Wheel hub diameter. Wheel bolts, nuts - reference information
On the wheel bolt there is a huge responsibility for the safe movement of the car and the life of the driver.
How to choose the right wheel bolt
The selection is based primarily on the type of drives that are installed on the car:
- Cast. For their reliable fastening, bolts longer and thicker are needed. That is, they should have an impressive width, length and size of the thread. But you can’t determine it by eye? The solution is very simple - when unscrewing the old bolts, count the number of turns they make. A quantity of at least six to nine is recommended. Absolutely any sample in terms of parameters, while for each wheel mounting bolt the price will be lower than in any auto parts store and will really please, can be found in "Matrix-Auto".
- Stamped. Here the situation is the other way round - the characteristics are much smaller and when buying you need to determine them as accurately as possible in order to avoid stopping the bolt in the hub and disrupting the normal functioning of the brake elements.
Wheel bolts and another important nuance
A significant moment when choosing them is the thread pitch. It is also not a constant parameter. The value of each is indicated by the automaker. Most often, the diameter is twelve or fourteen millimeters, but the pitch itself is about one and a half.
But this is just an average indicator in frequency of occurrence, it is important to know exactly your indicator.
Material from which the wheel bolt can be made
Two types of raw materials are mainly used - steel (which is usually coated with chrome or molybdenum, nickel) and ferrous metal.
Of course, the best option for car owners is the combination of aesthetic appearance and sustainability. Many choose a chrome price for which is quite acceptable. But recently, the development of the automotive industry has gone far ahead and this established standard has long lost its relevance.
Tracking all the innovations, “Matrix-Auto” offers a huge assortment of bolts of the most diverse type of manufacture at the lowest price.
Wheel Bolt: Perfect appearance
Reliably staffing your car, I want it to please the eye as well. It is on this site dedicated to the ideal wheel mount that has everything you need:
- A variety of colors.
- Perfect shine for every detail.
- Simple and harmonious equipment.
Replace:
http://prntscr.com/biky71
http://prntscr.com/bikycf
Any car owner who is considering buying alloy wheels should understand the differences in the design of nuts and bolts. In particular, the car owner must know the differences from those fasteners that are used in stamped discs. Bolts for alloy wheels are not universal. The same applies to mounts for stamped models - they can not be changed among themselves.
To ensure the operation of wheel sets with disks, it is desirable to have a pair of sets of nuts or bolts for them, as well as secret bolts.
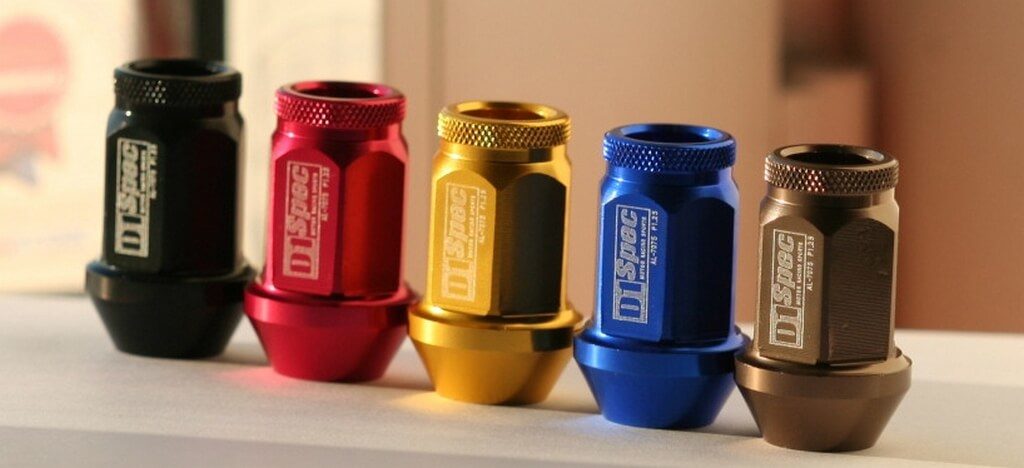

 Lightweight Wheel Nuts
Lightweight Wheel Nuts Key differences
Bolts and nuts for alloy wheels have a special design that directly follows from the wheels themselves. For example, stamped models are usually made of durable steel and are characterized by a small thickness that is present in the place of fasteners to the automobile hub. The nuts and bolts for them are provided with a flat cylindrical surface, and for a reliable connection of the bolts it is enough to have a flat hat.
Alloy wheels - on the contrary, are made of lighter alloys. They are characterized by less reliability. Products for mounting such disks are distinguished by a cone-shaped contact surface - it is larger than the same area of \u200b\u200bthe flat head used for stamping.
This is designed to reduce the load on the rims in places of fasteners. Such elements will also fit forged discs made of aluminum alloy.

 Chrome nuts and bolts for alloy wheels
Chrome nuts and bolts for alloy wheels Thus, the features in tightening bolts and nuts to discs are as follows:
- When using nuts with bolts from a stamped model and installing them on a cast disc, scratches quickly form at the junction, and the hole itself soon begins to crumble.
- Alloy wheels will need longer bolts. This is due to the softness of their alloy, which requires a greater thickness of the finished product.
- When tightening the nuts, pay attention to the final length of the bolts in the hub. If the number of full revolutions is less than 6 (about 10 mm), change the studs or put another model of discs for your own safety.
- Before installing, check all the characteristics of the bolts and nuts for their compliance with the disk. The angle of the fastening elements for standard cone-shaped products should be 60 degrees. It will need to be compared with bolt holes. In some models, it may differ from the standards. In addition, it will be necessary to check the thread and contact surface (fasteners for alloy wheels should have washers that increase the contact area).
You also need to understand that due to the implementation of cast disks of softer alloys over time, their connection with the hub may weaken with a higher probability. To avoid this, after every few tens of kilometers traveled, the owner must make sure that the fasteners are tight and tighten if necessary. In case of a loose fit, the disk will undergo cyclical impacts, and the bolts and nuts will continue to unwind.
 Due to the softness of the metal of the disk, it is necessary to regularly check the tightness of the bolts on the alloy wheels
Due to the softness of the metal of the disk, it is necessary to regularly check the tightness of the bolts on the alloy wheels Types of fasteners
Depending on the shape of the landing area, wheel bolts for alloy wheels are:
- with a round clamping part.
- with a cone-shaped clamping surface. They can be indented at the end of a clamp with a size of 1.3 mm (head) or be indented.
Depending on the size, the bolts are divided into:
- short (more often used to fix stamped disc models);
- long (suitable for alloy wheels).
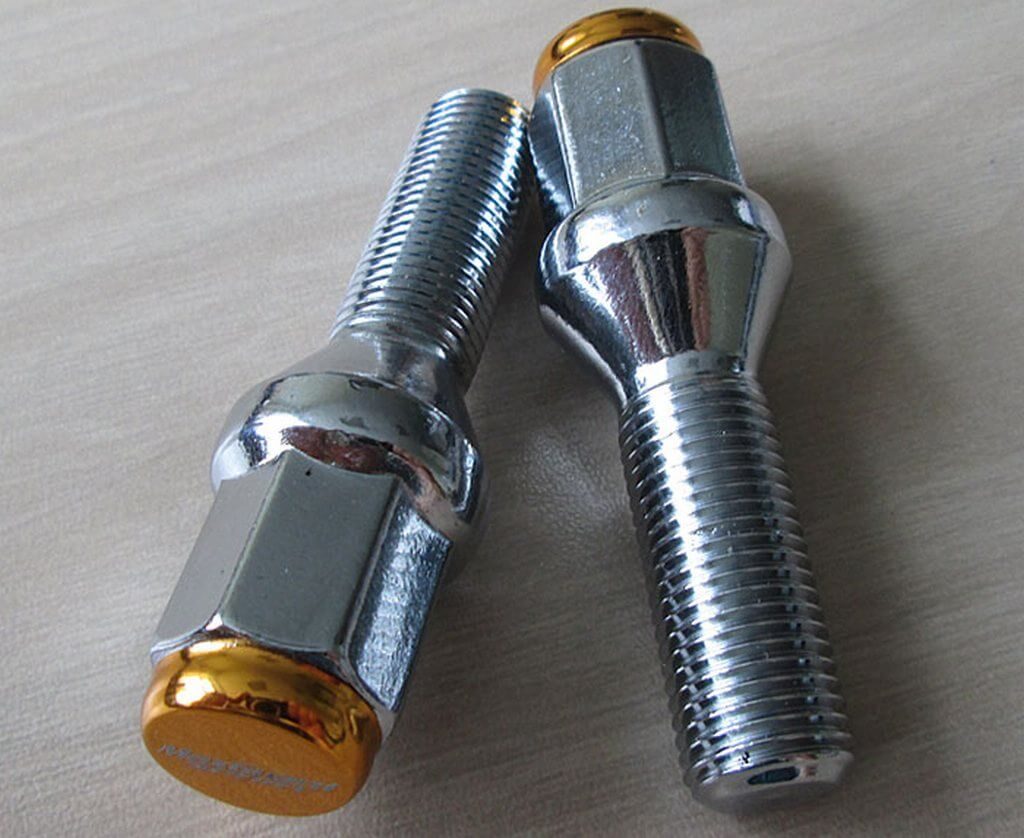

 Long bolts for car alloy wheels
Long bolts for car alloy wheels There are a number of criteria that help you find out which products are right for you:
- diameter;
- threaded pitch;
- manufacturing material (aluminum, steel, titanium);
- coatings (chrome of different shades, zinc).
There are also products on sale with a variety of coatings that can suit, for example, a shiny disc surface or body color. Despite the prevailing opinion that chromium spraying is better than other coatings prevents the formation and development of corrosion, the practical use of nuts and bolts shows that the service life of products made of ordinary ferrous metal is no less. Given that in the first years any detail will retain its original appearance, it is not worth choosing nuts or bolts, guided by aesthetic requirements.
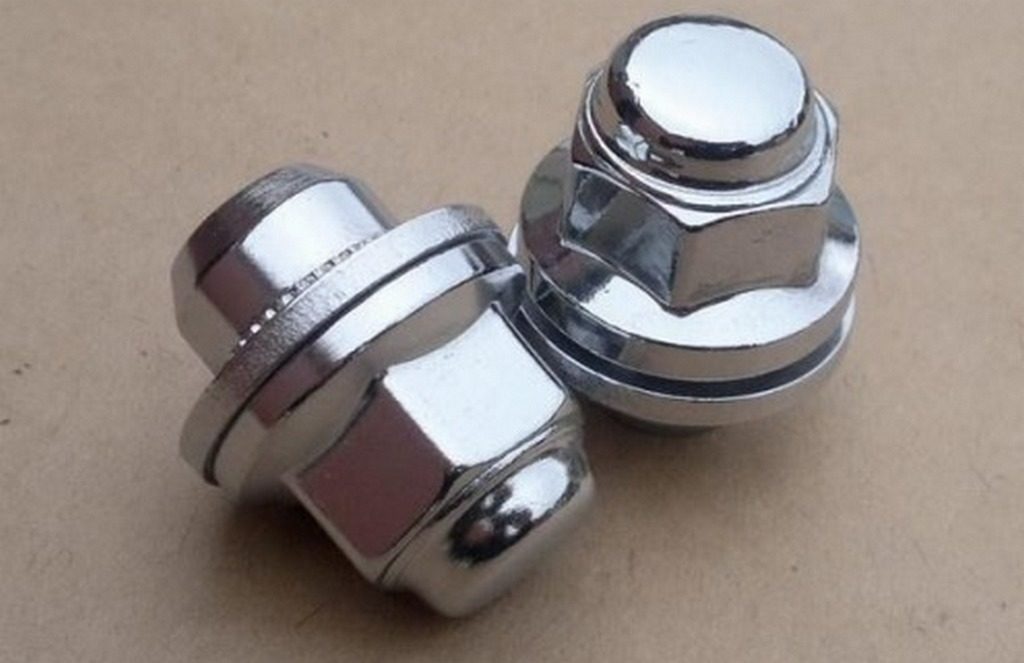

 Chrome alloy wheel nuts
Chrome alloy wheel nuts A special kind of mounts for alloy wheels are the "secrets". They protect the wheels of the car from intruders. Secret bolts, thanks to a location invisible to thieves, reduce the risk of theft to a minimum.
Their feature is the unusual shape of the nut. On the outside, the product is equipped with a moving sleeve. Thanks to this, the nut is removed with a separate key, and the adjustable wheel can no longer be removed. For each "secret" in the kit is an individual key, which is stored only with the owner.
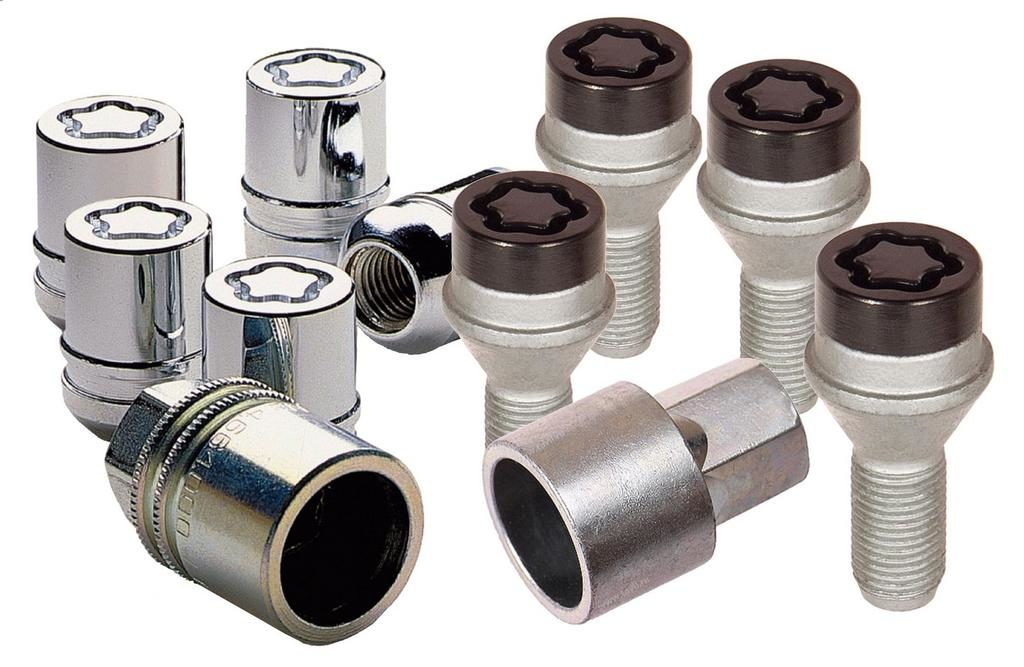

 McGard Secret Bolts and Nuts
McGard Secret Bolts and Nuts Tighten the alloy wheels
After selection, before installing the bolts and nuts in the seats for landing, you will need to grease them with graphite grease. Due to this, upon contact of the elements with the disk, they will be able to scroll, providing a more reliable fit and will not be locked due to the friction force.
If during installation you are faced with the problem of discrepancy between the size of the bolts on the wheel disc, then it can be solved by purchasing eccentric bolts (having a movable cone). For example, if the PCD size in the discs is 97 mm and 99 mm is required, the eccentrics will compensate for this by the cone that is on the product. The presence of a minimum distance between the inner fit and the outer diameter of the element will provide the possibility of movement indicated on the product by the word Variation.
When you select the connections for wheels with alloy wheels, pay attention to the size of the threaded surface of the products that are screwed into the hub. If the number of revolutions is less than 10 mm or 6 turns, you should buy a product bigger size, since short bolts significantly reduce the reliability of the wheels.
The wheels are attached to the hub of the car with bolts or studs with nuts (Fig. 1). In the second case, the studs are rigidly fixed in the hub. The most common thread diameters for wheel mounting are 12 and 14 mm in increments of 1.25 or 1.5 mm.
Fig. 1. Varieties of wheel mounting:
a - a bolt and a nut with a conical clamping part without a head, the sides of the head exit onto the cone; b - a bolt and nut with a conical clamping part and a head; c - a bolt and a nut with a spherical clamping part and a head.
The clamping parts of the wheel bolts and nuts can be conical or spherical and must necessarily coincide with the profile of the holes in the wheel disc, as they ensure the correct alignment of the wheel on the hub. This is especially important when fastening the wheel with nuts. If you fix the wheel only with the ends of the nuts (Fig. 2), the disk may slip out from under them when moving, the wheel mount will weaken, and the holes and studs will be broken. In the worst case, the car will “lose” the wheel - is it necessary to say how dangerous it is at high speed?
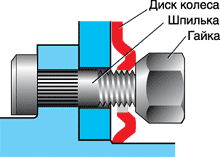
Fig. 2. Incorrect wheel mounting.
The disk, clamped by the end of the nut, and not by the cone, barely holds and slips out, it is worth the car to go.
With wheels bolted, this error is virtually eliminated. However, installing such a wheel is more difficult than fixing with nuts. To help the driver, 1-2 guide pins are screwed into the hubs of such wheels, and if they are not there, the wheel centers the belt of the hub, which enters the central hole of the disk.
Before installing the wheels, the seating surfaces of the hubs and discs should be cleaned of dirt and a thin layer of grease or graphite grease should be applied to them. It is also worth lubricating the threads of nuts (studs) and wheel bolts. It is better to replace bolts and nuts with crumpled edges and damaged threads in a timely manner with new ones that are necessarily similar to standard ones, not only in terms of thread size, but also in strength, i.e. not artisanal, but factory-made.
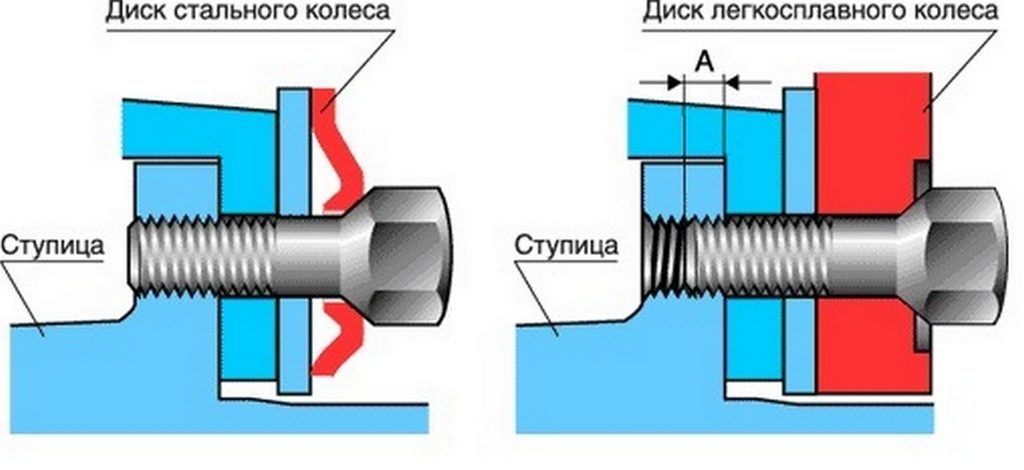
A light alloy wheel is always often thicker than a stamped steel disk, so longer bolts are used to mount cast or forged wheels (Fig. 3). The length of their threaded part (A) should be no less than the depth of the threaded hole in the hub, but no more, otherwise the bolts during rotation of the wheel may touch the parts of the stationary brake mechanism.

Fig. 3. Standard bolts are not suitable for mounting alloy wheels: need longer. Dimension A must be equal to the thickness of the hub flange.
The hardness of the material of alloy wheels is lower than steel, so the microroughness of the disk in the areas of contact with the heads steel bolts or with hubs, when the wheels are installed, they crumple after a while and the connection loosens. To avoid damage to expensive wheels, we recommend that after some time after installing them on the car, tighten the mounting bolts.
Wheel bolts or nuts are usually tightened with a torque of about 10–11 kgf · m, unless otherwise specified in the Owner's Manual. When the bolts are tightened, the wheel disc is deformed, the hole profile is broken, and the wheel ceases to be held on the hub with the necessary force. also crush the edges of the head of the bolt and even tear off the head.
To protect the wheels from theft, the so-called "secret" bolts (or nuts) are sometimes used. As a rule, in order not to damage the secret bolt or nut, less force is applied when tightening them. Therefore, they replace only one bolt (nut) securing each wheel. The "secret" fasteners are designed to be turned off only with a special, individual key, which is supposed to be available only to the car owner.
Designs of this kind are found on sale, as well as made by craftsmen. What to remember when buying them? Firstly, is the head of the "secret" really not accessible for turning away - not only with standard keys, but, for example, with powerful tongs or a hammer and chisel. Secondly, is the original hardware not able to fail from exposure to water and dirt, and most importantly, due to a breakdown of the counterpart - the key. Finally, a particularly bulky bolt can upset the wheel.
Prepared from the magazine “Behind the Wheel”
Even if you don’t get into the car’s device, you don’t notice wheel bolts impossible. They guarantee safety on the road: they fix the wheel to the hub. But if earlier the choice was reduced only to the required size, today there are much more options. Firstly, the variety of discs requires appropriate proposals. Secondly, the length and pitch of the thread must match the parameters of the disc manufacturer. Wheel bolts play a very important role in the design of the car, so do not neglect the advice of specialists and buy only completely suitable fasteners.
Why do I need to change bolts for alloy wheels?
Increasingly, cars are decorated with titanium or alloy wheels. This attribute looks impressive and is of high quality. But when making such a purchase, do not forget about the appropriate fastening - wheel bolts for alloy wheels are usually longer than for stamped ones.
Some motorists prefer not to splurge and leave old bolts for alloy wheels. This must not be allowed! There are two options for the development of the plot: if the bolt is short, then when loaded, the wheel can simply fall off. If the wheel bolt is long, the wheel may jam. There is one more nuance - the width of the thread pitch. If this parameter does not match, problems will arise in the future with the hub, and this is an extra expense for the repair and purchase of new spare parts.
You can choose the right wheel bolts for alloy wheels in Moscow on our website.