the basis of a contract by a legal entity or individual entrepreneur
- 32.1. Construction control over general construction works (groups of types of work N 1 - 3, 5 - 7, 9 - 14)
- 32.2. Construction control over well construction works (group of types of work N 4)
- 32.3. Construction control over drilling and blasting (group of types of work N 8)
- 32.4. Construction control over work in the field of water supply and sewerage (type of work N 15.1, 23.32, 24.29, 24.30, groups of types of work N 16, 17)
- 32.5. Construction control over work in the field of heat and gas supply and ventilation (types of work N 15.2, 15.3, 15.4, 23.4, 23.5, 24.14, 24.19, 24.20, 24.21, 24.22, 24.24, 24.25, 24.26, groups of types of work N 18, 19)
- 32.6. Construction control over work in the field of fire safety (type of work N 12.3, 12.12, 23.6, 24.10 - 24.12)
- 32.7. Construction control over work in the field of power supply (type of work N 15.5, 15.6, 23.6, 24.3 - 24.10, group of types of work N 20)
- 32.8. Construction control during the construction, reconstruction and overhaul of communication facilities (types of work N 20.13, 23.6, 23.28, 23.33, 24.7, 24.10, 24.11, 24.12)
- 32.9. Construction control during the construction, reconstruction and overhaul of oil and gas industry facilities (type of work N 23.9, 23.10, group of types of work N 22)
- 32.10. Construction control during the construction, reconstruction and overhaul of roads and airfields, bridges, overpasses and overpasses (type of work N 23.35, groups of types of work N 25, 29)
- 32.11. Construction control during the construction of railway and tram tracks (types of work N 23.16, group of types of work N 26)
- 32.12. Construction control during construction, reconstruction and overhaul in underground conditions (types of work N 23.17, groups of types of work N 27, 28)
- 32.13. Construction control over hydraulic engineering and diving works (group of types of work N 30)
- 32.14. Construction control during construction, reconstruction and overhaul of industrial furnaces and chimneys (group of types of work N 31)
- 33. Works on the organization of construction, reconstruction and overhaul by the attracted developer or customer on the basis of an agreement by a legal entity or an individual entrepreneur (general contractor):
- 33.1. Industrial engineering
- 33.1.1. Enterprises and facilities of the fuel industry
- 33.1.2. Enterprises and facilities of the coal industry
- 33.1.3. Enterprises and objects of ferrous metallurgy
- 33.1.4. Enterprises and objects of non-ferrous metallurgy
- 33.1.5. Enterprises and objects of the chemical and petrochemical industry
- 33.1.6. Enterprises and objects of mechanical engineering and metalworking
- 33.1.7. Enterprises and facilities of the forestry, woodworking, pulp and paper industries
- 33.1.8. Enterprises and objects of light industry *
- 33.1.9. Enterprises and facilities of the food industry *
- 33.1.10. Enterprises and objects of agriculture and forestry *
- 33.1.11. Thermal power plants
- 33.1.12. Nuclear facilities
- 33.1.13. Power supply facilities over 110 kV
- 33.1.14. Oil and gas facilities
- 33.2. Transport construction
- 33.2.1. Roads and road transport infrastructure
- 33.2.2. Railways and rail transport infrastructure
- 33.2.3. Airports and other aviation infrastructure facilities
- 33.2.4. Road and rail tunnels
- 33.2.5. Subways
- 33.2.6. Bridges (large and medium)
- 33.2.7. Enterprises and public transport facilities *
- 33.3. Housing and civil construction
- 33.4. Power supply facilities up to 110 kV inclusive
- 33.5. Heat supply facilities
- 33.6. Gas supply facilities
- 33.7. Water supply and sewerage facilities
- 33.8. Buildings and facilities of communication facilities
- 33.9. Maritime transport facilities
- 33.10. River transport facilities
- 33.11. Hydropower facilities
- 33.12. Dams, dams, canals, bank protection structures, reservoirs (with the exception of hydropower facilities)
- 33.13. Irrigation facilities
- 34. Works on the implementation of construction control by the developer, or by a legal entity or individual entrepreneur engaged by the developer or customer on the basis of an agreement during the construction, reconstruction and overhaul of nuclear facilities (types of work N 23.7, 24.32, group of types of work N 21)
- having an ISO certificate
- increased insurance coverage
SRO permit for especially dangerous work

Additional requirements for obtaining a permit for especially dangerous work
Types of design work - this is an official list of design work, for the implementation of which it is necessary to obtain a SRO permit without fail. The list was approved by the Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of December 30, 2009 No. 624, as amended by Order No. 294 of June 23, 2010.
- 1. Work on the preparation of a scheme for the planning organization of a land plot:
- 1.1. Works on the preparation of the master plan of the land plot
- 1.2. Works on the preparation of a planning organization scheme for the route of a linear facility
- 1.3. Works on the preparation of the scheme of planning organization of the right of way of the linear structure
- 2. Work on the preparation of architectural solutions
- 3. Work on the preparation of constructive solutions
- 4. Work on the preparation of information on internal engineering equipment, internal networks of engineering and technical support, on the list of engineering and technical measures:
- 4.1. Works on the preparation of projects for internal engineering systems of heating, ventilation, air conditioning, smoke ventilation, heat supply and refrigeration
- 4.2. Works on the preparation of projects for internal engineering systems of water supply and sewerage
- 4.3. Works on the preparation of projects for internal power supply systems *
- 4.4. Works on the preparation of projects for internal low-voltage systems*
- 4.5. Works on the preparation of projects for internal dispatching, automation and management of engineering systems
- 4.6. Works on the preparation of projects for internal gas supply systems
- 5. Work on the preparation of information on external networks of engineering and technical support, on the list of engineering and technical measures:
- 5.1. Works on the preparation of projects for external heat supply networks and their structures
- 5.2. Works on the preparation of projects for external water supply and sewerage networks and their structures
- 5.3. Works on the preparation of projects for external power supply networks up to 35 kV inclusive and their structures
- 5.4. Works on the preparation of projects for external power supply networks of not more than 110 kV inclusive and their structures
- 5.5. Works on the preparation of projects for external power supply networks of 110 kV and more and their structures
- 5.6. Works on the preparation of projects for external networks of low-voltage systems
- 5.7. Works on the preparation of projects for external gas supply networks and their structures
- 6. Work on the preparation of technological solutions:
- 6.1. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for residential buildings and their complexes
- 6.2. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for public buildings and structures and their complexes
- 6.3. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for industrial buildings and structures and their complexes
- 6.4. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for transport facilities and their complexes
- 6.5. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for hydraulic structures and their complexes
- 6.6. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for agricultural facilities and their complexes
- 6.7. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for special-purpose facilities and their complexes
- 6.8. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for oil and gas facilities and their complexes
- 6.9. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for objects of collection, processing, storage, processing and disposal of waste and their complexes
- 6.10. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for nuclear power and industry facilities and their complexes
- 6.11. Work on the preparation of technological solutions for military infrastructure facilities and their complexes
- 6.12. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for treatment facilities and their complexes
- 6.13. Works on the preparation of technological solutions for metro facilities and their complexes
- 7. Work on the development of special sections of project documentation:
- 7.1. Engineering and technical measures for civil defense
- 7.2. Engineering and technical measures to prevent natural and man-made emergencies
- 7.3. Development of a declaration on industrial safety of hazardous production facilities
- 7.4. Development of a declaration of safety of hydraulic structures
- 7.5. Development of justification for radiation and nuclear protection
- 8. Works on the preparation of projects for the organization of construction, demolition and dismantling of buildings and structures, extension of the service life and conservation *
- 10. Works on the preparation of draft measures to ensure fire safety
- 11. Work on the preparation of draft measures to ensure access for people with limited mobility
- 12. Work on the inspection of building structures of buildings and structures
- 13. Works on organizing the preparation of project documentation, attracted by the developer or customer on the basis of an agreement by a legal entity or an individual entrepreneur (general designer) * These types and groups of types of work require obtaining a certificate of admission to types of work that affect the safety of a capital construction object, in case such work is performed at the facilities specified in Article 48.1 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation - List of especially dangerous, technically complex and unique objects.
Types of work in engineering surveys - a list of engineering and survey works, for the performance of which it is necessary to obtain an SRO permit on a general basis. This list of activities was officially approved by the Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of December 30, 2009 No. 624, as amended by Order No. 294 of June 23, 2010.
- 1. Works as part of engineering and geodetic surveys
- 1.1. Creation of reference geodetic networks
- 1.2. Geodetic observations of deformations and settlements of buildings and structures, movements of the earth's surface and hazardous natural processes
- 1.3. Creation and updating of engineering and topographic plans on a scale of 1:200 - 1:5000, including in digital form, survey of underground utilities and structures
- 1.4. Tracing line features
- 1.5. Engineering and hydrographic works
- 1.6. Special geodetic and topographic works during the construction and reconstruction of buildings and structures
- 2. Works as part of engineering and geological surveys
- 2.1. Engineering and geological survey on a scale of 1:500 - 1:25000
- 2.2. Sinking of mine workings with testing, laboratory studies of the physical and mechanical properties of soil and chemical properties of groundwater samples
- 2.3. The study of hazardous geological and engineering-geological processes with the development of recommendations for the engineering protection of the territory
- 2.4. Hydrogeological research
- 2.5. Engineering and geophysical research
- 2.6. Engineering geocryological research
- 2.7. Seismological and seismotectonic studies of the territory, seismic microzoning
- 3. Works as part of engineering and hydrometeorological surveys
- 3.1. Meteorological observations and study of the hydrological regime of water bodies
- 3.2. Study of hazardous hydrometeorological processes and phenomena with calculations of their characteristics
- 3.3. Study of channel processes of water objects, deformations and processing of banks
- 3.4. Studies of the ice regime of water bodies
- 4. Works as part of engineering and environmental surveys
- 4.1. Engineering and environmental survey of the territory
- 4.2. Studies of chemical pollution of soils, surface and ground waters, atmospheric air, sources of pollution
- 4.3. Laboratory chemical-analytical and gas-chemical studies of samples and samples of soil and water
- 4.4. Research and assessment of physical impacts and radiation situation on the territory
- 4.5. Study of vegetation, wildlife, sanitary-epidemiological and medical-biological studies of the territory*
- 5. Works as part of engineering and geotechnical surveys
- 5.1. Sinking of mine workings with testing and laboratory studies of the mechanical properties of soils with the determination of characteristics for specific schemes for calculating the bases of foundations
- 5.2. Field tests of soils with the determination of their standard strength and deformation characteristics (stamp, shear, pressuremeter, shear). Tests of reference in-situ piles
- 5.3. Determination of standard mechanical characteristics of soils by methods of static, dynamic and drilling sounding
- 5.4. Physical and mathematical modeling of the interaction of buildings and structures with the geological environment
- 5.5. Special studies of soil characteristics according to individual programs for non-standard, including linear methods for calculating the bases of foundations and structures of buildings and structures
- 5.6. Geotechnical control of construction of buildings, structures and adjacent territories
- 6. Inspection of the state of soils of the foundation of buildings and structures
- 7. Works on the organization of engineering surveys by a developer engaged on the basis of a contract or an authorized legal entity or an individual entrepreneur (general contractor)
The norms and rules establish general requirements for the organization of construction production in the construction of new, as well as the expansion and reconstruction of existing facilities. These standards must be observed by all participants in the construction of facilities.
When we talk about the construction, reconstruction or repair of any construction projects, we are always talking about a whole range of activities. The order of production is regulated by rules, regulations and requirements, which will lead to the desired result in the form of a strong, reliable and aesthetic building. What is construction work? They are a separate area of construction, which is indispensable when performing major repairs in the premises, as well as in the process of erecting new buildings.
The definition of construction and installation work is a very broad concept. It is understood as an operational process, which includes multidirectional actions that differ from each other in many criteria. Differences may be in the timing of execution, the essence of the process, methods and algorithm of construction or installation operations. The definition of construction and installation works (CEW) is a set of actions aimed at the construction, reconstruction or repair of structures and other facilities. As a rule, it is difficult for one company to complete the entire operational cycle of events. Their scale is colossal, and it is often impossible to cover all the tasks set. Today, there are many companies on the market: some carry out the entire operational process, others carry out installation or construction work. The choice of a professional with a narrow specialization determines the quality of performance. Often, in order to save money, many owners of private construction projects do some kind of work with their own hands. To achieve the desired result, it is important to understand the operational process, its sequence, to study the manual and the rules for performing construction or installation operations.


To date, there are three main areas:
- General construction industry.
- Sphere of transport and loading and unloading operations.
- Specialized type of work.
Each of the main areas is regulated by production rules, safety standards during execution, technological maps, SNiP rules, state standards, and UNiR calculation rules.
The essence of general construction activities
The category of general construction activities is the most extensive. The concept of this type of work contains several important stages on which the construction of buildings of any purpose depends. The entire operational process, as they say, from A to Z, must comply with the regulations and rules. The list of multidisciplinary events looks like this:
- A complex of geodetic processes carried out at construction sites:
- control of geodetic parameters, calculations, characteristics;
- performance of production of geodetic shooting.
- Preparatory activities that involve:
- cleaning of the territory, preparation for the start of construction processes;
- if necessary, the dismantling of structures or structures;
- construction of temporary structures for the implementation of the main complex of construction activities.
- Excavation. The list of such activities involves the implementation of:
- production of excavations, arrangement of vertical layouts;
- production of trenches and digging of construction pits;
- work with soil, its compaction, arrangement of “soil cushion”;
- excavation works in non-standard conditions (when subsidence of heaving soil).


Important! Earthworks involve the production of the entire range of activities exclusively by professionals. The operational life of the building, its reliability, regardless of the functional purpose, depends on the quality of such work.
In addition to the preparatory complex, general construction works also include processes that complete the main stages of construction:
- Stone work is a special type of event, which is a set of works on the construction, strengthening of the walls of buildings, supports and pillars. Stone work also includes brick laying, decorative facade finishing. All this can be done with your own hands, but you need to know the rules, principles and technologies of construction. Having mastered the knowledge and following all the rules, you can do the work yourself, significantly saving, but without compromising the quality of construction.
- The list of concrete and reinforced concrete works includes:
- complex of reinforcing and formwork works;
- welding and installation operations;
- arrangement of monolithic structures.
- Roofing. This type of activity is referred to as installation work. The roof crowns any structure, serves as protection from heat loss and the effects of precipitation. The degree of comfort and safety of living in the house depends on the quality of execution. The subgroup of roofing activities includes:
- installation of roofs from any materials (rolled, piece, metal and sheet);
- arrangement of a roofing pie (steam and hydroprotection of structures);
- welding and installation work on the construction of frames;
- installation of windows of any type (including skylights);
- arrangement of a drain.


- Finishing work. This type of operation can be performed even by a beginner in the construction business, the main thing is to know the rules and carry out quality control at every stage. Finishing work includes:
- a complex of facade measures (decorative and protective cladding of the facades of buildings of any purpose);
- welding and assembly production of frames of internal partitions made of metal, laying bricks, drywall;
- painting and plastering complex, glazing production - aimed at decorative finishing of elements, protective cladding, glazing of structures.
- Complex of insulation works. Its essence lies in creating maximum comfort indoors, minimizing the external negative impact of the external environment, enhancing the properties of strength and practicality. This can also include insulation with bituminous materials, reinforcing shells, plates or bulk materials.
The list of general construction works, among other things, includes low-current works. They represent the installation of cables and wires, the voltage of which does not exceed 25 volts. The complex is necessary for telephone installation of the building, organization of fire safety systems, installation of alarms and security systems of any type.


Direction of civil works
To understand what civil works are, you need to know the very essence of construction. It is this area of activity that belongs to the title of one of the oldest and most revered areas. Undoubtedly, production and technological progress are moving forward, the production of new materials has been established, effective developments and innovative solutions are emerging. This development allows the construction of reliable and durable buildings, and the aesthetics of each completed object is excellent. There are two main branches of construction: capital and non-capital. The first type includes all buildings and structures that represent the category of real estate. This means that each building is connected to the ground by means of laying the foundation. There are several types of capital construction objects:
- All types of buildings that are equipped with underground structures (plinths, foundations), as well as the ground part. The system of buildings of this type includes engineering networks, the organization of water supply and sewerage, and ventilation systems. The general functional purpose of the category is the living and livelihoods of people.
- All types of structures, which are flat systems and load-bearing structures with above-ground and underground parts. Such facilities are intended, as a rule, for the movement of people or goods, the implementation of any production processes, as well as the storage of products. An example of this type of structures are dams, bridge structures, all types of roads (motorway, railway).
- All objects are representatives of the category of construction in progress. These include buildings for which, for a number of reasons, a permit for operation has not been made or their construction has been suspended. As long as the operational process is not completed, proper control and admission to operation is not carried out, the buildings are called typical objects of construction in progress.
Objects - representatives of the non-capital category of construction include all structures of a temporary nature. These are trade kiosks, household facilities (sheds, pantries, barns), pavilions or hangars with a collapsible design.


Types of objects and their classification
The purpose of the erected objects can be very different and perform various functions. These can be industrial facilities, residential buildings, structures for agricultural needs. In accordance with the functional purpose, construction is divided into several types:
- The field of civil engineering. These are buildings of any number of storeys for living or public and commercial activities (administrative, retail, municipal or office).
- Sphere of industrial construction. This category includes all work on the construction of workshops, factories or factories, any production areas, combines.
- The sphere of agricultural construction is the construction of structures for livestock farms or agriculture. This also includes the construction of veterinary clinics, greenhouses, agricultural facilities.
- Transport construction. The category includes the construction of bridges, tunnels, highways.
- Hydraulic engineering. The sphere involves the construction of reservoirs, dams or canals.
- military sphere. It involves the construction of any construction objects for military and defense purposes.
Important! All types of construction and installation activities are regulated by the norms and rules of SNiP, GOSTs, as well as ENiR standards.
The construction object is, in its own way, the final product. All costs for its production must be strictly calculated. For this, there is the ENiR system, which is a complex of pricing calculations and estimated rationing. Project budgeting without knowledge of ENiR norms is impossible. All stages should be taken into account: construction design, conclusion of contracts for the performance of work, costs for the purchase of building materials, remuneration of workers.


Levers of control
In order for the structure to meet all technical standards and comply with the highest safety class, control is necessary. We will talk about the supervision of construction and installation works, which in its essence is a complex of verification measures. The main goal is not to punish or apply fines, but to ensure that all project specifications are strictly observed. Technical control consists of the following stages:
- Financial check. Control and adjustment methods are applied, the goal is to minimize financial losses and risks. Evaluation and control takes place at all stages of construction. The supervisory mechanism is especially important when money from outside investors is used to build a building.
- Checking compliance with deadlines. At each stage, an act of completed work is issued, in accordance with which quality control is carried out.
- Control over the use of building materials. Production and construction technologies require the use of high-quality building materials with a set of required properties.
Important! Technical control is regulated by standards and documentation. The main levers of supervision include SNiP rules, ENiR regulations, compliance with established GOST standards.
In addition to quality control of work performance, technical supervision allows solving the following problems:
- To prevent an unreasonable increase in the cost of construction and installation work and to identify the inconsistency of expenses with the agreed estimate.
- Control of logging and technical documentation. Each operational process, the technology of its implementation is confirmed by an act. Data transparency allows timely detection of errors, deviations from SNiP standards or ENiR calculation rules.
- Supervision and detection of violations in the process of erecting structures, errors in parameters, inconsistencies with calculations.
- Solving problems with soil shrinkage, the appearance of cracks, deformation and other problems with violation of technical specifications.


Who is supervising? These are professionally trained people with valuable construction experience. The supervisor of construction and installation works can be design engineers, specialists in general construction works. Their main tasks are to control compliance with process technology, conduct intermediate acceptance of work, and participate in engineering inspections. As a result of the control, an inspection report is signed, which indicates the inaccuracies and the period in which the errors must be eliminated. During the construction and installation process, a technical supervision log is filled in, its maintenance is an integral part of the construction process. At the end of construction, an act of completed work is submitted.
Author's supervision as a type of control over construction and installation works
In addition to technical supervision, architectural supervision is one of the auxiliary levers for optimizing construction production and quality control at all its stages. The sphere of construction is very specific, it has rules that must be followed strictly. This is a guarantee of the success of the construction, delivery of the object of proper quality on time.
- Control can be exercised by management, legal entities and individuals on the basis of a signed cooperation agreement.
- It includes a number of functions for conducting intermediate checks in order to control quality and identify errors in construction technology.
- Supervision of compliance with all aspects of safety and compliance with environmental standards is carried out.
- The management can make suggestions to improve the quality and optimize the construction and installation work at the facility.


Any clauses established individually, depending on the functional and operational orientation of the construction object, can also be included in the contract.
Activation of works in the process of construction
The finished project is a complete complex. To make sure that the established norms of SNiP, ENiR and other regulatory standards are met, an act is issued. It is also necessary to draw up an act of hidden works. What it is? Hidden works are "hidden" behind subsequent constructions or already completed activities. Compliance with quality standards is confirmed by an act drawn up in accordance with all the rules. The list of hidden works includes laying the foundation, land surveying, fixing wall structures. The quality of each of the above named hidden works, compliance with the norms of SNiP and other standards is confirmed by the act.
Advice! For each object, a list of hidden installation and construction works is prepared at the design stage. Such an act is rarely filled out at the stage of finishing the buildings.
Each stage is subject to separate control, even if simple repairs are made in the apartment (priming, finishing, insulation or installation of communications, and much more). An act, or a form confirming the operational process, must be drawn up by an authorized person, which is regulated by the SNiP standards.


Important!Maintenance of accompanying technical documentation is a mandatory procedure.
The act of carrying out hidden construction work is taken into account in the sixth section of the general work log. The act must strictly comply with the established form, is prepared in duplicate and signed by representatives of the construction commission. The act contains the following information:
- A complete list of all work performed with quality control marks at each stage.
- All information about the project documentation, which confirms the entire operational process. The section may contain drawings, diagrams, explanatory notes.
- Entering into the act the results of measurements, calculations, which confirm the level of quality of the work performed.
- List of conclusions indicating compliance with the norms of SNiP, ENiR and other requirements.
Today, finding a standard act confirming any operational process, and a guide to filling it out, will not be difficult. There are samples on specialized construction sites.


Safety at height
As they say in the song of the same name, assemblers-workers from a height send us greetings! In fact, construction and welding installation activities at height are extremely dangerous work, requiring compliance with a number of safety rules. For such work at height, it is categorically not recommended to take on beginners without appropriate training and experience.
Important! It is necessary not only to know the specifics of work, to be instructed and to study the manual for organizing safety at height.
For the personal comfort of workers at the facility, equipping the construction site requires the arrangement of sanitary and hygienic facilities, washrooms and wardrobe facilities, specialized food points. Mandatory, prohibition and warning signs must be placed on the territory of the construction site. What activities relate to construction and welding and installation work at height?
- The implementation of the ascent or descent at a height of more than five meters vertically, the angle of inclination is not more than 75 degrees.
- All construction and welding and installation work that involves the risk of falling from a height of more than 1.8 meters or more. Including all welding and installation works that are performed on machines or mechanisms, protruding objects or structures, above the water surface.
- Any activity on platforms that are at least 1.8 meters high, located closer than two meters to an unfenced drop, and the height of the fences is less than one meter.


The list of basic safety requirements at height includes the following items:
- permission to work is given to a person who has reached the age of 18;
- before performing welding and installation work, the specialist must undergo a medical examination;
- there are certain requirements for the qualification of a specialist and his professional readiness to perform high-altitude work.
- the frequency of employee training should be at least once every three years (professional training and practical training are mandatory).
Important! Before the start of high-altitude welding and installation work, a planned inspection of the site and its preparation are required.
To give access to work, the possible causes of falls from a height, the reliability of fastenings, the presence of fragile, slippery or prone to destruction surfaces, and the strength of structures are first clarified. Climatic conditions for holding high-altitude events are necessarily taken into account, a list of tools needed at height and ways to deliver them to the top is drawn up. Basic safety rules at height:
- All authorized workers must be equipped with special safety belts. Each must have a test mark, admission to work with a belt that does not have a corresponding tag is prohibited.
- High-altitude welding and installation work should be carried out only in the daytime. If the regulations require the holding of night events, admission to work requires the installation of high-quality lighting on the site.
- The admission to work in the winter period implies periodic cleaning of the surface from ice and snow.
- The manual does not give permission to work if the wind force is 6 or more. During a thunderstorm, snowfall or fog, construction work at height is also prohibited.
- All decking, transitions, fences, scaffolds are installed by specialists, taking into account load calculations. It is forbidden to move or rebuild them.
- When moving an employee up or down, he is not allowed to hold tools or equipment in his hands. It is lifted on separate cables.


Important! In addition to the direct danger of falling from the height of the worker, there is a threat of injury to people who are below. To prevent this, warning signs and barriers are installed around the perimeter of the site.
The admission of unauthorized persons to the construction site is prohibited, the management is responsible for this. Employees may not use pneumatic tools for work at height, arbitrarily build stairs without preliminary calculation of loads, carry out any activity on sites without fences or faulty structures. Compliance with safety regulations in the production process at height is a guarantee of the personal health of the employee, as well as those who are below the facility. Safety is the responsibility of management. The implementation of construction and installation activities is the most important and responsible part of the production of the entire construction process. Only competent planning, budgeting in accordance with the ENiR data, the choice of professional specialists and the optimal organization of construction and installation work together will help to achieve the desired result.
Safety in construction.
Our company is known in Smolensk and beyond due to the quality and timely fulfillment of its obligations. We offer our customers a quick solution to all issues related to the production of construction works.
Specialists participate at all stages of production activities and make a careful selection of mechanisms and materials, as well as apply modern technologies to perform this type of work. Regular customers of our organization receive a number of additional services, which is a motivating condition for working with us in the future. You can get comprehensive information about all services on the website or by calling the phone number indicated in the contact details.
Definition of construction work
The production processes associated with the construction of buildings, structures, structures and other linear objects are called construction works.
Construction works are the most time-consuming and large-scale, they involve a large amount of equipment and human resources, and include many technological processes and operations. Thus, this process includes the following types of work:
- general purpose works - land, pile, concrete and others;
- special purpose works - heat-insulating, waterproofing, electrical installation and others;
The company provides land, pile, concrete and roofing as the main type of services. Our employees are highly qualified, knowledgeable in the field of modern technologies and production equipment. They are able to perform the most difficult tasks in this area. As a separate type of services provided, we perform works related to roofing of buildings and structures. Specialists go to the site, make measurements, select the type of material and carry out the planned work.
Land
Earthworks are the starting point in the production of construction and are one of the most voluminous and labor-intensive processes. This activity includes the following operations:
- overburden operations related to the movement and storage of soil and vegetable soil;
- construction of earth ramparts and embankments;
- digging trenches for cable lines and pipelines for various purposes;
- digging pits for the foundations of buildings and structures;
- organization of a network of drainage and drains;
- planning of the earthen surface in the building area;
- backfilling and compaction of soil in trenches;
- preparation of the base for the path of construction equipment;
- landscaping work.
All technological processes are carried out taking into account the requirements of SNiP and using modern mechanisms - excavators, cranes, graders and scrapers. When carrying out earthworks, it is also necessary to take into account the season and climatic factors that affect these processes.
pile
Pile work is necessary for the construction of structural supports that transfer the load from buildings and structures to strong and stable soil layers. Our team of specialists performs these types of work at a high level and in a short time.
Piles passing through all layers of the soil and transferring the load through their ends are called support piles. If the piles transfer the load only through the side area, then they are called hanging.
According to the type of material used, piles can be:
- concrete;
- reinforced concrete;
- steel;
- wooden;
- combined (combine different types of materials).
Piles, consisting of several types of materials, are widely used in construction.
According to the installation method, piles can be:
- driving;
- stuffed;
- placed in the thickness of the soil in a finished constructive form;
- constructed in a pre-prepared well.
When carrying out work, we deliver piles of the required design and prepare pile drivers for driving them, if necessary.
Concrete
Concrete work is a production process, without which no building can do. These works are the initial stage in the construction of foundations, buildings and other massive building structures. They include the following production and technological processes:
- preparation and movement of the concrete mix to the construction site;
- construction of formwork and reinforcement cage;
- pouring concrete and work on its compaction;
- hardening concrete care;
- removal of formwork from the finished structure;
- concrete surface treatment.
Our company has concluded an agreement with a concrete production plant and the organization's specialists can only deliver the mixture to the customer's construction site.
Roofing
Roofing is the process of covering the upper part of the roof with various waterproofing materials that protect the structural elements of buildings from atmospheric precipitation, and also ensure that water is drained to the ground. These works include the following steps:
- preparation of roofing material and waterproofing mastics;
- preparation of the base for the roof;
- roofing and fixing.
Our company occupies a leading position in the provision of services in the field of roofing in Smolensk. We offer our clients the most demanded materials for this type of work. This includes the following types:
- roofing material, isoplast and rubemast;
- steel profile;
- polymer membrane;
- tiles;
- asbestos cement slate.
We discuss in advance with the customer the type of material and the weather and climate conditions in which he will have to work.
Our company is a worthy partner for its customers in the construction services market in Smolensk.
Recently, the demand for all types of construction work has increased significantly. The reason for this is the constant desire for change. Some acquire new housing, others create a unique design. Construction and installation work, which will be discussed in the article, includes a huge range of activities. We will talk about them today.
Types of jobs
First of all, construction and installation works are divided into actions related to general construction and special manipulations. General processes include the following types:
- earthen;
- concrete or reinforced concrete;
- stone;
- finishing;
- carpentry;
- roofing.
Special events include:
The volume of construction work directly depends on the purpose and expected result. The more global the construction, the greater the volume will be.
Depending on how many processes are performed by machines, there are:
- fully mechanized work,
- partially mechanized,
- manual labor.
Types of construction work can also differ in the complexity of their implementation. Simple are those that can be carried out by one person or a small group of builders. At the same time, the processes are logically connected with each other according to the specifics of execution. Difficult consider those works in which a large number of people are involved, as well as various construction equipment. However, there are cases when a complex of simple manipulations is performed in the same way.
Home construction
If you are planning to build a house, then you will have to master all types of construction work. This happens in stages.

- The first thing it all starts with is the earthen processes, during which the foundation is being built, walls are being erected, and the basement floor is being made.
- The second stage of construction is work already above the ground, namely: installation of structures, laying walls from the selected material, construction of openings, manipulations with wood and roof.
- The third and final stage is the decoration of the house. At the same time, you are working with wiring and all electrical equipment in the room.
Overhaul
Repair and construction works are divided into two categories: capital and current. What is meant by these concepts? The need for a major overhaul of the building, first of all, is indicated by its appearance. It's not just scuffs and minor problems. As a rule, this is global destruction, collapses and strong faults.

Works that are classified as major repairs:
- restoration of the destroyed parts of the building, house, apartment;
- global restructuring and replacement of the main structures;
- strengthening of the elements that have become unusable.
Maintenance
The current repair is also a repair and construction work, but in terms of volume, such processes are much smaller and do not cover much of the area involved. Moreover, such orders are cheaper. It is worth saying that the prices for construction work completely depend on the volume and complexity of the process being performed.
The need to carry out maintenance appears much more often than the need for capital work. A person's need to live in comfortable conditions tells him when it's time to make an upgrade.

Types of construction work that are classified as current repairs:
- partial replacement of elements of the floor, walls, roof and other places;
- wall correction;
- door repair;
- change of wallpaper, parquet, linoleum;
- painting walls, floors, ceilings;
- work to eliminate cracks, cracks, leaks.
building materials
The quality of construction work largely depends on the qualifications of the master. However, the final result, that is, the external beauty and reliability of the structure, depends on the choice of material. In the modern market of construction products, there is a huge number of various companies offering their services. Sometimes it is difficult to choose high-quality material on your own, so trust the advice of experts. It is best if the choice is made directly by the executor of the order. This way you can file a claim at the end of the process. Otherwise, it will be difficult to do so.
Let us give an example of the choice of material for housing construction. For example, if you decide to build a house out of wood, then at your service:

Each of the materials has its own advantages and disadvantages. And the choice should be made by someone who knows all the features of the process and the purpose of construction. But these types of bricks are available for those who build a stone house:
- ceramic;
- silicate;
- facing;
- facade;
- furnace.
Already by the name it becomes clear for what purpose the brick was made, but still there are nuances in terms of manufacturer and quality. It happens that the same material from different manufacturers is fundamentally different from each other. Be careful when choosing such products, because this is half the success in construction.
Finishing
Construction and finishing work is the creation of a kind of "soul" of the room. It is at this stage that it acquires its final form. In some cases, all the work, including finishing the premises, is performed by the same contractor, but sometimes it becomes necessary to find another contractor. In the course of finishing, the flooring is being manipulated, wallpaper is being pasted, walls are being painted, work is being done with stone and wood. Using high-quality material, you guarantee yourself a unique look of housing. In addition, you need to think about its strength and safety.
Design
Describing the types of construction work, we sooner or later approach the design of the premises. This is a special science, accessible to not many people. The presence of finances and desire does not mean the presence of taste. Therefore, when developing a room design, we recommend that you seek advice from specialists if you are not sure of a good result. A professional will carefully analyze all the features of your premises and develop the option that will look best for you.

There are many design secrets. One of them is the process of selecting the color scheme of the room. Shades are of great importance in design. They show or hide flaws. Here are some examples:
- in a room that is constantly in the sun, it is better to use cold tones: blue, blue-green, blue-violet;
- on the north side, it is better to give preference to warm tones: red, yellow, orange;
- white, gray, black colors are considered neutral, so they can be used in any room;
- it is important to maintain color - colors that combine with each other, otherwise the room will look awkward;
- when combining colors, you can follow two directions: contrast and nuance. The first is acceptable for the kitchen, living room, hallway, and the second, more calm, suitable for bedrooms, nursery.
The mood of the people living in it depends on what design of the room you choose. This has been proven by scientists.
Style
When discussing construction and finishing works, one cannot ignore such a topic as the style of construction. After all, when a person plans to build a house, the first thing he imagines is how his housing will look like. What are the current styles of houses?

In many ways, the style of the building depends on the financial capabilities of the customer.
Rates
Construction work rates vary depending on the contractor and the complexity of the process. Each company has a price list with prices. Before placing an order, read all the documents and clarify the details. It is very important to find out the reasons for which the prices for the performance of certain works may be increased. It is best if the cost of the entire order is indicated initially. Then at the end of construction you will not expect an unpleasant surprise.
And lastly, work only with trusted companies. Nowadays, there are a lot of scammers or simply unskilled workers. The ideal option would be if you act on the recommendation.
Capital construction cannot be imagined without construction and installation works. Moreover, the object of construction and installation can be not only building metal structures, but also: foundations and supports, walls and roofs, window and door blocks, technological equipment, engineering systems.
Types of construction and installation works are always carried out taking into account the specific area of work of the construction object. The result of the project depends on the efficiency of construction and installation. Therefore, the types of construction and installation works are offered by the contractor and are listed in the terms of reference (TOR) of the customer. In this publication, we will consider the main types of construction and installation works necessary for the construction of buildings and structures from LMK.
Construction and installation work is the general name for all work in construction.
- Construction work is usually called general construction and is associated with the construction of building structures, buildings and structures.
- Installation work is carried out using ready-made metal structures, their elements, connections and mounting parts.
Types of construction and installation works can be combined, or they can be performed separately. Since our company is a manufacturer, designer and builder, we offer our customers any kind of construction and installation work in a comprehensive turnkey service. Read about the features of this form of service, as well as the benefits of a turnkey service, on this website. It is necessary to understand the main thing that turnkey service is a convenient and economical cooperation, with an optimal ratio of price and quality. For all questions about the turnkey service, please contact the company's managers by phone or in writing!

We list the main types of construction and installation works:
- Earthworks include digging pits, pits, trenches for foundations. Earthworks included the construction and installation of basements, underground utilities, transportation of soil, taking into account loading, removal, unloading, area planning, stripping, embankment, soil compaction.
- Pile work includes piling foundations, piling or piling.
- Stone works relate to the construction of walls, supports, vaults, pillars, large concrete blocks.
- Concrete and reinforced concrete works are related to the production of concrete and concrete mortar, its transportation, laying, formwork, concrete maintenance, taking into account the season and creating conditions for its hardening.
- Monolithic works are used for formwork and reinforcement of monolithic sections.
- Construction work is related to all, including general and special types of construction.
- Carpentry and joinery work is the installation of rafters, windows, doors, parquet flooring.
- Roofing works include roofing, attic roofs, etc.
- Finishing work is associated with plastering, cladding, wallpapering the walls of buildings, and the installation of industrial concrete floors.
- Installation work begins with the delivery of metal structures to the workplace, their precise installation, alignment and fixing.
There are also special works that are included in the types of construction and installation works, which include the construction and installation of engineering communications, the laying of power, telephone wires, the installation of sanitary, warehouse, technical, lifting equipment, as well as anti-corrosion and fire retardant protective coating of metal structures.
All of the listed types of construction and installation works are included in the turnkey service, on which the customer can save up to 40% of the construction budget. For all questions of cooperation, please call 209-09-40! We will be glad to hear from you!