Refueling capacities and norms. Filling capacities and standards Technical data gas 53 27
In the period from 1961 to 1993, he put on stream the production of medium-duty trucks GAZ-53. The carrying capacity of the car ranged from 3 to 4.5 tons, depending on the modification. The car in question belongs to the third generation of this class. This vehicle, taking into account all the transformations, has become the most massive in serial production from Soviet trucks. During the production period, more than four million cars were produced.
Model range (GAZ-53 F)
Until 1967, the GAZ-53 F was developed and produced. The car was equipped with a six-cylinder power unit with a four-speed gearbox. Fuel consumption was about 24 liters per hundred kilometers. The bridge assembly had bevel gears, the engine from the GAZ-11 was boosted to increase the compression of the mixture.
The considered model of the GAZ-53 car, the carrying capacity of which was 3.5 tons, was equipped with new tires and an increased base. On the basis of this machine, onboard milk carriers and so on were designed. Given the frequent failure of parts, low power and a number of design flaws, the car was not popular and was discontinued in 1967.
Series 53 and 53A
The period from 1964 to 1983 was marked by the release of the GAZ-53 and 53A models. These modifications were equipped with a more powerful power plant ZMZ-53 for 115 liters. The design provided an increase in speed up to 85 km / h with fuel consumption (l / km) - 25/100. To expand the functionality of the truck, it was provided for the arrangement of a dumping platform, a covered body, and a power removal device for a hydraulic pump.

The carrying capacity of the GAZ-53 was lower by 0.5 tons (3.5 and 4.0) than that of the 53A model. In addition, the second variation had the following advantages:
- More powerful middle axle.
- Structurally updated cardan.
- Refined steering gear.
- Updated radiator protection.
- Duplicate turn signals on the roof.
- New cabin heating and electric windshield wipers.
The model under consideration was awarded the State Quality Mark of the USSR.
Modification 53-12
This load capacity of which was up to 4.5 tons, was produced from 1983 to 1992. The car was equipped with a ZMZ-511 engine with a capacity of 120 horsepower, a speed maximum of 90 km / h. up to 30 liters per hundred, however, it became possible to install a gas installation for refueling with liquefied or compressed gas.
The truck is designed to transport various goods along the highway and dirt road at ambient temperatures from -40 to +40 degrees Celsius. The model in question is an improved version of the 53A series. The car received an improved engine, radial-type rubber, which made it possible to increase the dynamics and passable qualities of the vehicle. Cars with gas installations were produced under the indices 53-27 and 53-19.

The updated power unit was equipped with a sectional oil pump, full-flow filter elements, new cylinder heads, crankcase ventilation was carried out in a closed circuit. The axle beam, shock-absorbing and frame elements were also reinforced, exhaust toxicity decreased by almost 20 percent.
Export and upgraded variants
The carrying capacity of the GAZ-53 car, which is exported, reached 4.5 tons. Modifications of the 53-50 and 53-70 series were being sold abroad. Cars were in demand in Belgium, Finland, socialist countries. In Cuba and Bulgaria there were production facilities for assembling cars from kits received from the Gorky Automobile Plant.
The modernized and export series of late production were equipped with a front-view triplex, a contactless ignition unit, modern lighting elements, emergency sensors, a hydraulic vacuum booster, and a brake pressure distributor on all axles.
For example, the carrying capacity with the index 02 was more than 4 tons with a capacity of an all-metal self-tipping body platform of five cubic meters of cargo. The dump truck has been widely used in industry and agriculture. Due to the design features, unloading was carried out on a convenient working side.

Technical properties
Below are the main technical characteristics of the GAZ-53 car, electrical equipment diagram:
- The power plant is a piston type, carburetor, four-stroke, made of aluminum alloy.
- Volume (cubic cm) - 4,250.
- Power (hp) - 115.
- Liquid cooling.
- Design - frame, two-door with left-hand drive.
- Suspension unit - front (dependent, spring beam), rear (similar leaf spring).
- Gearbox - mechanics, four steps.
Electrical equipment consists of the following elements:
- Instruments located in the cabin.
- Accumulator (75 a / h).
- Starter, generator.
- Postings.
- Windshield wiper and heating motors.
- Elements of the ignition block.

The truck's fuel tank holds 90 liters, the maximum speed is 85-90 km / h with a fuel consumption of 24 liters per hundred kilometers.

Other data
GAZ-53, maximum load capacity and other characteristics are presented below:
- Length / width / height (m) - 6.4 / 2.38 / 2.22.
- Wheelbase (m) - 3.7.
- Track (front / rear), m - 1.63 / 1.69.
- Clearance (cm) - 26.5.
- The weight of the car in running order (t) is 3.25.
- Gross weight - (t) - 8.25.
- Maximum load capacity (t) - 4.0.
- Brake system - drum type on all axes, hydraulic booster.
- Clutch - disk, dry type with lever drive.
- Steel wheels.
These characteristics are given for the standard GAZ-53 model. The upgraded variations have slightly higher carrying capacity, dynamics and engine resources.
Pros and cons of the entire series
The domestic truck GAZ-53, the carrying capacity of which was sufficient to perform various economic tasks, has objective advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of a car include the following:
- Simplicity and reliability in service.
- Ease of management.
- Inexpensive and affordable maintenance, as well as minor repairs in almost any environment.
- With the timely replacement of oil and filters, the resource of the power unit before overhaul reaches 400 thousand kilometers or more.

Among the shortcomings are the following problems:
- Low service life of the brakes and clutch assembly.
- Decent fuel consumption.
- The unreliability of the connection of the elements of the cardan, distributor and variator.
- Leaking oil seal of the rear main bearing of the motor.
Despite all the shortcomings, the truck in question can still be found on domestic roads today, which further confirms its popularity, especially in rural areas.
Peculiarities
Considering the period of production, the GAZ-53 looked quite modern. The car has a one-piece radiator equipment at the level of the headlights. A strong frame serves to connect most of the units and blocks of the vehicle. If necessary, the chassis could be transported without a body part and a cab.
The fuel tank is located under the driver's seat, the fuel filler is located behind the cab at the edge of the driver's door. This decision played a positive role in the transition from gasoline to gas, since the unit is mounted under the body, where most cars have a gas tank.
The car was started with an electric starter, the comfort in the cabin was supported by a heating unit and electric wipers. The seat for the driver and passenger is combined into one single "sofa". The cabin has compartments for storing tools and accessories. Instead of an oil pressure indicator and an ammeter, signal sensors appeared, as well as a clock.
Internal stuffing
The high carrying capacity of the GAZ-53 car is ensured not only by a strong frame. An important role in the dynamics and performance of the truck is played by internal systems and mechanisms.
Cylinder blocks are made of Al-4 aluminum alloy. The design is a V-shaped monoblock, which is thermally processed, has a right angle along the axes. Piston elements are cast from Al-30 type alloy. The piston itself has a round shape with guide grooves cut into the body for the rings.
Valve seats, crankshaft are made of cast iron, guide bushings are made of copper-graphite mixture. Blocks and cylinder heads are fixed to each other using threaded studs with sealing gaskets. The crankshaft is protected from axial displacement by two washers mounted on both sides of the journal support.
Timing
The timing mechanism plays its role, including the load capacity of the GAZ-53, depending on the modification. On the standard model, this is a top-mounted valve mechanism. The node includes:
- Camshafts and pushers.
- Gears.
- Rockers and rods.
- Guides for bushings and springs.
The power supply system includes a fuel tank, pipes and hoses, a mechanical pump with a diaphragm, a two-chamber carburetor, and filter elements. The oil pump contributes to the supply of oil to the rubbing parts by gravity or under pressure. The air filter is of the inertial type, in which dirt particles settle in an oil bath.

The cooling system is a closed unit with a pump. The block consists of a water jacket, a pump, a radiator, a thermostat, a fan with a casing, shutters and connecting elements. The volume of the unit is 22 liters with a contact ignition circuit.
Conclusion
No matter how the Soviet automobile industry was scolded, there were quite a few samples that adequately performed their functions. One of these cars was the GAZ-523, the most massive truck with various modifications. He helped agrarians, industrialists, motor transport enterprises to fulfill the plan, was unpretentious in operation and repair. At the same time, the carrying capacity of the GAZ-53 (on-board version) is 3-3.5 tons, and more modern models and dump trucks can handle up to 4.5 tons of load.
Page 1 of 4
Vehicle GA3-66 - a two-axle truck with a carrying capacity of 2 tons, off-road with a drive on both axles.
Overview of KAMAZ and gas models: body volumes and dimensions
It is designed to replace the GAZ-63 car of the same type produced by the plant.
The GAZ-66 car has modifications:
GAZ-66-01 - a car with a tire pressure control system;
GAZ-66-02 - a car with a winch and a tire pressure control system;
GAZ-66-04 - a car with a tire pressure control system and shielded electrical equipment;
GAZ-66-05 - a car with a winch, a tire pressure control system and shielded electrical equipment.
When creating the GAZ-66 car, special attention was paid to obtaining high cross-country ability and driving stability.
to obtain a rational distribution of the load along the axes on a GAZ-66 car, the cab is located above the engine.
The GAZ-53A car with a carrying capacity of 4 tons with a drive to the rear axle is designed to transport various goods on all types of roads. The main components of the cars are interchangeable.
|
Name |
GAZ-53 |
GAZ-66 |
|
Load capacity, kg |
||
|
The greatest weight of the towed trailer with cargo, kg |
||
|
Vehicle weight in running order (without additional equipment), kg The weight of the vehicle equipped with a winch is 3640 kg. |
||
|
Vehicle overall dimensions, mm: height (over cab without load) height (on awning without load) |
||
|
Vehicle base, mm |
||
|
Front wheel track (on the ground), mm |
||
|
Rear wheel track (on the ground), mm |
||
|
The lowest points of the car (with full load), mm: drive axle housings front axle |
||
|
Turning radius along the track of the outer front wheel, m |
||
|
The highest speed of a car with a full load without a trailer (on a horizontal section of the road with improved surface), km/h |
||
|
Reference fuel consumption when measured in summer for a run-in vehicle moving at full load in fourth gear at a constant speed of 30-40 km / h on a dry, level road with improved coverage and short climbs not exceeding 1.5% (1˚), l/100 km |
||
|
Engine |
||
|
Number of cylinders and their location |
8, V-shaped |
|
|
cylinder diameter, mm |
||
|
Piston stroke, mm |
||
|
Working volume of cylinders, l |
||
|
Compression ratio (average value) |
||
|
Maximum power (limited by the regulator) at 3200 rpm, hp |
||
|
Maximum torque at 2000 - 2500 rpm, kGm |
||
|
The order of operation of the cylinders |
home » Heating and ventilation in the country.
How to calculate the volume of firewood in the back?
Determining the volume of firewood neatly stacked for storage is quite simple. It is much more difficult to find out how many cubic meters are in the car that they brought to you. Consider, for example, how many cubes of firewood are in the GAZ 53.
To begin with, we must find out the total volume of the car body. A standard Lawn has a body volume of approximately 4.8 cubic meters. If you see that firewood is loaded without a slide, then their volume obviously cannot be higher.
There are body modifications with silo (extended) sides, whose volume is increased by 1.5 - 2 times.
In addition to the volume of the body, how many cubes of firewood are in the lawn is affected by the laying method. More precisely, the presence of stacking: if the firewood is neatly stacked, then they occupy almost the entire volume of the body, but if they are piled in bulk, then there is a lot of free space between them. There is a special coefficient for converting the volume of bulk into the volume of storage cubic meters.
GAZ-53 - what are the dimensions of the body?
The coefficient depends on the length of the log. For example, for a log of a quarter meter, the correction factor is 0.8, and for a log of 3 quarters of a meter, it is already 0.73.
This means that 4 cubic meters of medium length firewood of 25 cm, brought in bulk, will turn into 3.2 cubic meters after laying.
Is it possible to fit 6 cubic meters of firewood in a GAZ 53?
As we have already said, if the car has extended sides or if you load the body with a hefty slide, then you can. This becomes more likely if firewood is loaded by stacking rather than in bulk. In the latter case, even in an 8-cube body there may be 2-3 cubic meters of firewood.
Let's consider how many cubic meters of firewood are in the GAZ 66. The volume of the body of this car may vary depending on the type, but, on average, it is 3 - 4 cubic meters, without extended sides. This is also the maximum volume of transported firewood, taking into account the normal stacking on the side.
So, in order to estimate the volume of firewood brought in, you need to know the volume of the body and the method of stacking firewood. The situation is somewhat more complicated when loading “with a slide”, but its volume can also be calculated by dividing the firewood into 2 conditional geometric shapes:
- Parallelepiped of the body on the side;
- Separate hill. For the convenience of counting, you can even level the hill, making it more gentle.
Adding the volume of both figures (obtained by multiplying the length, height and width) - we get the approximate volume of firewood.
Trucks GAZ-53
The GAZ 53 truck has become a legend and an outstanding achievement of the automotive industry of the USSR and Russia. As an honest worker, he always worked out the prescribed resource, and often served longer than the period that was provided for before decommissioning.

Classic truck brand GAZ-53
The release of the GAZ 53 has long ceased, but so far in the ads you can find offers to sell and buy this truck. The condition of some copies of the car is simply amazing - more than twenty years have passed since the last "fifty-third" rolled off the assembly line, and there are still quite combat trucks in decent shape.
From the history of the creation of GAZ 53
GAZ 53F
The GAZ 53 series of cars was built on the basis of the GAZ 51. The new model borrowed a six-cylinder in-line internal combustion engine (ICE) from the "fifty-first", only after a certain time other ICE options were already offered. The first prototypes of the new model appeared in 1959, and from October 1961 the GAZ 53 was put into mass production. The brand received the index "F" and became known as GAZ 53F. 
The release of the truck modification continued until January 1967. At first, the car's carrying capacity was 3.5 tons, but in 1964 it was reduced to 3 tons.
GAZ 53A
In 1964, continuing the development of the GAZ 53F, the giant plant began production of modifications: the base GAZ 53 and the updated GAZ 53A model. In 1965, they decided to leave only the GAZ 53A, and this brand lasted until 1983, that is, almost 20 years.
The GAZ 53A model was equipped with an eight-cylinder engine (115hp, volume 4.24 l) and the carrying capacity was increased to 4 tons.
The truck could reach speeds of up to 85 km per hour (at GAZ 53F it was no more than 74 km per hour).
GAZ 53 12
Since 1983, the GAZ 53 12 has become the base model. The new modified internal combustion engine received the ZMZ 511 index (120 hp), and the load capacity became even greater (4.5 tons). GAZ 53 12 was produced until January 1993, then the production of GAZ 53 was completely stopped.

This is how the GAZ 53 12 model looks like
Additional modifications of GAZ 53
In addition to the basic models GAZ53F, GAZ 53, GAZ 53A and GAZ 53 12, there were quite a few special modifications of the Lawn. Basically, they differed in body type and purpose. The basic version is the GAZ 53 onboard. On this base, the plant produced chassis - GAZ 53 dump truck (GAZ 53 02), chassis for a truck tractor (GAZ 53 05).
For army needs, the GAZ 53N was developed. The performance characteristics (TTX) of the military vehicle differed from the civilian version. As standard, military equipment came with a larger fuel tank (105 liters), a starting heater and additional equipment. Accordingly, GAZ 53N was painted in protective green.

GAZ 53N model variant
There were versions designed specifically for hot climates, chassis for KAVZ buses were produced, two models were equipped with gas equipment - to run on methane and propane.
Design features GAZ 53 12
Total information
The GAZ 53 12 car has the following dimensions:
The weight of the car is 3200 kg, for a fully loaded GAZ 53 12, the mass cannot exceed 7850 kg. The front wheel track is 1630 mm. The track size of the rear wheels is 1690 mm, the size is taken without taking into account the second wheels, which are outside on the rear axle.
The fuel consumption declared by the manufacturer should be 24 liters per 100 km at a speed of 40 km per hour. But such a norm in practice has nothing to do with this figure.

Comparative table of fuel consumption of GAZ vehicles of various modifications
The actual fuel consumption is somewhere around 30 liters per 100 km. The standard fuel tank is designed for 90 liters. The car was filled with gasoline A-76 and A-72. It is not clear what kind of fuel GAZons are now filling with, such brands of gasoline have not been produced for a long time.
Cabin
For those times when the GAZ 53 only appeared on the roads of the country, its appearance seemed very modern and stylish. But this view remained almost the same throughout the entire time the truck was produced. For more than 30 years on the cab, only the headlights with sidelights changed places and the position lights changed, the radiator grille took on a different look. Strictly speaking, the GAZ 53 is not a supercar, its main task is to carry goods, which it coped with brilliantly.
Inside the cabin looks simple.  There is no plastic trim, almost everything around is iron. The seat is not divided into driver and passenger. It consists of two main parts - a solid back and the seat itself, also solid. The halves come off very easily. Below, under the seat, there is a place for a tool and other things.
There is no plastic trim, almost everything around is iron. The seat is not divided into driver and passenger. It consists of two main parts - a solid back and the seat itself, also solid. The halves come off very easily. Below, under the seat, there is a place for a tool and other things.
The instrument panel is elementary:
- speedometer;
- ammeter;
- oil pressure gauge;
- temperature sensor.
And on the first GAZ 53, the shield was even simpler - instead of pressure and temperature sensors, there were two signal lamps.
The cabin has a weak point - the wings and footboards quickly rot, they constantly have to be welded.
Body and chassis
If we talk about the basic models, then you can describe the body structure in a few words. 
The design of the onboard GAZ 53 is frame, and the body itself is made of wooden boards fastened with an iron frame. The body was attached to the frame.
Internal combustion engine
Most likely, the old 6-cylinder GAZ 51 engine should not be taken into account, it is already hopelessly outdated. But ZMZ 511 is still rolling along the roads of the Russian Federation.
Characteristics of ZMZ 511:
- eight cylinders in a v-arrangement;
- piston size in diameter 92 mm;
- piston stroke 80 mm;
- aluminum cylinder block;
- two aluminum cylinder heads;
- engine displacement 4.24 l;
- compression ratio 7.6.
The internal combustion engine is considered a weak point in the GAZ 53. The crankshaft cannot withstand constant loads, and increased oil consumption at ZMZ 511 is almost the norm.

It looks like an engine for GAZ 53
The rear oil seal also leaked very often.
The leak occurred at the junction of stuffing box packing with rubber seals.
In Soviet times, sealants were not yet widely popular, so it was quite difficult to fix such a malfunction.
Chassis
The undercarriage of the legendary truck is simple. The front suspension is easy to repair, while it has good technical characteristics.
The composition includes:
- bearing beam;
- pivot knuckles;
- hydraulic shock absorbers;
- springs.
The rear suspension consists of a rear axle and leaf springs. The rear springs are reinforced with separate additional sheets. The brake system is drum type, there are two vacuum brake boosters.
Transmission
The gearbox on the GAZ 53 12 is a mechanical four-speed. The cardan shaft consists of two knees, three crosspieces and an average intermediate support. The movement of the wheels is carried out using the rear axle.
Steering
Steering GAZ 53 12 consists of a steering gear with a worm gear, a steering column, steering rods and a steering wheel. The steering wheel is three-spoke, large, but thin. The steering column is fixed rigidly and is not adjustable. Due to the lack of power steering, it is quite difficult to turn the steering wheel, especially if the car is stationary. We can say with confidence that driving a GAZ 53 is a completely unfeminine occupation.

Steering diagram GAZ 53
The main malfunctions and shortcomings of the GAZ 53
Having found out all the features of the operation of the truck, all the shortcomings can be combined into one list.
The main shortcomings and malfunctions of the GAZ 53:
- High fuel consumption, the declared rate is clearly underestimated;
- Tight steering, power steering is clearly not enough;
- There are many complaints about the internal combustion engine, this is mainly due to technical flaws;
- Weak springs, do not withstand the maximum loaded weight;
- The cab is corroded.
The main advantages of GAZ 53
There are flaws and shortcomings in any design. But the advantages of the GAZonchik are much greater. Such an unpretentious truck is still hard to find. Actually, it doesn't break very often.
It is very easy to repair - breakage can be repaired in any field.  There are still no problems with the availability of spare parts for the GAZ 53 truck, moreover, the prices for spare parts do not bite much. And even an amateur can deal with repairs.
There are still no problems with the availability of spare parts for the GAZ 53 truck, moreover, the prices for spare parts do not bite much. And even an amateur can deal with repairs.
The “fifty-third” has an almost “indestructible” body. The frame is made of thick durable metal - the car is already being scrapped, but the frame is still intact.
The truck "drags" almost any weight and volume that can be loaded into it. And the GAZ 53 dump truck does an excellent job with its task. The norm for him is not the limit - they are often loaded to the eyeballs.
The advantages include the cost of the car itself. For this reason, there is no particular concern that it will be stolen. It's not scary if the bumper is dented, as they say, not the chassis.
Conclusion
GAZ 53 has become a legend for a reason.
Dump truck GAZ-53
Trucks of the Gorky auto giant transported a huge mass of goods. Until now, many lawn workers are working on highways. And it would be very cool if such legends arose more often.
http://avtomobilgaz.ru
Used bodies KAMAZ, ZIL dump truck, gas 53 - Free classified ads "Auto parts, accessories" Skopin (Skopin.Verro.ru)
You see a publication about the offer presented to you “Body used KAMAZ, ZIL dump truck, gas 53”. The announcement was posted on the site on December 8 by a private trader from Skopin. Internet visitors most often search for a similar product using the tags: body, kamaz, dump truck, board, basket, mount, hydraulic cylinder, desire, restore, option, manipulator, account, loading, exchange, condition, gazelle, steer, subframe, dump, etc. similar. The more details you describe your product when placing an ad on the free classifieds board "Verro.ru", the attention of the more people in Skopin you will attract. Specify everything down to the smallest detail. Be sure to write a clear and complete title of your publication. Try to keep all the words in your ad as simple and as clear as possible for a potential consumer. And the result will not keep you waiting.
For onboard, an excellent option (17,000 rubles) will be more expensive to buy metal. I can deliver by a manipulator (at your expense), I will provide loading for FREE. I will consider the exchange options. There is a flatbed body from GAZ 53 (15000 rubles), the condition is very good, you can install it on a gazelle, bullock or others. The body from ZIL 130 is tipper (without a subframe) = 10000 rubles. BODY on ZIL-45085 Mining dump truck (rear dump only) is very strong. ". For a quick and easy search for your offer, specify tags (keywords) for it, for example: Skopin, Spare parts and accessories. If all recommendations are met, your ad will easily find its buyer.
List of cities in the Ryazan region:
Information about Skopin:
| A country: | Russia, Russia |
| Subject of the federation: | Ryazan regionRyazan region |
| City district: | Skopin |
| Coordinates: | 53°49′00″ s. sh. 39°33′00″ E / 53.81667° N sh. 39.55000° E d. / 53.81667; 39.55000 (G) (O) (I)Coordinates: 53°49′00″ s. sh. 39°33′00″ E / 53.81667° N sh. 39.55000° E d. / 53.81667; 39.55000 (G) (O) (I) |
| Chapter: | Oleg Aseev |
| Based: | 1597 |
| First mention: | 1597 |
| City since: | 1778 |
| Square: | 30.9 km² |
| Center Height: | 150 m |
| Population: | ↘28,092 people (2014) |
| demonym: | skopinets, skopinets |
| Timezone: | UTC+3 |
| Telephone code: | +7 49156 |
| Postcode: | 391800-391803, 391825, 391840, 391842, 391846-391847 |
| Car code: | 62 |
| OKATO code: | 61 415 |
| OKTMO code: | 61 715 000 001 |
| Official site: | skopin-gorod.ru |
The Soviet automotive industry, like the manufacturing sector as a whole, was massive, often to the detriment of quality. However, GAZ 53 can definitely be called an exception to this rule. Four million copies have found their application in almost all areas of activity both in the USSR and abroad. There was not a single large or medium-sized ATP, factory, state farm or collective farm, a car fleet that did not include several GAZ 53 units. The car was exported to all European countries of the socialist camp, to Cuba, Vietnam, Laos and North Korea. Serial production started at the Gorky Automobile Plant in 1961, and the last GAZ 53 left the gates of the enterprise in 1997. Not a single model of a truck produced in the USSR was able to intercept the palm from the GAZ 53 in terms of mass. Initially, when designing the machine, the designers laid down parameters that made it possible to reduce the cost of production as much as possible and create a reliable truck with low operating costs. Throughout the entire period of production, changes were made to the design that increased the consumer properties of the machine, but in general the machine remained unchanged. The main competitor for the GAZ 53 in its class was the ZIL 130 truck of the Moscow Automobile Plant. Likhachev, however, in terms of mass character, he still lost to the Gorky model. Despite a lot of improvements and modernization carried out in 1992, the GAZ 53 completely gave way to the more modern GAZ 3307 on mass production lines by the beginning of 1993.
Article navigation
Purpose
The main purpose of the GAZ 53 is the transportation of goods on paved roads over short distances. The car showed itself perfectly both when working in the city and in the countryside. Equipped for milk trucks, cars often delivered milk from livestock complexes to processing enterprises. Equipped with rigid bodies, GAZ 53 delivered bread, delivered mail, and even served as collection vehicles. In the municipal sphere, they served as garbage trucks and sewers. For the transportation of repair teams of urban emergency services, KUNG was often placed in the side body, and there was room for repair equipment. On the basis of the truck, several varieties of fire engines were also created. In agriculture, as a rule, GAZ 53 was used with side bodies, on which extensions were mounted, which made it possible to transport significant volumes of hay, straw and freshly cut fodder. To transport sugar beets and potatoes, dump platforms with hydraulic telescopic cylinders were installed on the chassis. Onboard versions of the machine were used in almost all types of construction and production. Transporting food and industrial goods between warehouses and shops was a common job for GAZ 53 drivers. Like most popular trucks, the GAZ 53 also had many military specialties. On the basis of the car, engineering equipment, weapons and communications systems were installed. The car showed reliable operation both in severe frosts and in the summer heat. All aggregates, components and mechanisms have been working without accidents for a long time in conditions of increased dustiness in the steppe regions of the country. Some modifications of the machine are specially adapted to certain operating conditions.
Modifications
Like many other events in the life of a large country, the release of GAZ 53 was timed to coincide with an important event - the 22nd Congress of the CPSU, held in 1961. However, work on the creation of an 8-cylinder power unit specifically for the new model has not yet ended. Therefore, the new GAZ 53 had to install the usual, forced, in-line six-cylinder engine from the GAZ 51. As a result, the first modification of the GAZ 53 immediately received the index “F”, which means “forced”. Engine power was increased to 82 hp, so a reinforced clutch had to be installed. The rear axle was also borrowed from the GAZ 51. The car clearly lacked power and carrying capacity, and its production was discontinued in January 1967. As a result of multiple improvements, new modifications of the machine subsequently began to appear:
- GAZ-53 is a modified and modernized basic modification of the car, the production of which was launched in June 1964. The car received a new eight-cylinder V-shaped engine ZMZ-53 (Zavolzhsky Motor Plant) with a capacity of 115 hp, reinforced clutch, a rear axle with a hypoid gear, as well as a radiator lining with lower headlights;
- GAZ-53A - an improved basic version of 1964, the production of which was launched in 1965. The main innovations include the installation of a new oversized cardan drive with a splined joint, a reinforced front axle with an increased long beam (from 1430 to 1490 mm), an updated steering mechanism, and increased rigidity shock absorbers. As a result of the work carried out, the carrying capacity of the machine increased from 3 to 4 tons. GAZ 53A became the base chassis on the basis of which the Gorky Automobile Plant itself developed many different modifications, and specialized vehicles were assembled at other assembly plants;
- GAZ-53N - an army modification, on which an additional fuel tank with a capacity of 105 liters was installed to increase the fuel range. and special equipment included an engine preheater, blackout equipment, a shovel, a canister and other equipment;
- GAZ-53-56 - export modification in the performance of an onboard vehicle. It was equipped with an English diesel engine Perkins 4.236 with a power of 90 hp;
- GAZ5-3-40 - an elongated chassis for the assembly of small-class buses KAvZ-685, SArZ-685, and TArZ-002, the production of which was launched at the Kurgan, Semenovsky (Nizhny Novgorod region), and Tokmaksky (Kyrgyzstan) bus plants;
- GAZ-53-50 - export version for countries with a tropical climate;
- GAZ-53-12 - reinforced chassis, modernized in 1983, for specialized vehicles for the national economy and the army, production of dump trucks and buses. Along with equipping with gasoline engines, specimens with gas-balloon equipment running on liquefied gas were produced. To improve road safety, a light car alarm was first used on the car, with the inclusion on the instrument cluster.
In addition to more than three dozen serial modifications, the car had a number of experimental samples, and cars produced by separate industrial-experimental batches:
- GAZ-53K - a truck tractor for work with dump semi-trailers;
- GAZ-53S is an on-board vehicle with an insulated cabin with double glazing, an increased power cabin heater, a 6-ST-81EMS battery, fog lights, and rubber products made of special rubber capable of withstanding severe frost. In the lubrication system of the engine and units, frost-resistant grades of fuel and lubricants were used. The car was intended for operation in the northern regions of the country (marking "C" - northern);
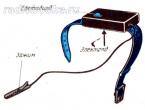
- GAZ-53-17 - a car with a ZMZ-53-27 engine for running on natural liquefied gas and gasoline. The total number of issued units is 47 pcs.
The exact number of modifications and complete sets of the car, perhaps, is not in any automobile directory, which only confirms the popularity and prevalence of the model.
Specifications
Throughout the entire period of production, GAZ 53 was constantly modified and changed. The years of greatest modification are 1964, 1983, and 1992. The basic parameters for most modifications are:
- Layout - rear-wheel drive, front-engine;
- Wheel formula - 4X2 with double rear tires;
- Cabin - hood, all-metal, double;
- Overall dimensions of the basic version - length 6395 mm, width 2020 mm, height 2220 mm;
- Curb weight - 7850 kg;
- Load capacity - 3000 kg;
- Gearbox - mechanical, four-speed, with synchronizers in 2nd and 3rd gear;
- The maximum speed on the highway at full load is 80 km / h;
- Fuel tank capacity - 90 l.
Features and operation
Initially, GAZ 53 had a carrying capacity of 2.5 tons, which was clearly not enough. Subsequently, with changes made to the design of the car, it was possible to raise it to 4.5 tons, but the work did not stop there. Together with the employees of NIIAT (Research Institute of Motor Transport, Moscow), the plant's designers developed a three-axle truck based on GAZ 53 with a carrying capacity of six tons. The main content of the work was to increase the frame and load platform with the installation of an additional lifting axle. In this case, it was supposed to use standard components and parts manufactured by the plant. Several prototypes were produced, but the model did not go into series. According to experts, the elongated frame could not cope with the required load. All other modifications have found their application in various branches of life. Despite the fact that the gearbox required a double clutch release when shifting gears, which caused inconvenience to inexperienced drivers, experienced drivers always spoke warmly about the car. The design of the machine was simple and reliable, and in the event of a breakdown, repairs could often be done on their own.
Video
Engine
On the largest number of GAZ 53 modifications, ZMZ-53 engines were installed.
Basic information about the ZMZ-53 engine
- Manufacturer - Zavolzhsky Motor Plant, Zavolzhye, Nizhny Novgorod Region;
- Type - gasoline, four-stroke, carburetor, water-cooled;
- The number and arrangement of cylinders - 8, V-shaped;
- Working volume - 4250 cm3;
- Power - 115 hp;
- Compression ratio - 7.6;
- The ecological class according to the modern classification is Euro-0.
Price
You can buy a GAZ 53 with mileage from private individuals and organizations for 50 thousand rubles. The onboard version in good technical condition of the early nineties is sold on average for 100 thousand rubles. The cost of cars with installed hydraulic lifts and other technical equipment can reach up to 700 thousand rubles.
On the territory of the domestic space, one of the most common and popular vehicles of small tonnage was the GAZ 53 truck. Even today it can be found in almost every city. Over the entire period of production, which took more than 30 years, the machine was constantly modernized and slightly changed. Its latest version was the GAZ 53 12 car, the start of production of which was laid in 1983.
History of creation
Cars of the Gorky Automobile Plant are among the oldest and most popular Soviet brands. There were the following modifications of the GAZ 53:
- 53F - from 1961 to 1967;
- 53A - from 1965 to 1983;
- 53-12 - from 1983 to 1993.
The developer made the first car in 1959, but serial production began only in 1961. The number of vehicles produced in the entire history of their assembly has exceeded 4 million units.
October 1961 was the beginning of the production of the GAZ 53 F, which is a 3.5-ton car with a capacity of 82 horsepower. In 1954, the production of model 53 was launched, the mass of which reached 9 tons, and the power was 114 horsepower. Later the name was changed to 53A. In various versions, the car was produced until 1983. Significant changes between them were only in the chassis used.
Since 1983, the production of GAZ-5312 has been carried out for 10 years, which increased its carrying capacity, acquired several new parts, modernized certain types of units, etc.
In 1990, a model called GAZ 3307 additionally appeared for a short time, but its release was short and not as popular as before.
Special Models
In addition to the basic models, the manufacturer produced a number of special vehicles based on the Lawn. Their differences were in the type of body used and in purpose.
The GAZ 53 onboard was always considered the basic option. But the plant has also developed options for a dump truck and a truck tractor. In the first case, a chassis called 53 02 was used. It was on it that the structures for transporting goods were located. At the same time, the GAZ 53 truck tractor was equipped with a GAZ 53 05 chassis.

For the army, the plant produced a special model 53N. First of all, the car differed in tactical and technical characteristics. In addition, the mass of the GAZ 53 onboard was slightly less than the military version of the car.
It is also worth noting that the GAZ 53, used as a truck tractor, has not received distribution. This was due primarily to the low power of each of the modifications of the car.
Truck Specifications
One of the GAZ 53 indicators - the weight of the car, is only 3.2 tons. Its gross weight is 7.85 tons. Thus, the carrying capacity of the vehicle is at the level of 4.5 tons. But such indicators relate only to modification 53 12, for which the cars were designed only for 3 tons of cargo.
Model 53 dimensions are as follows:
The permissible vehicle speed is 90 kilometers per hour. But in reality, he can go much faster if the mass of the load is not very large. The fuel consumption of the car is 24 liters per 100 kilometers. But most often this figure rises due to excessive loads and poor car care.

As a power unit on the car, a V-shaped carburetor engine with 8 cylinders is used. Its volume is 4252 cubic centimeters. The engine needs 10 liters of oil. The gearbox has 4 gears and 1 reverse. The fuel tank capacity is 90 liters. The car runs on A-76 gasoline.

Conclusion
Various modifications of the GAZ 53 car have gained due popularity in the post-Soviet space. This vehicle won the sympathy of motorists, which is why it is still in operation in many cities. The car still has certain problems, but in comparison with other domestic trucks, it is one of the best truck models in terms of cost and quality.
GAZ 53 has been produced for more than thirty years and has gained immense popularity among the population of our country. Since the start of production, the model has been constantly upgraded, and the GAZ 53 12, which has been in production since 1983, is considered the last base model.
Classic GAZ 53 early modification
It is one of the most famous and popular Soviet trucks. It belongs to the family of the 3rd generation of medium-duty trucks. Produced since 1959 (serial production since 1961) and until the beginning of 1993 at the Gorky Automobile Plant. With its modifications, it was the most massive truck in the USSR. The total number of produced cars is more than 4 million.
In October 1961, the 3.5-ton GAZ-53F, 82 hp, began to be produced. In July 1964, in fact, the GAZ-53 itself began to be produced - a 4-ton truck with a V-shaped 8-cylinder, 115 hp. In 1965, the name changed to GAZ-53A.

This model was produced in various modifications for many years until 1983. For, for buses - GAZ-53-40, specialized vehicles used the GAZ-53-11 chassis.
Since 1983, the GAZ-53-12 model has been released. The radiator has a different lining, a new cylinder head has appeared, the chassis has also undergone changes. The carrying capacity has become 4.5 tons.
In 1990 appeared. This is where the history of the GAZ-53 ended, but quite a few of these vehicles are still in use today.
Interior and exterior of GAZ-53
The GAZ-53 looked very modern for its time. A one-piece radiator lining was made flush with the headlights. The frame was very durable. The gas tank is located under the driver's seat. The filler neck was at the edge of the driver's door, behind the cab. 
When converting to gas fuel, this circumstance turned out to be very convenient, since the gas cylinder could be installed under the body, while other trucks had a gas tank there.
Starting technology was modern at that time - an electric starter with a retractor relay, there was a good heating system and electric windshield wipers.
The driver and passenger seats were made as one piece. But, nevertheless, it was comfortable to sit in the cockpit even in winter in warm clothes. There are places for tools, spare parts and other necessary things.
Vehicle export
GAZ-53 was exported to the countries of the socialist camp: Poland, the GDR, Romania, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Hungary, Vietnam, Mongolia, and also to Finland. From 1983 to 1991, the GAZ-53-12 was assembled by the Bulgarian company Madara.

Trucks of this assembly had a diesel engine of their own production, which was produced under license from Perkins (England).
Specifications
The truck has a rear wheel drive and a frame structure. In the factory configuration, the GAZ 53 12 is equipped with an eight-cylinder internal combustion gasoline engine with a V-shaped arrangement of cylinders.
Read also
Valve adjustment GAZ-53
Dimensions and performance
GAZ 53 has a curb weight of 3.2 tons, gross weight - 7.85 tons. 
The car is designed for a load capacity of 4.5 tons, but in reality it is often overloaded, which makes it necessary to repair or change the springs. The carrying capacity of 4.5 tons appeared only in the GAZ 53 12 model, the first GAZ 53F cars were generally three tons.
Dimensions
- Length - 6.4 m;
- Width - 2.4 m;
- Height (taken by the cab, car without cargo) 2.2 m.
The truck is designed for a maximum constant speed of up to 90 km / h, although in reality it can go at a higher speed (110 km / h), but in an unloaded state.
Wheel specifications

According to factory data, GAZ 53 should consume 24 liters per 100 kilometers on a flat road at a speed of 40 km / h. But, apparently, the fact that the car is not loaded, the weather is dry and warm, the car is rolling is taken into account. In reality, it is almost impossible to achieve such an indicator, at least the GAZonchik consumes 27 liters. Depending on the loaded state, the flow rate can increase up to 30 liters.
General characteristics
- GAZ-53 is equipped with a 120 hp / 3200 rpm engine;
- V-shaped 8-cylinder, carbureted, 4-stroke, with a volume of 4254 cc;
- With bore/stroke 92/80 mm;
- Gearbox : 4+1 back;
- With a length of 6395 mm, a width of 2280 mm, a height of 2190 mm, a base of 3700 m;
- Curb weight 3200 kg;
- Load capacity 4500 kg;
- Tank capacity 90 l.
Refueling tanks

Cabin and chassis
All-metal, two-door, designed for two passengers. But the passenger seat is very wide, and if desired, three people, including the driver, can fit in the cabin. The seats in the cabin are solid, not divided by the number of seats. That is, there is one common "seat" and one back.
The chassis design is frame, and the cabin and body are attached to it. The body may be different:
- onboard;
- Van;
- Dump;
- Special Purpose.

Cabin from the car GAZ 53
The frame is the connecting link of all components and assemblies of the car, therefore, if desired, the chassis can move independently even without a cab and a body.
Read also
Generator on GAZ-53
Engine
The GAZ 53 car was equipped with only two types of gasoline engine. But the six-cylinder engine, which was installed on the car at the very beginning of production, was only on the GAZ 53F model, and it was produced until 1967. After that, only an 8-cylinder ICE with a volume of 4.25 liters was installed on the "lawn".
The motor only changed the index over time and minor upgrades were carried out, the design itself remained unchanged.
The overhead valve arrangement, aluminum block and cylinder heads in the sixties of the last century were an innovation, a fresh engineering solution. A similar engine design exists to this day - it only changed the volume of cylinders and added minor technical nuances. 
The engine on the GAZ-53-12 is the ZMZ-53, an overhead valve with an aluminum block and cylinder head. The distributor and ignition coil often failed due to design flaws. Before the overhaul, the car managed to cover 400 thousand kilometers. The motor was not particularly economical. To somehow fix this, instead of a single-chamber carburetor, they later began to use a two-chamber one.
GAZ-53 is equipped with a spring dependent suspension. Telescopic shock absorbers are installed on the front suspension. The steering wheel does not have a hydraulic booster, which is why only physically strong people could drive such a car. To shift gears, you need to apply a double clutch release. The cardan transmission consists of 2 shafts, which are interconnected using Hooke's hinges.

Despite some shortcomings, the GAZ-53 was notable for its simplicity of design and suitability for repair, and there were always enough spare parts for this car.
An example is the ZMZ 5234 motor installed on the PAZ bus.
Characteristics of ZMZ 53
- Type - 4-stroke;
- Number of cylinders - 8;
- Compression ratio - 7.6;
- Type of gasoline used - A-76;
- Piston diameter (standard size) - 92 mm;
- Piston stroke - 80 mm;
- The diameter of the main journals of the crankshaft ¬– 70 mm;
- The diameter of the connecting rod journals of the crankshaft is 60 mm;
- Cylinder volume - 4.25 l;
- Power, nominal value - 115 liters. With.
The engine is liquid cooled. In Soviet times, water was almost always used as a coolant, and antifreeze or antifreeze was not used on trucks.  In frost, after a shift, I had to drain the water from the radiator, and the next day I had to run around with buckets in the morning. On the other hand, hot water was poured, and therefore the motor quickly started in any cold.
In frost, after a shift, I had to drain the water from the radiator, and the next day I had to run around with buckets in the morning. On the other hand, hot water was poured, and therefore the motor quickly started in any cold.
Since the engine has two rows of 4 cylinders, there are also two cylinder heads (cylinder heads). The ZMZ 53 block is cast from aluminum, and the cylinder head is made of the same metal. Between the heads is a massive intake manifold, a carburetor is installed in the center of the manifold.
The first GAZ 53 models had a K126B carburetor, then it was replaced with K135 (later K135M).
The direction of rotation of the crankshaft of the engine is right, however, like all automobile internal combustion engines. Cylinder operation order 15426378, non-contact electronic ignition, with commutator amplification of the spark on the spark plugs. The first models of the "lawn" (GAZ 53F and partially GAZ 53A) had a contact system.