How deep should the foundation for the house be. What should be the depth of the strip foundation What should be the thickness of the strip foundation
Despite the fact that the depth of the strip foundation is not the only indicator of reliability and durability, it plays a huge role in the integrity of the entire house during its operation. Reinforced concrete tape of any size and brand of concrete may burst over time if it is incorrectly placed in the ground, not taking into account its features.
In order not to get confused in all types of foundations and soils, let's try to understand everything in order. First, we will analyze the types of monolithic tapes, and then, specifically for each type of strip foundation, we will determine the depth of the foundation.
Factors affecting the depth of strip foundations
It is probably worth starting with the fact that the strip foundations themselves are divided into three main types:
- Unburied
- Shallow
- Buried
Each of these types is laid to a certain depth, which depends on several main factors:
- Soil freezing depth
- Soil type
- Ground water level
It is worth noting that strip foundation depth- this is the distance from the soil surface to the base of the foundation, and not the depth to which the trench is dug. In the trench, in addition to the foundation, there may be a pillow.
Now let's see how these factors affect each type of strip foundation separately.
Unburied strip foundation
An unburied strip foundation is extremely rarely used in the construction of private houses, because it is a very weak support for the future structure. As a rule, it is all located on top of the ground, and inside there is only a sand or sand and gravel cushion.
I won’t write much about the non-buried strip foundation, especially since a whole article was already devoted to it earlier. And in general, the very concept of the depth of laying in such a foundation is absent.
Calculation of the depth of laying strip shallow foundations
 This is the most capricious, in terms of the depth of the foundation. Firstly, it is not as reliable as buried, and secondly, in order for such a strip foundation to withstand the load of the structure, and also to restrain all the heaving forces transmitted from the ground, its calculation must be approached with special responsibility.
This is the most capricious, in terms of the depth of the foundation. Firstly, it is not as reliable as buried, and secondly, in order for such a strip foundation to withstand the load of the structure, and also to restrain all the heaving forces transmitted from the ground, its calculation must be approached with special responsibility.
How to fill in, I have already described in detail in one of the previous articles. Therefore, we will not go into details.
Such a strip foundation is laid to a depth that is much higher than the depth of freezing of the soil, which is why it is called shallow. It, in contrast to the buried one, can be largely affected by the forces of heaving of the soil.
Also, an important difference between shallow foundations is that it must be made monolithic not only below the ground level, but immediately, after putting up the formwork, pour the above-ground part of the foundation - the basement. This will greatly strengthen the entire strip foundation.
The depth of laying a shallow foundation directly depends on all three factors described above. In order not to get confused, let's look at the table.
Table No. 1: Depth of laying a strip shallow foundation (minimum), depending on the type and depth of soil freezing
| Depth of soil freezing, m | Depth
foundation, m |
|
| The soil is slightly heaving | The soil is not porous,
hard rocks |
|
| over 2.5 | - | 1,5 |
| 1,5 - 2,5 | 3.0 or more | 1,0 |
| 1,0 - 1,5 | 2,0 - 3,0 | 0,8 |
| less than 1.0 | less than 2.0 | 0,5 |
|
Note:In order to find out what the depth of soil freezing is in your region, look at table No. 2 below, where the values \u200b\u200bare given for some cities, taking into account the type of soil. Click on the table to enlarge. |
||
Table No. 2: Depth of soil freezing in some regions

Note: In addition to the fact that the depth of freezing and the type of soil affect the depth of the strip foundation, one more very important factor should not be discarded - the level of groundwater, which we will talk about later.
The dependence of the depth of laying the strip foundation on the groundwater level (GWL)
There are two options for the location of groundwater - when they are located below the freezing depth of the soil, and when - above.
The groundwater level is below the freezing depth of the soil
 This can be considered a good indicator, and in this case, groundwater in most types of soils does not have a particular effect on the depth of the installation of a monolithic reinforced concrete tape.
This can be considered a good indicator, and in this case, groundwater in most types of soils does not have a particular effect on the depth of the installation of a monolithic reinforced concrete tape.
The only limitation, in this case, is that in such soils as loams, clays and the like, the tape must be laid at least half the freezing depth of such soil. In other, “good” soils, this factor does not affect the laying of the foundation.
In other words, if the freezing depth in your region is, for example, 1.5 meters, then the tape shallow foundation must be arranged at least 0.75 meters.
The groundwater level is above the depth of soil freezing
If groundwater is high, then the depth of digging a trench for strip foundation does not depend on their level only on rocky soils, sandy coarse-grained, gravel and the like.
On any other types of soils with a high GWL, the monolithic tape will have to be buried below the freezing depth by 10-20 cm (table No. 2). In this case, it will become a deep foundation.
Buried strip foundation
 A recessed strip foundation is considered the most reliable of all tapes. It is laid below the freezing depth of the soil by 10-20 cm. Another condition for its construction is that the soil under its sole must be more or less solid.
A recessed strip foundation is considered the most reliable of all tapes. It is laid below the freezing depth of the soil by 10-20 cm. Another condition for its construction is that the soil under its sole must be more or less solid.
In the case of swampy soils, peat bogs and the like, the strip foundation is laid to a depth that is below these layers. In some cases, it is enough to dig a trench to hard ground, and then arrange a sand or sand and gravel cushion to a level that is slightly below the freezing depth of the soil in your area.
When the soil at the construction site is very bad for laying a strip foundation, or its installation is very expensive, you can try to calculate another type of foundation, for example, slab. Perhaps it will be both cheaper and more reliable.
How to reduce the depth of the strip foundation
After carrying out all the calculations on the depth of laying the strip foundation, it often happens that, taking into account the soil and the region, it must be laid very deep. This raises the question of how to cut costs and reduce depth.
There are several ways to reduce the depth of strip foundations, all of which are based on reducing the importance of the main factors affecting the foundation.
Reducing the depth of soil freezing
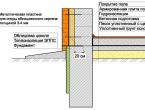
 Of course, we will not be able to change the climate in the region, but we will be able to change the depth of freezing, specifically under the base of the foundation, by insulating the foundation itself and the soil adjacent to it from the outside.
Of course, we will not be able to change the climate in the region, but we will be able to change the depth of freezing, specifically under the base of the foundation, by insulating the foundation itself and the soil adjacent to it from the outside.
In this way, we can reduce the depth of the foundation, as well as reduce the cost of it.
Groundwater drainage from the strip foundation
Another effective way to reduce the depth of the strip foundation is to drain water from it.
This is done with the help of a good drainage system, which will divert a significant part of the water from the foundation and prevent it from adversely affecting it.
Sand or sand and gravel cushion under the foundation
In the case when heaving layers of soil lie deep enough on the site, strip foundation will also have to be laid to a greater depth. You can reduce it by replacing the heaving soil with a sandy or sandy-gravel cushion.
In other words, it is necessary to dig a deep trench to hard ground rocks, and then arrange a massive sand and gravel cushion there, which will distribute the load from the foundation and the house to the ground evenly and prevent heaving forces from adversely affecting the foundation.
It is advisable to make a pillow not only under the sole of the foundation, but also next to it, as shown in the diagram. 
It should be noted that the most reliable method for reducing the depth of the strip foundation is the combined method, i.e. and a pillow device, and insulation, as well as a drainage device, if necessary.
Strip foundation height
The maximum height of the above-ground part of a monolithic strip foundation with internal filling of the space limited by the tape with soil (sand) should be equal to four dimensions of the width of the strip foundation. (Foundation height above ground = 4x foundation width)
|
Section width. |
Section height, mm |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
*The table is given according to the table3.2 from the design manual "Reinforcement of elements of monolithic reinforced concrete buildings", Moscow, 2007.
For example, the total height of the underground and aboveground parts of a strip foundation 40 cm wide should have an optimal height of 80 cm to 120 cm.
According to English recommendations, the aboveground part of a monolithic shallow strip foundation cannot be larger than its underground part, but can be arbitrarily smaller than the underground part of the foundation. The most common option is the depth of laying a monolithic shallow strip foundation and its height above the ground equal to 50 cm, that is, the total height of the strip is 1 meter (if the conditions of the underlying soils allow). If you need an above-ground plinth 80 cm high, then it is recommended to arrange the underground part of the strip foundation with a depth of at least 80 cm. These English recommendations (like many others) are not confirmed by the requirements of Russian building codes, but may be useful when designing reliable strip foundations.
The length of the building on the strip foundation
Extended buildings should be cut along the entire height into separate compartments, the length of which is taken: for slightly heaving soils up to 30 m, medium heaving soils up to 25 m and strongly heaving soils up to 20 m, excessively heaving soils up to 15 m [VSN 29-85].
Strip footing width
Minimum structurally limited. the width of the foundation strip is 15 cmand not less than the width of the shoulder of the concrete cushion protruding from under the tape [ BR 2010 A1/2, paragraph 2E2-c] ,
and for strip foundations for country houses, the minimum width is at least 25 cm - 30 cm. The width of a strip shallow foundation cannot be less than the width of the wall supported on it. The minimum width of the strip foundation for light garden buildings (arbors, sheds, sheds, small baths) must be at least the minimum allowable width of a reinforced concrete beam, that is, 15 cm.
In addition to the minimum design restrictions, there are also requirements set by bearing capacity of soils under foundations. The specific load from the building per unit area should not exceed 70%
from the bearing capacity of the soil. You can regulate the amount of load using the area of \u200b\u200bsupport of the foundation on the ground. The larger the support area, the lower the specific load transferred to the ground.
For single-family (individual) frame residential buildings, which make up a fairly large proportion of all summer cottages, there are separately prescribed standards for the depth of foundations in the Code of Rules SP 31-105-2002 “Design and construction of energy-efficient single-family residential buildings with a wooden frame”. They are applicable when the following conditions are met simultaneously:
the span of floor beams resting on foundations (basement walls) does not exceed 4.9 m;
calculated uniformly distributed loads on floors do not exceed 244 kgf/m2;
design soil resistance is not less than 0.75 kgf/cm2.
Table number 20. The minimum width of the strip foundation for an individual frame house.*
|
Number of overlaps |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(floors) |
under the outer walls |
under interior walls |
under columns at a step of 3 m, m2 |
|
|
Values at very high groundwater levels (depths less than foundation width) |
||||
|
Number of overlaps |
Minimum width of strip foundation, mm |
Minimum area of the base of the foundation |
||
|
(floors) |
under the outer walls |
under the outer walls lined with bricks |
under interior walls |
under columns at a step of 3 m, m2 |
|
Note: The area of the base of the foundations for columns located with a step different from that given in the table should be taken in proportion to the decrease or increase |
||||
Many land owners dream of a large and bright house, with a staircase and an attic. To translate such fantasies into reality, it is necessary to calculate and build a foundation for a two-story house.
Types and features
The bearing system for a two-story building must be more rigid than for a small building. This is due to the great pressure of the house on the ground, exerted by two floors and a large number of interior partitions.
Photo - strip foundation project for a two-story house
There are several types of supports for a private house:
- strip foundation;
- Columnar;
- Monolithic.
The pile foundation is categorically not suitable because of its instability. Stilted options can support a one-story brick house, but a tall two-story building, even from a bar, will be too heavy. Screw piles can be useful when installing a small two-story utility building, but they are not recommended for home construction - it will be difficult to legalize the construction later.
Columnar is installed under the usual tape, as in the photo. This helps to further strengthen the structure. In most cases, this option is used on moving soils or swampy areas.
 Photo - pillar foundation
Photo - pillar foundation The strip foundation for a private two-story house is easy to do with your own hands, it is this type of construction that modern masters most often resort to. The tape allows you to ensure the correct distribution of loads between walls and nodes, and save a significant amount of money on concreting. When choosing such a design, it is very important to calculate the loads that will be placed on the carrier system in order to calculate the optimal depth and width of the support and sole.
A monolithic slab is the most expensive, but also the most reliable type of foundation for a private building. Despite its high cost, such a fill is often used in individual construction, because with the correct calculation of the dimensions of the foundation, it provides a reliable foundation for the house. The reliability of such a foundation is undeniable, it is believed that even during the movement of the earth (for example, during heaving or small tremors), a correctly calculated monolithic foundation will remain intact.
 Photo - an example of a foundation design
Photo - an example of a foundation design Video: which foundation to choose
Foundation calculation
The height and thickness of the foundation for a two-story house are the main parameters that you need to know in order to calculate the bearing capacity of the system.
To build a foundation for a house of foam blocks, gas silicate or silicate bricks, you need to find out the minimum width of the base of the support system:
In this case, the value may change with an increase in the level of groundwater. If you plan to build a house in a swampy area, then you also need to calculate the height of the drains. This is important not only for the level of depth, but also for calculating the width. If, during the rise of groundwater, the depth of the proposed base becomes smaller than the width, then the values \u200b\u200bchange upwards:
The thickness of the foundation tape depends on the level of soil freezing, you need to understand that this indicator and the depth of the support are one and the same. To correctly calculate this indicator, you need to know the level of soil freezing in your area. In the Russian Federation, the freezing level varies between 1 meter and 1.8. At the same time, in the middle lane, you need to adhere to indicators of 1.5 - they are optimal. You can find out more exact values in any geological bureau of your region.
If the house is planned with a basement, then also be sure to check the level of groundwater. In some cities, it is so high that even drainage does not save. But even these indicators are not final. In addition to internal parameters, you also need to calculate the height of the foundation above the ground. This value depends on the building materials of the house and the supporting system. For example, for a support made of aerated concrete and foam concrete, this value is 300 mm, for a conventional concrete mortar - 200 mm.
 Photo - an approximate calculation of the foundation for a two-story house
Photo - an approximate calculation of the foundation for a two-story house In this case, the monolithic slab should be smaller. In most cases, for a cement poured foundation, a height of more than 150 mm above ground level is sufficient, and the width of the sole is taken with indicators 50 mm wider than the walls of a two-story house.
Reinforcement
Strengthening the support is necessary to give the structure additional rigidity. You need to install reinforcing units at the intersections of the walls, as well as under the bearing walls. Reinforcing wires are connected using bundles or welded joints.
 Photo - reinforcement for strip foundation
Photo - reinforcement for strip foundation The foundation for a brick two-story house must be additionally reinforced. This will help protect the base from stretching and deformation during operation. It is best to use ribbed reinforcement for a tall building. It is suitable for a frame building and a house made of gas blocks or gas silicate. Due to the uneven structure, it is this wire that provides maximum adhesion to the concrete mortar of the foundation.
 Photo - strip foundation options
Photo - strip foundation options How to pour the base
To make a foundation for a wooden, brick or block two-story house, you will need to mark out the site. There should be no communications in the marked area, since when digging trenches, pipes can be damaged. Pits of the selected size are dug, after which the walls are compacted. Next, you will need step by step guide:

Do not forget that depending on what material will be used for the foundation, it may need to be isolated from moisture. All types of foam blocks, aerated concrete slabs will need to be covered with a special film on all sides before installation. To do this, install the film on a sand cushion and carefully mount building materials on it.
Any foundation, regardless of type and device, is characterized by such parameters as the depth and width of the supporting structures. Many developers take the thickness of the load-bearing walls of the house as the width of the foundation, but this calculation is not always correct. The depth of the sole is also calculated by eye, taking into account personal experience and minimal knowledge in this area, but this is not worth doing.
In fact, the dimensions of the tape base depend on many factors, here the length of the tape is not taken into account, because these are the dimensions of the future home. But the width of the strip foundation and the depth of occurrence is calculated separately, and this must be done for each building individually.
Important parameters for determining the dimensions of the base

- The design of the future building, as well as building materials that will be used in the construction of the structure.
- The mass of all building structures, taking into account the weight of load-bearing walls, ceilings and roofs.
- External climatic factors, such as the duration and snowiness of winter, the accumulation of wet snow, the duration of showers.
- Soil type and arrangement.
There are no clear standards, where there are all the necessary formulas for calculating the maximum allowable size of a house. There are empirical calculations, according to which the strip foundation is then built, and the overall dimensions of the structure will be provided by the architectural service.
Determining the type of soil

Not only the depth of the base device, but also the width of the bearing sole depends on the type of soil. Since there is a factor of heaving of the soil in winter, and this property of the soil can lead to irreparable destruction of the foundation and the house.
It is possible to determine the type of soil not only with the help of specialists, but also by artisanal methods. To do this, it is enough to take the earth and moisten it with water, and then bend it into a ring. Clay will retain its structure. Loam crumbles into several parts, and sandy soil immediately crumbles into powder. So you can determine the structure of the soil. Sandy soil with a fraction of 1.5 mm perfectly withstands heavy loads, it is optimal for the construction of strip foundations and does not contain much moisture.
Then, you need to determine the depth of groundwater. To do this, you can go to the nearest well and measure the depth of the water reservoir, this should be the maximum height of the ground horizon. With the help of small mathematical calculations, the depth of the aquifer will be calculated.
You don't have to do a soil analysis yourself. It is enough to contact the geodetic service. It will give a complete map of the composition of the soil, even taking into account the depth of soil freezing, and this parameter for choosing the depth of the sole will be considered key.
How to calculate the depth and width of the base

As soon as the composition of the soil and the depth of groundwater are clearly defined, you can begin to calculate the size of the base. If the building is massive enough, high and has several floors, then the depth of immersion of the base should be large, up to the border of soil freezing.
Developers who have the financial resources are trying to deepen the foundation even lower, thus providing the foundation with greater strength and reliability. The height above the zero level should be up to 30 cm, sometimes more, for arranging the basement and the blind area.
So, the minimum depth of the strip base for massive buildings should be GPG + 60 cm. GPG is the depth of soil freezing. This tabular value is different for each region and soil composition. For light buildings, it is enough to equip the foundation at a depth of the freezing line or below 50 cm. In such cases, it is believed that due to the mass of the structure and the tape of the base itself, the soil will spread evenly under the sole, and swelling of the soil should be minimal.
The standard thickness of the strip is 40 cm, it can be increased as needed, but it should not be less than the thickness of the building's load-bearing walls.
Calculation of the area of the sole of the foundation

The sole area is responsible for the uniform distribution of the mass of the entire structure, together with the base on the ground. Therefore, it will not always correspond to the width of the tape, in most cases it is larger. Moreover, the sole is also responsible for such functions:
- Uniform distribution of the mass of the building.
- Prevents local heaving of the soil due to seismic shocks or the impact of deep soil layers.
- It strengthens weak soils with its mass and presses them to strong soils.
- Provides uniformity of the device of the building itself on a horizontal plane.
The sole area is calculated by the formula:
S = k(n)*F/k(c)*R
- k(n) – reliability coefficient, taken as 1.2. This coefficient means that already initially the sole area will be 20% more than the calculated one;
- F - Estimated load on the base. It consists of: the mass of the building, the loads from the soil, the mass of the foundation;
- k(c) - coefficient of working conditions, taking a value from 1 for clay and rigid structures with stone walls, to 1.4 for coarse sand and non-rigid structures;
- R is the design resistance of the soil (these are tabular data). You can find them in reference books for all types of soils.
In fact, all parameters are reference, so it remains only to calculate the load from the building itself.
Building load calculation
 Table with the calculation of the width of the strip base, depending on the material of construction (for a house made of foam blocks and bricks, a house made of timber) in the middle lane
Table with the calculation of the width of the strip base, depending on the material of construction (for a house made of foam blocks and bricks, a house made of timber) in the middle lane This parameter is calculated by summing up all the loads that the building creates on the base:
- Masses of load-bearing walls and ceilings (here the amount of building materials necessary for the construction and their total weight are calculated).
- Coated roof masses.
- Masses of a snowball that can be fixed on the roof and press down with its mass, transferring the load to the load-bearing walls and foundation.
- The weight of all furniture, appliances and laid communications (this indicator is insignificant, it is often neglected or a coefficient of 1.1 is set).
- The weight of the foundation itself. This is where the difficulty in the calculations already arises, because the area of \u200b\u200bthe sole also affects the mass of the base. Therefore, a strip width of 40 cm is taken, knowing the length of the building, the density of concrete (2400) from the project, all this is multiplied and the weight of the foundation is obtained.
Estimated foundation height
 Estimated depth, width and height of the strip base for a house made of foam blocks, bricks or timber in the middle lane
Estimated depth, width and height of the strip base for a house made of foam blocks, bricks or timber in the middle lane The height of such a base must be large enough to withstand horizontal ground movements and groundwater. The height of the strip foundation, knowing the depth of freezing of the soil, is also not difficult to calculate. But at the beginning of the construction of the foundation, the height will be completely different, and here's why. It consists of the following layers:
- First you need to make a sand and gravel cushion at the bottom of the trench, on which the foundation itself will lie. The thickness of the layer varies between 25 - 40 cm (depending on the type of soil), and this is an additional height of the structure.
- Depth of soil freezing (reference data).
- You also need to make a base up to 30 cm, sometimes more, depending on the type of soil and design solutions.
Now that there are all the necessary parameters for the future strip foundation, it is not difficult to calculate the required amount of reinforcement and concrete mortar for its arrangement. If the filling is carried out strictly according to the technology, then the base will last the maximum possible period.
When erecting a strip foundation, it is important to correctly carry out all preliminary calculations and determine the parameters of the foundation. One of them is the width of the foundation, which is directly related not only to the calculated value of the base foot area, but also to the thickness of the bearing wall that will be erected on the foundation tape. In this article, we will talk about how wide the strip foundation should be, and how it should be calculated in specific cases.
What affects the final width of the foundation
In the article where we gave an example of calculating the foundation, considerable attention was paid to the selection of the main parameters of the foundation for the house - including thickness. If we consider only the strip foundation, then the width of the tape depends on:
- the total calculated value of the area of \u200b\u200bthe sole of the foundation, which is considered based on the loads from the building (how to calculate them, you can) and the soil itself, or rather its bearing capacity indicators. First, we calculate the total value of the area, starting from which we take the minimum value of the width of the foundation;
- the thickness of the bearing walls that are planned to be erected on the foundation strip. Given this indicator, the thickness of the foundation should be at least 100 mm greater than the thickness of the walls. This value should be enough for the subsequent finishing of the facade of the house;
- reinforcement of concrete monolith. It must be taken into account that the reinforcement for the foundation must work in conjunction with concrete, and for this, a distance (at least 200 mm) must be maintained between the longitudinal bars. We wrote about how to calculate reinforcement for the foundation in a feature article - we recommend that you take the information provided into account
Calculation of the width of the foundation based on the area of the sole of the foundation
Suppose we carried out all the calculations for the soil and loads and found that the minimum value of the area of \u200b\u200bthe sole of the foundation for a house of 6 × 9 m turned out to be 5 square meters. m. We take the width of the tape equal to X, then the total area of \u200b\u200bthe tape is calculated as follows:
2×9×X+2×X(6-2X)=5,
18X+12X-4X²=5
Where X1=0.17 m and X2=7.3 m. Obviously, in our case, the value X1=0.17 m is relevant. This will be minimum allowable the width of the foundation strip.
What should be the width of the base of the house if the thickness of the walls is known
However, the above value is only indicative. Let's say that load-bearing walls with a thickness of 300 mm are laid in the project of the house, which is almost twice the calculated value of the width of the strip foundation. Taking into account the fact that the width of the tape should be 100 mm larger, we obtain the calculated value: 300 + 100 = 400 mm. In total, the foundation width margin will be: 0.4: 0.17 × 100-100 = 135% more than the minimum.
Reinforcement dependency
Usually, reinforcement with a diameter of 12, 14 or 16 mm is used for strip foundations. To assess whether the selected material fits into the selected base parameters (in this case, its width), it is necessary to calculate the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe tape and the percentage that is allocated in the monolith specifically to the reinforcing cage for the foundation. To do this, we take the height of the tape, for example, 0.8 m (depending on the project) and, using the table below, we calculate whether in this case 4 longitudinal reinforcement bars with a diameter of 12, 14 or 16 mm can be used.

The cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe tape will be equal to: 40 × 80 \u003d 3200 square meters. cm.
Provided that the reinforcement should occupy 0.001 part of the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe tape, we have: 3200 × 0.001 \u003d 3.2 square meters. see The table above shows that this value is relevant when using 4 bars of reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm.
The value of the width of the foundation is chosen correctly.