Wood boiler with heat accumulator. Heating system with heat accumulator. Wood boilers - installation requirements
Solid fuel boilers are excellent equipment for heating a private house in a rural area or in the suburbs, away from gas mains. Like any other equipment, solid fuel boilers are undergoing changes, being modified and improved, therefore modern models are represented by pyrolysis apparatuses, boilers with heat accumulators, pellet equipment, equipped with automation and parameters control tools. The standard heating scheme with a heat accumulator deserves special attention, as it saves fuel, which is already expensive - after all, you have to pay not only for firewood, peat, pellets or coal, but also for their delivery. A heat accumulator for electric and solid fuel heating boilers will show itself more efficiently if electricity is calculated at day and night rates.
Heating device with TA
A heat accumulator (TA) for heating boilers is an integral part of the heating system that works to increase the time interval between cycles of fuel supply to the combustion chamber. Structurally, this is a sealed, insulated large-volume container filled with coolant from the heating system, which constantly circulates along the circuit (contours). As a heat carrier, traditional liquids are used - distilled water, antifreeze, water-glucose solutions.
The only feature that must be taken into account when deciding on inclusion in the TA scheme is the volume of heated premises. The smaller it is, the less sense there is in installing a heat accumulator - the power of the boiler and heating devices (radiators, batteries) is quite enough to heat small rooms. How heating with a heat accumulator functions - a simplified connection diagram:
- The heat accumulator is included in the gap between the boiler and the piping, that is, the liquid heated in the boiler is immediately sent to the tank;
- From the battery, hot liquid flows into the heaters through piping;
- On the return flow, the liquid is again sent to the accumulator, and from it to the boiler for a new heating cycle.

The supply and return flows must be constantly mixed - this is a condition for the efficient operation of the heat accumulator. But the heated coolant rises, and the cooled coolant goes down, so the difficulty in ensuring the system's operability lies in creating conditions under which a certain volume of hot liquid sinks to the bottom of the accumulator to heat the cooled liquid from the return. A charged battery is a reservoir in which the entire volume of the coolant has the same temperature.
After the combustion of the next portion of solid fuel, the boiler stops heating water, and the TA starts to work. The hot coolant continues to move in the system, giving off heat and cooling in the batteries. The circulation will continue until the coolant cools down completely, or a new portion of firewood or coal is loaded into the boiler.
In the presence of an automation system, critical cooling of the coolant is not allowed, since the supply of solid fuel in the system is controlled by temperature sensors: when a certain value is reached, which means that the boiler has ceased to support combustion, the sensor sends a signal to the executive system, which opens the fuel supply valve - coal, pellets or peat.
Disadvantages of the heating system with a heat accumulator for country and garden houses with seasonal residence:
- The rooms take longer to warm up;
- Due to the small size of the TA, the volume of the heating circuit increases, so the cheapest coolant for such systems is water. Antifreeze and other synthetic fluids will cost too much.
But each time upon arrival, refilling the system with water is a troublesome task, and if you go to the dacha two or three times a month, it is simply pointless. Therefore, additional steel spiral pipes are built into the TA, which act as heating circuits. The coolant flowing through the spirals does not come into contact with the coolant in the heat exchanger, but is a separate and autonomous heating or hot water circuit. By implementing such a simple technique, it is possible to achieve the universality of the use of any boiler, even the simplest single-circuit one. Moreover, the efficiency of such equipment will be used to the maximum.

The role of such passive spirals can also be performed by active elements - electric heating elements, which can be connected to the electrical network or be autonomous - run on solar energy (solar batteries). This method of heating the coolant or hot water supply is considered auxiliary.
Tying scheme with thermal accumulator
Heating schemes with a solid fuel boiler and a heat accumulator can be developed as much as you like - everything will depend on the actual operating conditions of heating, the location of the premises, their area, the equipment used, etc. The traditional and standard piping of a solid fuel heating boiler circuit with a heat accumulator works as follows:
In the figure below, the arrows indicate the movement of the coolant through the system, while the return cannot move upward. To take the coolant from the return, a circulation pump is included in the circuit between the battery and the boiler, which pumps more liquid than the pump to the TA. Thus, a pressure difference is formed in the pipes, and the liquid is taken from the return pipe into the tank. A slight disadvantage of this circuit is that the circuit will take longer to heat up. 
To reduce this time period, such a heating device is implemented (figure below in the text) with a closed boiler heating cycle. The circuit works like this: the coolant does not enter the boiler from the TA until it is heated in the boiler jacket to the specified temperature. After reaching the set value, a certain volume of liquid from the supply pipe enters the accumulator, and a part is mixed in the system with liquid from the TA, and again fed into the boiler. 
As a result of the implementation of such a scheme, the boiler always receives a heated liquid, which will increase its efficiency, reduce the heating circuit warm-up time and allow you to organize an autonomous operation mode by turning on two bypasses:
- When the pump is not running and the lower bypass valve is closed, the check valve works;
- When the pump is not running and the non-return valve is running, the lower bypass works.
Due to the high resistance of the check valve to the coolant flow, it can be omitted from the circuit:

In case of an emergency power outage, the ball valve is opened manually. When the circuit is operated only with forced circulation of the coolant, the piping with the TA is done according to the following scheme: 
How to calculate the required volume of a heat accumulator
Too large or too small a reservoir for accumulating heat in the form of a heated coolant is an inefficient solution, therefore the required volume of the reservoir is subject to mathematical calculation, the exact results of which are difficult to obtain due to approximate initial data - heat losses in the room, properties of wall insulation and the foundation of the house, heat-insulating qualities of building materials of walls, ceilings and partitions, the same parameters of window and door openings. But it is still possible to approximately calculate the heat accumulator, and such a technique is designed specifically for ignorance of the exact heat losses of the building, especially if it is only to be built.
The choice of the size and volume of the tank for the heat accumulator can be made based on the following parameters:
- The total area of heated premises;
- Thermal power of heating equipment.
These two parameters determine the volume of TA.
Suppose it is necessary to calculate the volume of a heat accumulator for a heating system, based on the heated area of \u200b\u200bthe room. The formula for calculating is simple: the area in square meters is multiplied by four (Sx 4). For example, for a house with a total heated area of 50 m 2, a tank of 200 liters will be required. With such a volume of TA, as practice shows, it is possible to load the boiler with solid fuel only once a day. This is a very good economy and a very good efficiency.

Knowledgeable owners will say that you can simply install a pyrolysis boiler that will work the same way. But the operation of such a boiler is a little more complicated and less efficient, since:
- First, the fuel ignites and flares up;
- Then the air supply is limited;
- The last fuel smoldering (pyrolysis) is activated.
When the fuel ignites, the coolant temperature rises sharply, and the pyrolysis process maintains it at a given level, and during the pyrolysis, a lot of thermal energy simply disappears into the chimney pipe, heating almost nothing. Another disadvantage is that at the peaks of heating, the coolant can boil and splash out of the expansion tank, and when using PVC pipes for heating distribution, they fail faster from high temperatures.
Wood-burning boilers for home heating are still popular, despite the variety of models of gas and electric boilers, and there is a simple explanation for this: firewood is the most affordable type of fuel for country houses that are not connected to the main gas.
The efficiency of modern wood-burning boilers is quite high, their efficiency reaches 85%, while not only firewood, but also pellets, as well as woodworking waste can be used as fuel.
Wood-burning boilers used for heating a country house are easy to connect and use - they are even easier to handle than a stove. They are safe as long as they are properly installed and operated. The only serious drawback of wood-burning boilers is the low level of automation of the process: fuel must be loaded into the boiler manually. The way out of the situation can be a boiler with a long burning function or a combined boiler that runs on solid fuel and has an additional diesel or gas burner or an electric heating element.
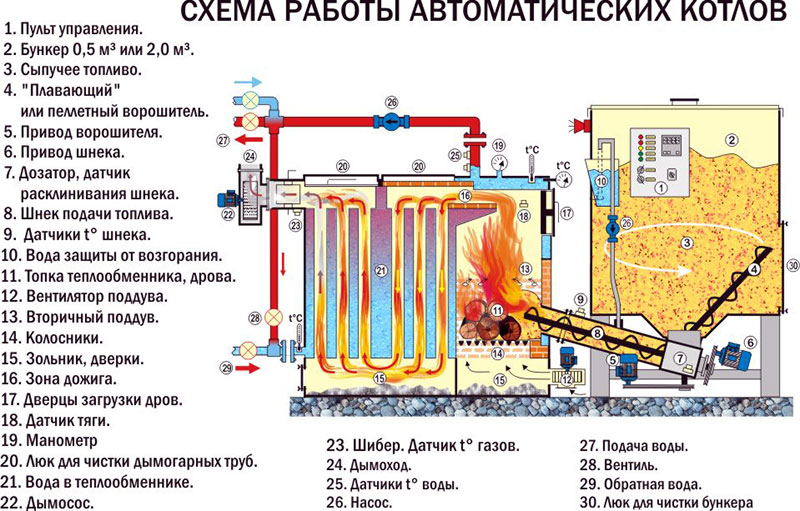
Despite the huge selection of models of wood-burning boilers, their device does not differ so much. Any wood-burning boiler for home heating necessarily has a fuel combustion chamber, a water heat exchanger, a chimney and an ash pan. The simplest wood-burning boiler resembles a potbelly stove with a water jacket: when wood is burned in the furnace, the water heats up and enters the heating system. The efficiency of such a boiler is low, and the consumption of firewood is significant, due to incomplete combustion of fuel, part of the money flies into the pipe in the literal sense of the word. The design of modern boilers with a long-term burning function is, of course, more complicated; the device of such a boiler and its main elements are shown in the figure.
Firewood is loaded into the boiler through the top loading door at once in a large volume. The initial fuel combustion takes place in the gasification chamber. The flow of air, and with it the oxygen necessary for combustion, into this chamber is limited - this is how the intensity of combustion is regulated. In this mode, the firewood does not burn, but smolders with the formation of more heat, while the water is heated in the heat exchanger. But the combustion process does not end there: during smoldering, smoke is formed containing combustible gases. These gases enter the second chamber - the combustion chamber, which also serves as an ash pan. The air supply to this chamber is no longer limited, and with a sufficient amount of oxygen, afterburning of gases occurs. The combustion temperature of the gas-air mixture is very high, and the heating efficiency of the water heat exchanger in this chamber is also very high. As a result, the smoke is cleaned of ash and harmful combustible gases, which makes the new generation wood-burning boilers very environmentally friendly.
Pyrolysis is a process of long burning
Video - the principle of operation of a long-burning wood-burning boiler
Smoke is removed through a chimney channel connected to the chimney and pipe. To supply cold and discharge hot water from the heat exchanger, the boiler is equipped with branch pipes. They are connected to the heating system according to the selected scheme. Boilers of the new generation are equipped with automation, which makes it possible to simplify the maintenance of the boiler as much as possible:
- a temperature sensor that sends a signal to the primary air supply fan;
- pressure sensor, signaling the excess of the normal value;
- water pressure sensors in the system.
The efficiency of solid fuel boilers directly depends on the type and quality of fuel. If the boiler is designed to work on wood, coal and peat briquettes must not be loaded into it! This will reduce the efficiency of the boiler and may damage it. It is also not recommended to use poorly dried firewood and softwood for burning a wood-burning boiler - they burn with the formation of a large amount of steam, tar and soot, and the boiler will have to be cleaned much more often.
Wood boilers - choice
The choice of a wood-burning boiler must begin with the calculation of the required power - this parameter is indicated in the passport for the boiler and is measured in kilowatts. One kilowatt of boiler power is enough to heat ten square meters of a well-insulated room. For example, in the middle lane, a boiler with a power of 10 kW is needed to heat a house with an area of 100 square meters. For frosty days and poorly insulated rooms, a power reserve of 20-30% is required. When choosing, it is worth paying attention not only to the rated power, but also to the entire range in which the boiler can operate - in autumn and spring it is not advisable to heat the boiler at full power. If you plan to use the boiler also for hot water, then you will need an external boiler and an additional boiler power reserve based on the number of people permanently living in the house.
An important role is played by the material of the boiler - steel or cast iron. Steel boilers are lighter and have a simpler design of the furnace, which is easier to clean - just remove the ash from the ash pan. The smoke channel of steel boilers is longer, so the heat carrier is heated more efficiently. In cast iron boilers, the smoke channel is shorter, and a large heat exchange area is achieved due to the ribbed surface in which combustion products settle; the cast iron boiler will have to be cleaned using brushes, scrapers and a poker. At the same time, the heat capacity index of the boiler itself is higher for cast-iron models.
Electric wood boilers can be distinguished as a separate type, which, with the help of electricity, further increase efficiency. Modern automation monitors the combustion process and influences it with the help of valves that regulate the flow of incoming air into the furnace, so you can control the temperature in the furnace at a given level!
Wirbel steel wood burning boiler
An important indicator is the ratio of the volume of the loading chamber to the power of the boiler. In simpler terms, how many times a day you will have to approach the boiler to load fuel. For steel boilers, this figure is usually higher - an average of 1.5-2.5 l / kW versus 1.1-1.4 l / kW for cast iron ones - therefore, loading is carried out less often.
Be sure to check the availability of an emergency cooling system and clarify how it works. This system may be needed in case of overheating of the boiler and boiling water in the heat exchanger. Boilers with a separate emergency cooling circuit are safer, but if emergency cooling is arranged by abruptly draining the water from the heat exchanger and replacing it with cold water, make sure that the boiler is resistant to thermal shock.
Protection against burns is an important indicator, especially if unauthorized people or children have access to the boiler room. A useful option is heat-insulated firebox handles, protective casings and grates, thermal insulation of the most heated surfaces of the boiler.
Thermal protection of boilers is a prerequisite for safety
Wood boilers - installation requirements
Efficient and safe operation of a wood burning boiler is not possible without proper installation. How to install the boiler with your own hands without violating safety rules?
Installation location
Any wood-burning boiler consumes a fairly large amount of air during operation, therefore, for small-capacity boilers that can be installed in the common areas of the house, supply and exhaust ventilation is performed, and with a boiler power of more than 50 kW, it is necessary to equip a separate boiler room with a useful room volume of 8 cubic meters. Wood boilers are installed on a solid, even base with a fireproof coating - concrete, tile, porcelain stoneware. The walls must also be lined with non-combustible materials. The boiler room is equipped with forced ventilation.
Chimney Requirements
The chimney for a wood-burning boiler is made of stainless steel, ceramic or thick-walled metal pipe. Sandwich type stainless steel chimneys are the best choice. They are easily assembled from various elements - pipes fastened with clamps, roof passages, unloading platforms. When bending such a chimney, bends at a certain angle are used. It is allowed to lead the chimney of the boiler not through the roof, but through the wall of the building. The height of the straight part of the chimney for stable draft in the boiler must be at least 6 meters for a 16 kW boiler and at least 10 meters for a 32 kW boiler, with a pipe diameter of 200 mm.
Service and Maintenance
It is also necessary to clarify the terms of service and warranty service of the selected boiler model, the proximity of service centers and the possibility of calling specialists for installation and repair. It may happen that servicing a cheaper model will cost much more than analogues of well-known companies that have service centers in large cities.
Video - self-installation of solid fuel boilers
Wood boilers for home heating after installation are connected to the water heating system. For uninterrupted operation of the system, you can additionally install a heater tank on electric heating elements in it, in this case you do not have to throw firewood during a night's rest or absence from home.
Modern solid fuel boilers are an excellent alternative to gas and electric heat generators. Due to their design features, as well as the availability of fuel, and their installation, it is possible to achieve the most high-quality and efficient operation of the heating system, to guarantee its reliability and functionality.
There are a lot of options for connecting solid fuel boilers to the heating system of the same country house or any other object. A very popular and common option for completing the piping of the unit is the use of special storage tanks - heat accumulators.
Thermal accumulator: what is it
Structurally, a solid fuel heat accumulator is a special container with a heat carrier, which quickly heats up during the combustion of fuel in the boiler furnace. After the heating unit stops working, the battery gives off its heat, thereby maintaining the optimum temperature in the building.
Combined with a modern solid fuel boiler, the heat accumulator makes it possible to achieve almost 30% fuel savings and increase the efficiency of the system. In addition, the number of loads of the thermal unit can be reduced up to 1 time, and the equipment itself works at full capacity, burning all the loaded fuel as much as possible.

All thermal accumulators are made (and this can be seen in many photos or videos on our website) in the form of some buffer tanks - tanks that are insulated with special materials. At the same time, the volume of such tanks can reach 350-3500 liters. The devices can be used both in open and closed heating systems.
The principle of operation of the heating system with a heat accumulator
As a rule, the main difference between a system with a solid fuel boiler and a heat accumulator from a conventional one is cyclic operation.
In particular, there are two cycles:
- The product of two bookmarks of fuel, burning it in the maximum power mode. At the same time, all excess heat does not fly out “into the pipe”, as with the traditional heating scheme, but accumulates in the battery;
- The boiler does not heat up, and the optimal temperature regime of the coolant is maintained due to heat transfer from the tank. It should be noted that when using modern heat accumulators, it is possible to achieve downtime of the heat generator up to 2 days (it all depends on the heat loss of the building and the outside air temperature).
Advice. To achieve maximum savings and downtime of the heating boiler, high-capacity heat accumulators should be used.
The main functions of heat accumulators
A solid fuel boiler with a heat accumulator is a very profitable and productive tandem, due to which you can make the heating system more practical, economical and productive.
Heat accumulators perform several functions at once, among which are:
- Accumulation of heat from the boiler with its subsequent consumption at the request of the heating system. Often, this factor is provided by the use of a three-way valve or special automation;
- Protection of the heating system from dangerous overheating;
- Possibility of simple linking in one scheme of several different heat sources;
- Ensuring the operation of boilers with maximum efficiency. Actually, this function appears due to the operation of equipment at elevated temperatures and a decrease in fuel consumption;

Heat accumulators as per selection
- Stabilization of temperature conditions in the building, reducing the number of fuel loadings into the boiler. At the same time, these indicators are quite significant, which makes the installation of such equipment a more efficient and financially profitable solution;
- Providing the building with hot water. Mandatory installation of a special thermostatic safety valve at the outlet of the heat accumulator tank is required, since the water temperature can reach more than 85C.
The calculation of the heat accumulator for a solid fuel boiler can be done in various ways. But, if you need to quickly perform all the calculations, then it is better to use the option proven in practice - at least 25 liters of volume should fall on 1 kW of solid fuel boiler power. The higher the power of heat engineering, the larger the volume required to install the battery.
Important. The volume of the heat accumulator should be chosen with a margin. Thus, it will be possible to achieve the most productive operation of the thermal unit, reduce the amount of fuel consumed, and increase efficiency.

The use of a heat accumulator: when equipment is needed
The instructions for heat accumulators of solid fuel boilers indicate that such units should be used in several main cases:
- The need for efficient hot water supply in large volumes. For example, if the house has two or more bathrooms, a large number of taps, then heat accumulators cannot be dispensed with, because the equipment significantly increases water production without extra financial costs;
- When using solid fuels with different heat release coefficients. Due to this technique, it is possible to smooth out the combustion peaks and reduce the number of bookmarks;
- If there is a need in the house to charge the batteries with heat at the “night rate”;
- When using heat pumps. In the event that, in addition to a solid fuel boiler, there is also an alternative heating system in the building, the battery will help optimize the operating time of the compressor of the installation.
Choosing a heat accumulator: what to look for
When it comes to choosing a heat accumulator with your own hands, it is important to take into account a number of features and characteristics of the equipment. It should be noted that not only the price depends on this, but also the durability, performance and uptime of the equipment.

Among the main operating parameters of heat accumulators are:
- Overall dimensions, weight, volume. It is the volume and weight that should be given special attention in the process of selecting heat accumulators. As we discussed earlier, the volume of the tank is selected depending on the power of the boiler. But, it should be noted, the larger the volume of the heat accumulator, the better, because it is possible to achieve maximum performance and efficiency of the system.
It should be noted that if for some reason the dimensions of the battery tanks do not allow them to be installed in the house (for example, this applies to volumetric 2000-liter containers), then you can replace them with several, but of a smaller volume;
Advice. Since heat accumulators have rather significant dimensions, it is best to provide a place in advance for the installation of such units. This may be the basement of a residential building or a special capital extension.
- pressure in the heating system. A very important and significant factor that determines the thickness of the tank walls, as well as the shape of the roof and bottoms. In the event that the maximum pressure in the heating system of the building does not exceed 3 bar, then conventional heat accumulators will suffice.

In the same case, when the operating pressure fluctuates between 4-8 bar, it will be necessary to choose tanks with toroidal covers. Of course, the price of such equipment is somewhat higher, but in terms of their characteristics they are more preferable;
- Materials. Almost every solid fuel heat accumulator made in Europe consists of ordinary carbon steel coated with moisture-resistant paint. But, it should be noted, it is best to choose stainless steel tanks that are resistant to corrosion and the effects of various additives that contain coolants.
Advantages of using heat accumulators for solid fuel units
- Increasing the period of efficient and trouble-free operation of the system;
- Productive and trouble-free operation of equipment under various operating conditions;
- Absence of sharp jumps in temperature during the transfer of heat from the boiler to the heating system of the house;
- Saving solid fuel up to 30%;
- The possibility of obtaining heat even with complete combustion of the fuel.
Conclusion
At the moment, heat accumulators are modern and efficient technology, which can significantly increase the performance of heat generators, ensuring their reliability, efficiency and reliability. Therefore, if you are looking to create an economical system, you should pay attention to this equipment.
Features of solid fuel boilers
Solid fuel boilers use various solid fuels to produce heat: coal, peat, oil shale, firewood. According to the organization of combustion, they can be divided into types: classical, pyrolysis, automatic, long burning.
A feature of the combustion of a solid fuel boiler is its temperature cycling, due to the need to lay a new portion of fuel. That is, a sequence of operations is traced: ignition with a minimum temperature, combustion at a maximum temperature, attenuation with a gradual decrease in temperature. The temperature cyclicity in the furnace is affected by the corresponding fluctuations in the temperature of the coolant.
The problem of temperature fluctuations has been solved to a greater extent in automatic boilers that maintain temperature stability by automatically supplying fuel and blowing the burner fan.
Thermal processes
Let us consider in more detail what happens to the solid fuel boiler, the heating system and the room as a whole, as a single heating system. 
Cycle start- ignition: a sharp increase in temperature in the furnace from 40C after loading the fuel, up to 600C within 5-10 minutes. Depending on the parameters of the system, due to the heat capacity, the ability to accumulate heat, the temperature in the furnace heat exchanger can be from 40C to 70C. At minimum temperature - the worst case scenario: thermal shock to the heat exchanger and heating system.
Cast iron heat exchangers, as the most fragile, cannot withstand such a regime for a long time, they burst. More often, this mode occurs at night, when the need for a new fuel filling is simply overslept, the boiler goes out, the temperature of the coolant drops significantly. If the circulation rate is insufficient during rapid heating, the coolant may boil, which is a hydraulic and thermal shock to the heating system. Plastic pipes are the first to suffer from temperature changes.
The pipes begin to warm up in the room, the air is cold.
mid cycle- further heating of the coolant. The temperature in the furnace rises to 1000C for firewood, up to 1300C for coal, heating the coolant. In the absence of control, the heat carrier is heated up to the maximum temperature of the boiler - 95C. But modern solid fuel boilers allow you to control the temperature of the coolant within certain limits by adjusting the air supply with a valve. They do not allow to rise to a dangerously high temperature, maintain the set temperature until the fuel is completely burned.
The pipes are hot in the room, the air begins to warm up.
End of cycle- the fuel burns out to the formation of embers, the temperature in the furnace drops to 600-400C, - the most comfortable mode for the system. There is a slow cooling of the coolant, the air in the room cools slightly. After the formation of embers, the process of cooling the coolant and air in the room is accelerated.
History, solutions
It cannot be that in the entire history of solid fuel heating, mankind has not come up with a way to solve uneven heating. The solution suggests itself - to increase the thermal capacity of the heating device, compensating for pauses without heating.
The national way to solve this problem is to use an array of brick ovens as a heat accumulator. Even in the conditions of significant forest reserves in central Russia, constantly heating the stove is very expensive: harvesting, transporting, cutting and chopping firewood. It is rational to heat the stove 2 times a day, combining heating with cooking. The Russian stove weighs from 3 to 7 tons, accumulating heat with all its volume and giving it evenly all the time between the fireboxes.
In winter, Indian wigwams lined the hearth with large boulders - heat accumulators.
Modern solutions
What do modern technologies offer to solve the problem of heat accumulation? There are many ways to change the aggregate state of matter. But water turned out to be the cheapest, as one of the substances with the highest specific heat capacity.
The transition from the heat capacity of stone to water allows you to reduce the amount of heat accumulation to a capacity of 1-3m3. Is it a lot or a little? - no difference. The specified volume can be placed in any convenient place, having warmed it well, even in the attic space. 
The solution of a water accumulator of heat is implemented in a modern dwelling in two ways.
Method number 1.
Between the heating boiler and the heating system, a container of the appropriate volume is installed. The main purpose of which is, as a buffer, to compensate for the thermal emissions of the boiler and the accumulation of heat from the boiler, ensuring long-term heating in the absence of a combustion process.
Method number 2.
Everything in our home accumulates heat: walls, ceiling, floor, furniture, etc. Warm floors with an increased layer of coating over the pipes are a worthy legacy of the Russian stove. Underfloor heating throughout the room is a fairly large heat accumulator, but much smaller than a capacitive heat accumulator.
Way of implementation
The most successful way of practical application of a thermal accumulator of a solid fuel boiler is implemented in the following scheme. 
- Solid fuel boiler.
- Circulation pump boiler-accumulator.
- Thermal sensor for switching on the circulation pump of the boiler-accumulator.
- Circulation pump accumulator - heating system.
- The temperature sensor of the heating system, a variant of air temperature control is shown.
- Domestic water heating coil.
- Heat storage tank.
Often, to solve private heating problems, the exit from the boiler to the heat accumulator is made by a coil - position No. 7. For example, when there is antifreeze in the heating system, which is undesirable for the boiler and circulation pump.
The system works as follows. When the fuel starts burning in the boiler, the temperature sensor turns on, starting pump No. 2 to work. This pump will work all the time until the temperature in the furnace drops below 60C. Heated water from the heat accumulator is consumed by means of pump No. 3, the required temperature in the room is maintained with the help of temperature sensor No. 5.
Advantages and disadvantages
Having spent money on installing a thermally insulated tank and pipes to the boiler, what did we get?
Advantages:
- Protection of the boiler and heating system from overheating by diluting the overheated coolant with a large heat storage capacity;
- Accumulation of heat from a working boiler;
- The most economical mode of operation of the boiler is implemented for fuel combustion, and not for maintaining the set temperature;
- Reducing the number of furnaces to 1-2 per day, there is no need to heat at night, improving the thermal comfort in the room by stabilizing the temperature of the coolant;
- The heat accumulator allows you to receive heat from any heat generators: solar plants, heat pumps, gas boilers, fireplaces, etc.
- Just realized the heating of water for domestic needs.
Flaws:
- The high cost of capacity, insulation, piping;
- A place for installation of a tank of at least 500 liters with a solid base is required.
Conclusion
The presence of a buffer capacity in the form of a heat accumulator does not exempt the heating system from excess protection methods - temperature and pressure. It is necessary to provide for the operability of the heating system in the absence of electricity.
To calculate the minimum volume of the heat accumulator capacity, the following calculation method was adopted: 25 liters of liquid are needed for 1 kW of boiler power, optimally 50 liters per 1 kW.
For a heating system with a heat accumulator, a boiler 30% larger than the rated output is preferable.
Warmth for your home.




