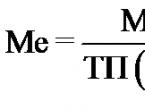How to calculate a heat pump for heating a house. Calculations. Heat pump power calculation
Many owners of private houses decide to create an autonomous heating system in their home. In carrying out the work on its creation, they have to face a number of difficulties. Already at the very beginning, they are forced to decide which energy carrier to use in the system.
If a main gas pipeline passes near the site, then in this case the choice is obvious. To bring gas into the house, it is enough to submit documents for gasification, and after a while, specialists will connect the home to natural gas. However, in our country, despite the high rates of gasification of regions and districts, many people do not have the opportunity to supply gas to their private homes. So they have to use bottled gas.
What to do in such a situation? Using a conventional wood and coal stove for heating is a troublesome task. And if you install equipment powered by electrical energy, it will be quite expensive, although in this case cold air will flow in less. However there are new solutions that have recently entered the market. Installing equipment that uses alternative energy sources during operation is an opportunity to provide heat in a home at minimal cost. In the case of this heating option, heat is obtained from the earth, water and air.
It makes it possible to extract heat from the earth, water and air.
One of the new solutions that is available on the market is a heating system that provides a heat pump as the main working element. It is not necessary to buy this equipment if you decide to use it as part of your heating system. It is quite possible to make such a pump with your own hands. The main thing is to have a desire.
The heating system, based on a heat pump, includes, in addition to this equipment, devices for the intake and distribution of heat. If we talk about the composition of the internal circuit of such pumping equipment, then we select the following components:
Note that the basic principles of operation of this equipment were developed two centuries ago and known as the Carnot cycle. The heat pump works as follows:
- An antifreeze liquid is used as a heat carrier, which is supplied to the collector. The freezer may be:
- water diluted with alcohol;
- brine;
- glycol mixture.
- These substances have the ability to absorb thermal energy and transport it to the pump.
- Once in the evaporator, the heat is directed to the refrigerant. This substance has a low boiling point. Under the influence of thermal energy, the refrigerant boils. The result is steam.
- A running compressor raises the vapor pressure, which causes an increase in air temperature.
- The transfer of heat from water to the heating system is carried out through another element - a condenser. The refrigerant, in order to squeeze out additional heat, is cooled again, turns into a liquid, and then goes to the collector.
- Then this process is repeated in the same cycle.
In simple terms, a heat pump is an equipment that works almost on the same principle as a refrigerator, only in reverse. If we take a conventional refrigerator, then in it the refrigerant moving along the circuit receives heat from the food being stored. At the end of the cycle, he brings it to the back wall. The same heat is used in the case of a heat pump, only it is used to heat the coolant, thanks to which air heating is provided.
A heating system based on a heat pump, of course, consumes electrical energy. But, we note that its amount required for operation is immeasurably less than for a conventional electric boiler. So, spending 1 kW of electrical energy, a boiler that heats water produces 5 kW of thermal energy.
 The costs that arise when purchasing this equipment and during the installation of a heat pump are quite high. They are more than the costs of installing a heating boiler powered by electrical energy. Here, anyone who is thinking about creating their own autonomous heating system in the house may have a question: Is it profitable to arrange such a system? On this occasion, we can say the following: if the system is installed in a house with an area of 100 square meters, then the additional costs incurred for the installation of equipment will pay off within 2 years. Further, the owner of the dwelling will only save on heating.
The costs that arise when purchasing this equipment and during the installation of a heat pump are quite high. They are more than the costs of installing a heating boiler powered by electrical energy. Here, anyone who is thinking about creating their own autonomous heating system in the house may have a question: Is it profitable to arrange such a system? On this occasion, we can say the following: if the system is installed in a house with an area of 100 square meters, then the additional costs incurred for the installation of equipment will pay off within 2 years. Further, the owner of the dwelling will only save on heating.
The heating system based on a heat pump has one important advantage: it can not only heat the room, but also cool the air, that is, it can work as an air conditioner. Therefore, in the summer, in order to get rid of unnecessary heat in the premises of the house, you can turn on a special mode of operation of the heat pump.
How to calculate equipment?
When calculating the power of a heat pump, first of all, it is necessary to focus on the level of heat loss in your home. Naturally, before arranging such a heating system in a dwelling, it is necessary carry out insulation work Houses. It is necessary to insulate not only the walls and floor, but also the roof and windows.

It is optimal if such a heating system is laid still at the design stage of the building. This will create a heating system that provides the most efficient heating of the premises of the building in the winter.
Practical experience shows that the best option for a heating system based on a heat pump is a water heated floor. When installing it, it is necessary to take into account the type of flooring. Ceramic tiles are the ideal flooring material. But carpets, laminate and parquet have low thermal conductivity, therefore, when using such a system, the water temperature should be above 8 degrees.
How to make a heat pump with your own hands?
 The cost of a heat pump is quite high, even if you do not take into account the payment for the services of a specialist who will install it. Not everyone has sufficient financial resources to immediately pay for the installation of such equipment. In this regard, many are beginning to wonder if it is possible to make a heat pump with your own hands from improvised materials? It is quite possible. In addition, when working, you can use not new, but used spare parts.
The cost of a heat pump is quite high, even if you do not take into account the payment for the services of a specialist who will install it. Not everyone has sufficient financial resources to immediately pay for the installation of such equipment. In this regard, many are beginning to wonder if it is possible to make a heat pump with your own hands from improvised materials? It is quite possible. In addition, when working, you can use not new, but used spare parts.
So, if you decide to create a heat pump with your own hands, then before starting work, you must:
- check the condition of the wiring in your home;
- make sure that the electric meter is working and check that the power of this device is at least 40 amperes.
First of all, it is necessary buy a compressor. You can buy it in specialized companies or by contacting a refrigeration repair shop. There you can buy an air conditioner compressor. It is quite suitable for creating a heat pump. Next, it must be fixed to the wall using the L-300 brackets.
Now you can proceed to the next step - the manufacture of the capacitor. To do this, you need to find a stainless steel tank for water up to 120 liters. It is cut in half, and a coil is installed inside it. You can make it with your own hands, using a copper tube from the refrigerator for this. Or you can create it from a small diameter copper pipe.
In order not to experience problems with the manufacture of the coil, you need to take a regular gas cylinder and wrap it with copper wire. During this work, it is necessary to pay attention to the distance between the turns, which should be the same. In order for the tube to be fixed in this position, you should use a perforated aluminum corner, which is used to protect the corners of the putty. Using turns, the tubes should be positioned so that the turns of the wire are opposite the holes in the corner. This will ensure the same pitch of the turns, and in addition, the design will be strong enough.
When the coil is installed, the two halves of the prepared tank are connected by welding. In this case, care must be taken to weld the threaded connections.
To create an evaporator, you can use plastic water containers with a total volume of 60 - 80 liters. A coil is mounted in it from a pipe with a diameter of ¾ inch. Ordinary water pipes can be used to deliver and drain water.
On the wall with the right size L-bracket the evaporator is fixed.
When all the work is completed, it remains only to invite a refrigeration specialist. He will assemble the system, weld copper pipes and pump freon.
Do-it-yourself heat pump installation
Now that the main part of the system is ready, it remains to connect it to the heat intake and distribution devices. This work can be done independently. There is nothing difficult in this. The process of installing a heat intake device can be different and largely depends on the type of pump that will be used as part of the heating system.
Vertical ground water pump
Here, too, certain costs will be required, since when installing such a pump, it is simply impossible to do without the use of a drilling rig. All work begins with the creation of a well, the depth of which should be 50-150 meters. Next, the geothermal probe is lowered, after which it is connected to the pump.
Horizontal ground water pump
 When such a pump is installed, it is necessary to use a manifold formed by a pipe system. It should be located below the freezing level of the soil. The accuracy and depth of the collector placement largely depend on the climatic zone. First, a layer of soil is removed. Then the pipes are laid, and then they are backfilled with earth.
When such a pump is installed, it is necessary to use a manifold formed by a pipe system. It should be located below the freezing level of the soil. The accuracy and depth of the collector placement largely depend on the climatic zone. First, a layer of soil is removed. Then the pipes are laid, and then they are backfilled with earth.
You can also use another way - individual pipe laying for water in a pre-dug trench. Having decided to use it, you first need to dig trenches, in which the depth should be below the level of freezing.
Conclusion
If it is expensive for you to use an electric boiler for heating your home, then you can opt for a heating system based on a heat pump. To save money, you can make a heat pump yourself. Its design is simple. You just need to set aside a little of your time to carry out this work and purchase the necessary parts and components. Having made it, you will receive a heating system that will allow you to create a warm atmosphere at minimal cost.
How to calculate the cost of heating a country house?
Calculations are made on the basis of the following parameters:
The first parameter is operating costs. To determine these costs, it is worth considering the cost of the fuel that will be used to generate heat. This item also includes maintenance costs. The most profitable in this parameter will be heating, the energy carrier of which will be the supplied main gas. The next most efficient is the HEAT PUMP.
The second parameter is the cost of purchasing equipment and its installation. The most profitable and economical at the stage of purchase and installation will be the purchase of an electric boiler. The maximum costs are expected if you decide to purchase boilers, where the energy carriers are liquefied gas in gas tanks or diesel fuel. Here, too, the HEAT PUMP is optimal.
The third parameter should be considered the convenience when using heating equipment. Solid fuel boilers in this case can be noted as the most demanding of attention. They require your presence and reloading of fuel, while electric and gas powered ones work independently. Therefore, gas and electric boilers are the most comfortable to use when heating country houses. And here the HEAT PUMP has an advantage. Climate control is the most comfortable feature of heat pumps.
As of today, the price situation in the Moscow Region is as follows... Connecting gas to private houses costs about 600,000 rubles. It also requires design work and appropriate approvals, which sometimes stretch for years and also cost money. Add here the cost of the equipment and the relatively short period of wear (which is why gas workers offer more powerful gas boilers so that wear and burnout of the boiler takes longer). Heating on heat pumps is already comparable to the above price, but does not require any approvals. A heat pump is an ordinary electrical household appliance that consumes 4 times less electricity than a conventional electric boiler and is also a climate control device, i.e. an air conditioner. The motor resource of modern heat pumps, and even more high-quality ones (premium class), allows them to work for more than 20 years.
We give examples of calculating heat pumps for various types and sizes of houses.
First you need to determine the heat loss of your building, depending on the region of location. Read more in "Full News"
First of all, it is necessary to determine the power of the heat pump or boiler, as this is one of the decisive technical characteristics. It is selected based on the magnitude of the heat loss of the building. The calculation of the heat balance of the house, taking into account the features of its design, should be carried out by a specialist, however, for an approximate assessment of this parameter, if the house building is designed taking into account building codes, you can use the following formula:
Q = k V ∆T
1 kWh = 860 kcal/h
Where
Q - heat loss, (kcal/h)
V is the volume of the room (length × width × height), m3;
ΔT - maximum difference between the air temperature from outside and inside the room in winter, °С;
k is the generalized heat transfer coefficient of the building;
k \u003d 3 ... 4 - building from boards;
k \u003d 2 ... 3 - brick walls in one layer;
k min-max \u003d 1 ... 2 - standard masonry (brick in two layers);
k \u003d 0.6 ... 1 - well-insulated building;
An example of calculating the power of a gas boiler for your home:
For a building with a volume of V = 10m × 10m × 3m = 300 m3;
The heat loss of a brick building (k max \u003d 2) will be:
Q \u003d 2 × 300 × 50 \u003d 30000 kcal / h \u003d 30000 / 860 \u003d 35 kW
This will be the required minimum boiler power, calculated to the maximum ...
Usually, a 1.5-fold power reserve is selected, however, factors such as constantly operating ventilation of the room, open windows and doors, a large glazing area, etc. should be taken into account. If it is planned to use a double-circuit boiler (space heating and hot water supply), then its capacity should be further increased by 10 - 40%. The additive depends on the amount of hot water consumption.
An example of calculating the power of a heat pump for your home:
At ΔT = (Tvn - Tnar) = 20 - (-30) = 50°С;
The heat loss of a brick building (k min \u003d 1) will be:
Q \u003d 1 × 300 × 50 \u003d 15000 kcal / h \u003d 30000 / 860 \u003d 17 kW
This will be the required minimum power of the boiler, calculated to the minimum, since there is no burnout in the heat pump and the resource depends on its motor resource and cycling during the day ... To reduce the number of on / off cycles of the heat pump, heat storage tanks are used.
So: You need the heat pump to cycle 3-5 times per hour.
those. 17 kW/s hour -3 cycles
You will need a buffer tank - 3 cycles - 30 l / kW; 5 cycles - 20 l/kW.
17 kW*30l=500l storage capacity!!! The calculations are approximate, here a large battery is good, but in practice they put 200 liters.
Now let's calculate the cost of a heat pump and its installation for your home:
The volume of the building is the same V = 10m × 10m × 3m = 300 m3;
Approximate power we calculated -17kW. Different manufacturers have a different range of capacities, so choose a heat pump according to quality and cost together with our consultants. For example, Waterkotte has a 18kW heat pump, but you can also supply 15kW, since in case of insufficient power there is a 6kW peak closer in each heat pump. Peak reheating takes a relatively short time and therefore there is no need to overpay for a heat pump. Therefore, you can also choose 15 kW, because in the short term 15+6=21kW is higher than your heat needs.
Let's stop at 18kW. Specify the cost of a heat pump with consultants, since today the delivery conditions are "to put it mildly" unpredictable. Therefore, the site presents the factory.
If you are in the southern regions, then the heat loss of your house based on the above calculations will be less, since ΔT \u003d (Tvn - Tnar) \u003d 20 - (-10) \u003d 30 ° С. and then ΔT \u003d (Tvn - Tnar) \u003d 20 - (-0) \u003d 20 ° С. You can choose a heat pump with a smaller power and, moreover, according to the principle of operation "air-water". Our air source heat pumps operate efficiently down to -25 degrees and therefore no drilling is required.
In central Russia and Siberia, geothermal heat pumps operating on the "water-to-water" principle are much more efficient.
Drilling for a geothermal field will cost differently, depending on the region. In the Moscow region, the calculation of the cost is as follows:
We take the power of our heat pump -18kW. The electrical consumption of such a ground source heat pump is approximately 18/4=4.5 kWh from the socket. Waterkotte has even less (this characteristic is called COP. Waterkotte heat pumps have a COP of 5 or more). According to the law of conservation of power, electrical power is transferred to the system, being converted into thermal power. We receive the missing power from a geothermal source, i.e. from probes that need to be drilled. 18-4.5 = 13.5 kW from the Earth for example (since the source in this case can be a horizontal collector, a pond, etc.).
The heat transfer of soils in different places, even in the Moscow region, is different. On average, from 30 to 60W per 1 rpm, depending on soil moisture.
13.5 kW or 13500 W divided by heat transfer. on average it is 50W so 13500/50=270 meters. Drilling works cost an average of 1200 rubles / m.p. We get 270 * 1200 \u003d 324000 rubles. turnkey with input to the heat point.
The cost of an economy class heat pump = 6-7 thousand dollars. those. 180-200 thousand rubles
The cost of TOTAL 324 thousand + 180 thousand = 504 thousand rubles
Add the cost of installation and the cost of a heat accumulator and you will get a little more than 600 thousand rubles, which is comparable to the cost of supplying main gas. Q.E.D.
A ground source heat pump is the most economical way to heat and cool a building. The cost of a heat pump is high, but continues to decline as demand increases. Such a system is ideal for installing underfloor heating or heating radiators, designed for a low coolant temperature. When designing it, the main thing is to choose the optimal power. In the last article, we considered the self-assembly of a heat pump, but for most, information on how to choose a heat pump, how much does it cost and what to consider will be more important?
Heat pump power calculation
When choosing equipment, it is necessary to take into account the heat loss of the house. But this is not always possible or very expensive, and the purchase of a heat pump with a large power reserve hits the pocket hard. Therefore, it is necessary to have a backup source of heat in case of severe frosts (for example, a wood-burning boiler). This will allow you to choose a heat pump with a capacity one third less than necessary to compensate for heat losses in the coldest weather. This equipment can operate in any of three modes:monoelectric, monovalent and bivalent . The choice of mode depends on the level of consumption.
How to calculate heat consumption depending on the area
It is necessary to take measures to insulate the building and reduce heat losses to 40-80 W/m². Then for further calculation we will take the following data.
- A house without thermal insulation requires 120 W/m² for heating.
- The same for a building with normal thermal insulation - 80 W / m².
- New building with good thermal insulation - about 50 W / m².
- House with energy-saving technologies - 40 W/m².
- With passive energy consumption - 10 W/m².
Here is an approximate calculation of a heat pump, with which you can determine how to choose a heat pump. Suppose the total area of all heated premises of the house is 180 m². The thermal insulation is good and the heat consumption is around 9 kW. Then the heat loss will be: 180 × 50 = 9000 W. A temporary power outage is taken into account as 3 × 2 = 6 hours, but 2 hours will not be taken into account, since the building is inert. We get the final figure: 9000 W × 24 hours = 216 kWh. Then 216 kWh / (18 hours + 2 hours) = 10.8 kW.
Thus, to heat this house, it is necessary to install a heat pump with a capacity of 10.8 kW. To simplify the calculation, 20% must be added to the heat loss value (that is, 9000 W increased by 20%). But this does not take into account the cost of heating water to meet domestic needs.
Accounting for energy consumption for heating water
To determine the total power of the pump, let's add the energy consumption for heating water (up to t = 45 ˚С) at the rate of 50 liters per person per day. Thus, for four people, this will be equal to 0.35 × 4 = 1.4 kW. Hence the total power: 10.8 kW + 1.4 kW = 12.4 kW.
Dependence of power on the operating mode
Heat load calculation must be carried out according to the mode of operation.
- Monovalent mode involves the use of this equipment without auxiliary (as the only one). To determine the total heat load, it is necessary to take into account the cost of compensating for an emergency power outage (for a maximum of 2 hours, 3 times a day).
- Monoenergeticmode: it uses a second heat generator, for which the same type of energy (electricity) is used. It is connected to the system, if necessary, to increase the temperature of the coolant. This can be done automatically (installation of the heat pump also includes temperature sensors and control equipment) or manually. But even in severe winters, there are not so many cold days and the additional heat generator does not have to be activated often. But such an organization of heating allows you to save on equipment: a less powerful heat pump is 30% cheaper, but it will be enough to provide heat during 90% of the heating period.
- With bivalent mode, the heat pump is assisted by a gas or oil-fired boiler. The process is controlled by a processor that receives information from temperature sensors. Such equipment can be installed as an additional (during the reconstruction of the building) to the existing one.
Overview of the heat pump market
There are various types of equipment on the market today. It is worth noting the geothermal heat pumps of the Austrian company OCHSNER : they have been perfected by the manufacturer for 35 years. Well established brand waterkotte : boilers with an external coating of this brand have the highest performance. Among the Russian equipment, one can single out the one produced under the trademark " HENK".
To make it easier to imagine the upcoming costs, we will indicate the cost of the main equipment and work on its installation.
1. Ground probe heat pump:
- drilling work - 6 thousand euros;
- heat pump price - 6 thousand euros;
- electricity costs (per year) - 400 euros.
2. With horizontal manifold:
- the cost of the pump itself is about 6 thousand euros;
- drilling work will require 3,000 euros;
- electricity costs - 450 euros for the heating period.
3. Air type heat pump:
- pump price - 8 thousand euros;
- installation work - 500 euros;
- electricity - 600 euros.
4. Water-to-water pump:
- the pump can be purchased for 6 thousand euros;
- well drilling - 4 thousand euros;
- electricity costs (per year) - 360 euros.
These are approximate data for equipment with a capacity of about 6 - 8 kW. In the end, everything depends on many factors (on installation prices, on the depth of drilling, on the pump of the required power, etc.) and the costs can increase several times. But choosing heating with a heat pump, the customer gets the opportunity to gain independence from the rising prices for traditional heat carriers and refuse the services of heat and power enterprises.
An overview of the use of a heat pump system can be viewed in this video
The use of low-potential ambient heat for water heating and heating becomes economically beneficial with long-term use of the system. An obstacle to the wide distribution of such devices is the high initial cost of the equipment and its installation. Therefore, a complete or partial installation of a heat pump with your own hands is always relevant, which allows you to save significant funds.
Rice. 1 Heat pump water-to-water in the house
When creating heat pumps for heating, natural low-grade heat of air masses, soil and water is used. Aquatic species absorb thermal energy from wells, wells, ponds and other open water bodies. A heat pump works like a refrigerator, taking heat from the refrigerator compartment and expelling it outside through an external radiator.
During installation, the primary heat exchanger with a circulating coolant is placed in a container with water, from which heat is taken. Water is sucked in by a water pump, passes through the pipe system and then enters the evaporator - in the device, when the liquid is heated, it evaporates. In the evaporator, the coolant transfers heat to freon, for which a small positive temperature of 6 - 8 C is the boiling point, and the gaseous refrigerant enters the compressor.
 Fig. 2. Diagram of a water-to-water heat pump
Fig. 2. Diagram of a water-to-water heat pump There, it is compressed, leading to an increase in the temperature of the gas, and further supplied to the condenser. In the condenser, thermal energy from gas with a temperature of 40 - 70 C is transferred to water in the heating system, the cooled gas condenses and enters the pressure reducing valve (throttle). Its pressure decreases - this leads to a greater cooling of the gas to a liquid state, in which it is again fed into the evaporator. The system operates in a circular closed cyclic mode.
Heat pump calculation
To design a do-it-yourself system, first of all, it is necessary to perform a calculation taking into account the needs for thermal energy (pumps can additionally be used to provide hot water at home) and possible losses. The calculation algorithm consists of the following operations.
- The area of the heated room is calculated.
- Based on the values obtained, the total amount of energy required for heating is determined based on the calculation of 70 - 100 watts per square meter. The parameter depends on the height of the ceilings, the material of manufacture and the degree of thermal conductivity of the house.
- When providing hot water, the value obtained is increased by 15 - 20%.
- Based on the received power, a compressor is selected, the main components of the system are calculated and designed: pipeline, evaporator, condenser, electric pump and other components.
Accessories for a heating system with a heat pump for self-manufacturing
It is quite difficult for an ordinary homeowner to compete with domestic and foreign industrial heat pumps, however, its installation and manufacture of individual components are not impossible jobs. The main task in the construction of a heat pump remains the correctness of the calculations, because in the event of an error, the system may have low efficiency and become inefficient.
Compressor
For installation, you will need a new or used one. the compressor is in working condition with an unused resource of suitable power. The usual compressor power should be 20 - 30% of the calculated one, you can use standard factory units for refrigerators or scroll air conditioners, which have a higher efficiency compared to piston devices.
Evaporator and Condenser
To cool and heat liquids, they are usually passed through copper pipes placed in a container with a heat exchanger. To increase the cooling area, the copper pipe is arranged in the form of a spiral, the required length is calculated by the formula for calculating the area divided by the section. The volume of the heat exchange tank is calculated based on the implementation of efficient heat exchange, the usual average value is about 120 liters. For a heat pump, it is rational to use pipes for air conditioners, which initially have a spiral shape and are sold in bays.
 Rice. H Copper pipe and heat exchanger tank
Rice. H Copper pipe and heat exchanger tank
Many manufacturers of heat pumps have replaced this method of designing heat exchangers with their own hands for a more compact one, using heat exchange according to the “pipe in pipe” principle. The standard diameter of the plastic pipe for the evaporator is 32 mm, a copper pipe with a diameter of 19 mm is placed in it, the evaporator is thermally insulated, the total length of the heat exchanger is about 10 - 12 m. 25 mm can be used for the condenser. metal-plastic pipe and 12.7 mm. copper.
 Fig 4. Assembly and appearance of a heat exchanger made of copper and plastic pipes
Fig 4. Assembly and appearance of a heat exchanger made of copper and plastic pipes To increase the area and efficiency of the heat exchanger, some craftsmen twist a braid of several copper pipes of small diameter, shift them with thin wire and place the structure in plastic. This makes it possible to obtain a heat exchange area of about 1 cubic meter on a 10-meter segment.
expansion valve
A properly selected device regulates the degree of filling of the evaporator and is largely responsible for the performance of the entire system. For example, if the refrigerant intake is too high, it will not have time to completely evaporate, and drops of liquid will enter the compressor, leading to disruption of its operation and a decrease in the temperature of the gas at the outlet. Too little freon in the evaporator after increasing the temperature in the compressor will not be enough to warm up the required volume of water.
 Rice. 5 Basic equipment for the heat pump
Rice. 5 Basic equipment for the heat pump Sensors
For ease of use, operation monitoring, troubleshooting and system configuration, built-in temperature sensors are required. Information is important at all stages of the system operation, only with its help, using formulas, it is possible to establish the most important parameter of the installed equipment for water heat pumps - the COP efficiency indicator.
Pump equipment
During the operation of heat pumps, the intake and supply of water from a well, well or open reservoir occurs with the help of water pumps. Submersible or surface types can be used, usually their power is low, 100 - 200 watts is enough to supply water. To control the operation, protect pumps and the system, filters, a pressure gauge, water meters and simple automation are additionally mounted.
 Rice. 6 Appearance of a self-assembled heat pump
Rice. 6 Appearance of a self-assembled heat pump Do-it-yourself assembly of heat pump equipment does not present great difficulties with the ability to handle a special tool for welding and soldering copper. The work performed will help save significant funds - the cost of components will be about 600 USD. That is, the purchase of industrial equipment will cost 10 times more (about 6000 USD). A do-it-yourself design, with proper calculation and tuning, has an efficiency (COP) of about 4, which corresponds to industrial designs.
The heat output of an air-to-water heat pump (HP), otherwise, the amount of renewable heat extracted from the environment, is directly proportional to the outdoor temperature. The colder the air, the more expensive it is to extract heat from it. The COP conversion factor varies with ambient temperatures: the lower the outside temperature, the more energy the air source heat pump consumes.
Determining the power and choosing a heat pump is a rather complicated matter. Usually, real figures and performance diagrams are supplied by heat pump manufacturers, as well as special software for calculating and selecting equipment. Here you enter data for a specific object located in a specific temperature region.
Heat pump: heat output for heating and domestic hot water
Let us analyze on what factors the HP power and, accordingly, the cost of HP units, as well as the efficiency of its operation depend.
Radiators or underfloor heating
A heat pump heating system is usually implemented on the basis of a radiator distribution and/or a system with underfloor heating, wall heating or a fan coil system. At the same time, the heating medium heating temperature differs from 35-45 °C - for warm floors, up to 65-75 °C and higher - for the radiator system, which affects the power of the HP. The lower the temperature of the coolant in the heating system, the lower the energy consumption, the lower the heat output, the cheaper the equipment. For the modernization of heating systems with radiators when replacing expensive gas boilers, high-temperature air heat pumps with heating of the heat carrier up to 80 °C can be installed. For example, Hitachi YUTAKI S 80 heat pumps. Even if the coolant is heated to 65 degrees and above, such a system is several times more economical than a gas boiler.
Implementation scheme: HP only, HP + reserve boiler
TN. If only the heat pump is running, it must fully solve the problems of heat supply and water heating, connecting the built-in electric heater at peak times.
HP + boiler. If a gas or pellet boiler is previously installed, it can take over some of the peak loads and reduce the overall energy consumption of the heat pump.
There are various schemes of HP operation, selected individually for each object: monoenergetic (only on electricity), monovalent (HP + heating element) or bivalent (HP + boiler). The optimal temperature that is economically advantageous for switching to a backup heat source is called the “bivalence point”. For Kyiv and the region it is -7 °C.
Thermal insulation of the building
When choosing a heat pump for heating a house, you should know that a more insulated house will require several times less heat than a building without thermal modernization. The values of heat losses (specific heat loads) for various types of buildings are given in the table.

From this it can be seen that in order to compensate for the heat loss of a room of 100 m2 in a well-insulated house, you will need:
Q H \u003d 50 W / m2 x 100 m2 \u003d 5000 W or 5 kW of thermal power.
Estimated heat loss values are given based on the calculated minimum temperature, for example, for the Kyiv region it is -22 °C.
Accordingly, for a poorly insulated house we get:
Q H \u003d 200 W / m2 x 100 m2 \u003d 20,000 W or 20 kW of thermal power.
Such a difference: 5 kW and 20 kW makes it necessary to take steps to carry out thermal modernization (insulation) of the building, and then choose a more affordable and cost-effective heat pump.
Heat pumps for heating and water heating (DHW)
When choosing a heat pump for a private house, the operation of a heat pump for heating water for a kitchen, bathroom or shower is usually taken into account. At the same time, the daily distribution of loads is taken into account. They use hot water more often in the evening or in the morning, and in winter, the work of HP for heating also joins these loads. Usually, for heat pump systems, the tasks of hot water supply are more priority, and then heating, the calculation is based on the total heat loads: for heating and hot water.
To determine the thermal power of a HP for heating water for domestic needs, they use standard data on the consumption of water of a certain temperature and total heat consumption, based on the number of people living in the house.

For one person, let's take a rate of 50 liters of water with a temperature of 45 ° C, which corresponds to a consumption rate of 0.25 kW of thermal power.
We get that for a family of four people living in a private house of 100 m2, the heat output is needed:
Q W \u003d 0.25 kW / person * 4 people. = 1.0 kW
Now it is possible to carry out an average calculation of the thermal power, taking into account the total loads for heating the coolant for the heating system and heating water for domestic needs.
The total thermal power for heating and hot water for a well-insulated house:
Q SUM \u003d Q H + Q W \u003d 5 kW + 1 kW \u003d 6 kW.
The total thermal power for the heating system and hot water for a poorly insulated house:
Q SUM \u003d Q H + Q W \u003d 20 kW + 1 kW \u003d 21 kW.
And for the conditions of the “bivalence point”, when it is -7 ° C outside, and it is necessary to maintain +20 ° C inside the house of 100 m2, it will be required, taking into account the temperature difference:
Q cal.. = 6 * (20-(-7))/(20-(-22)) = 6 * 27 / 42 = 3.86 kW of heat from the heat pump.
And in the second example, for a building without thermal insulation, it is necessary:
Q cal.. = 21 * (20-(-7))/(20-(-22)) = 21 * 27 / 42 = 13.5 kW of heat from the heat pump.
Based on these data, taking into account the temperature of the “bivalence point” and with a power margin, a close larger value of the heat pump heat output is selected from the model range.
What is the power reserve?
- Inlet water temperature fluctuations. Everyone knows that tap water is much colder in winter and the temperature difference between the water entering / leaving the HP is greater in winter.
- The need to heat water to the desired temperature in the storage tank if it is not used from it for a long time.
- Increased consumption of hot water and its heating to a higher temperature in winter.
According to the tables offered by the manufacturer, based on the outlet water temperature and the outside air temperature, the set of the indoor unit and the corresponding outdoor unit of the heat pump is selected according to the power. An example is a technical data sheet for Hitachi Yutaki S series high-efficiency air-to-water heat pumps. For the calculated data, a model with a heating capacity of about 5.0 kW is suitable.
What determines the cost of a heat pump?
The more powerful the heat pump, the higher its price.
How to reduce the cost of a heat pump?
- Properly and professionally perform calculations and selection of equipment.
- Insulate the building.
- Minimize heat loss through windows and ventilation.
- Install low-temperature underfloor heating or fan coil units or a mixed system (radiators + underfloor heating, fan coil units + underfloor heating).
- Apply a bivalent HP + boiler scheme to reduce the load on the HP.
- Take part in the IQ energy program and save up to 35% of the cost of equipment and installation.
A more accurate selection of a heat pump, in order to avoid unnecessary costs or losses, is best left to professionals.
To choose the right heat pump, the prices for which and for installation services would be reasonable and justified, contact the competent experienced specialists of AKLIMA. We have extensive experience in the implementation of modern heat pump systems and offer high-quality services for the installation and maintenance of such equipment throughout Ukraine.